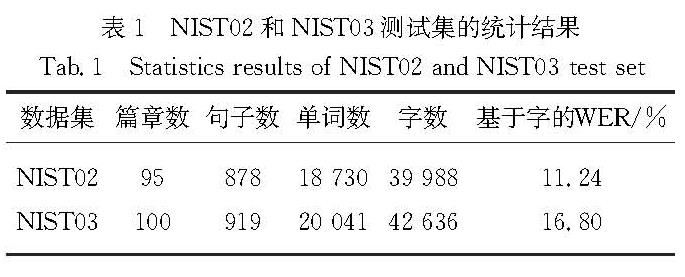
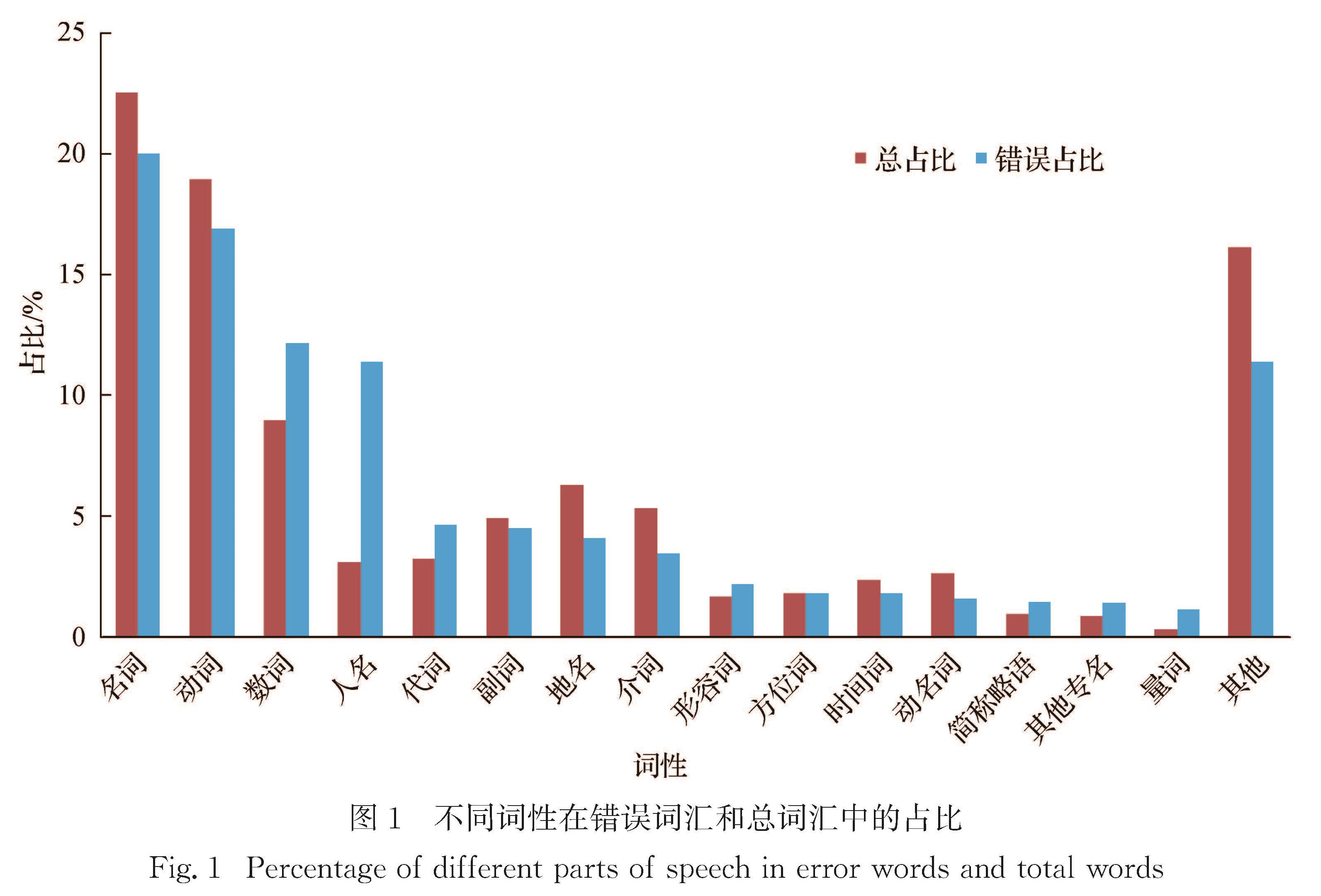
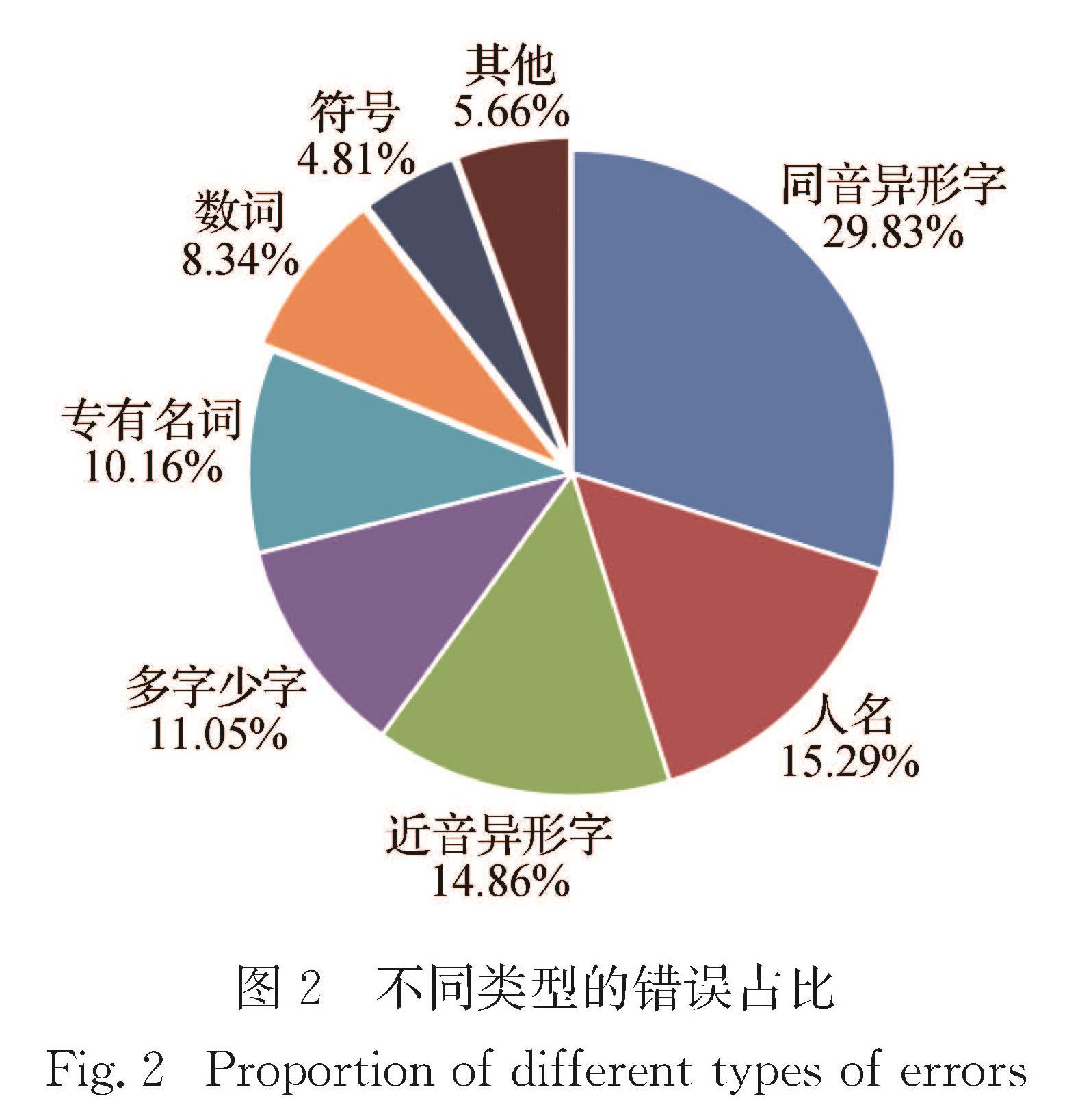
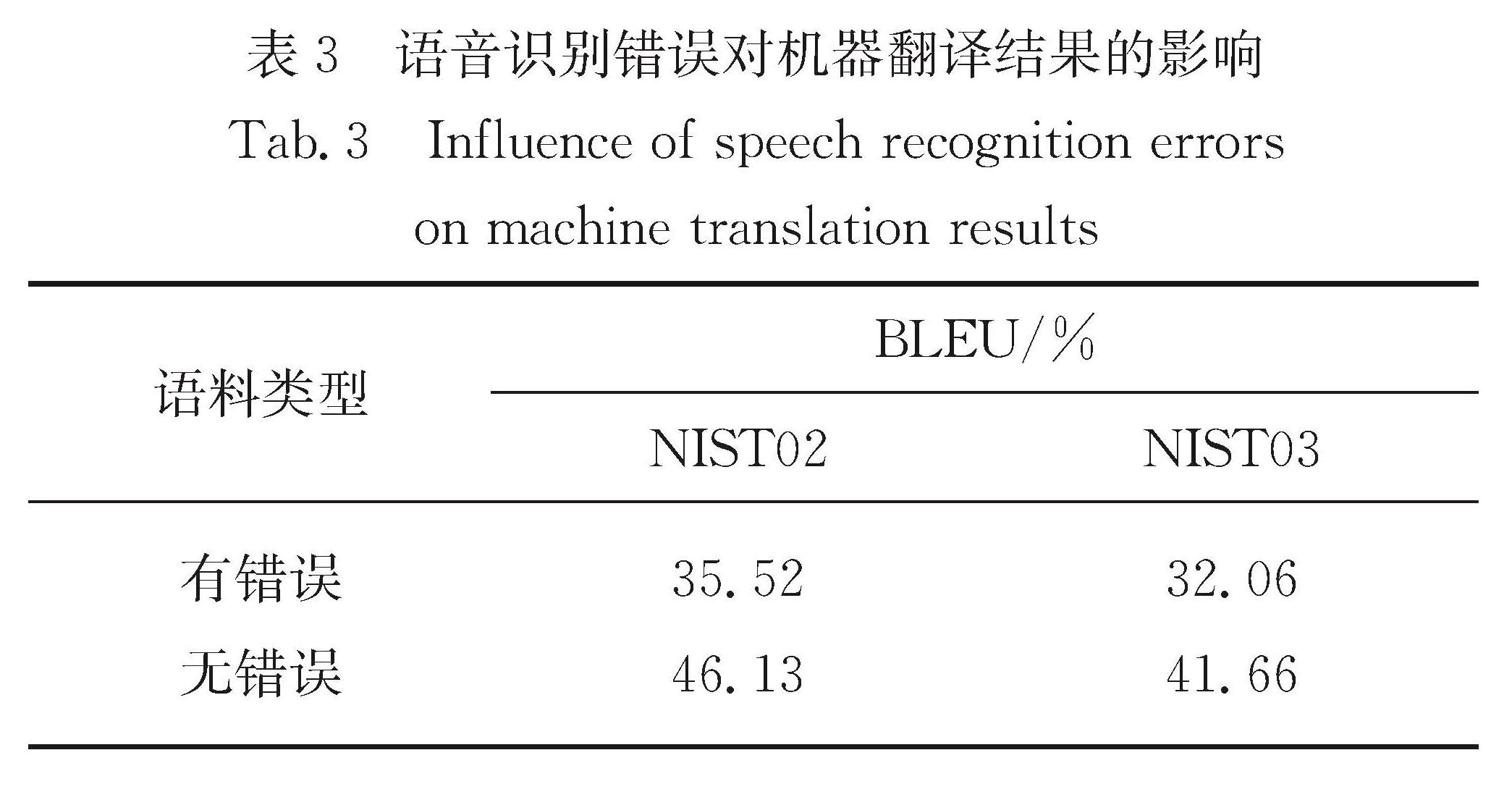
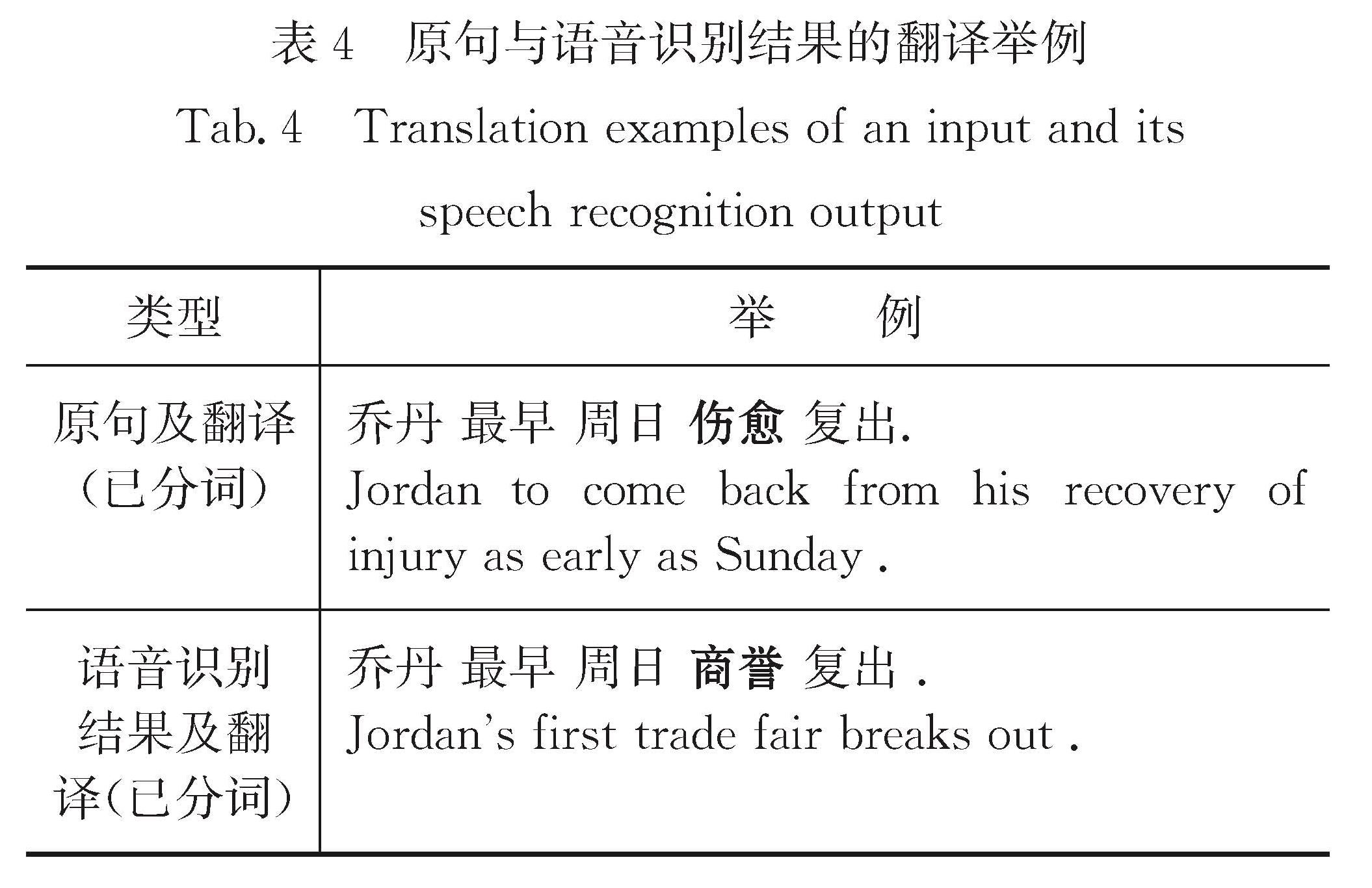
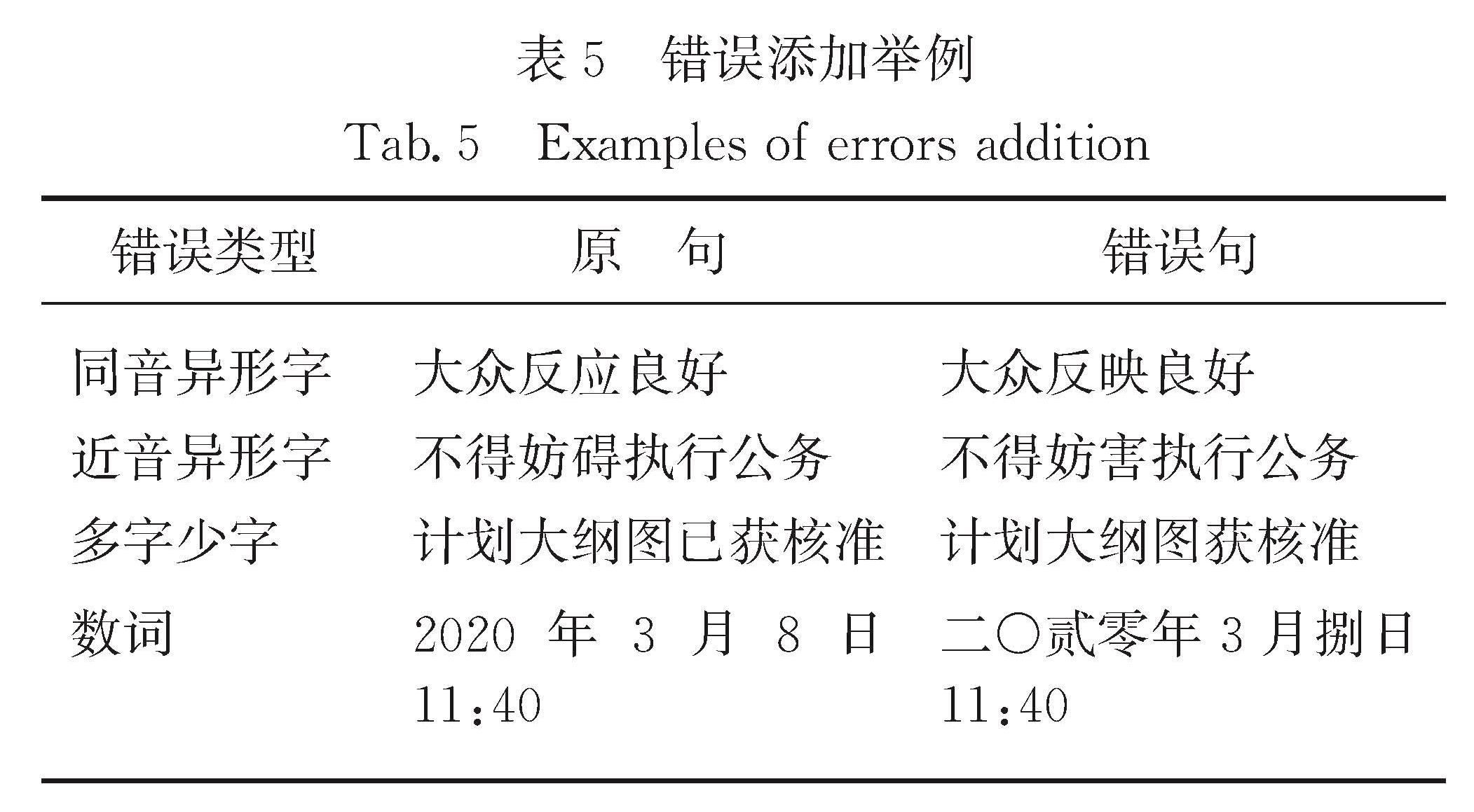
传统的机器翻译模型均基于无噪声环境,即输入的数据是无错误的.但在实际同声传译中,语音识别不可避免会存在错误,这些错误在机器翻译过程中会直接影响其他内容的翻译.因此,统计分析语音识别错误的种类及产生的影响对提高机器翻译的鲁棒性具有指导意义.为了模拟真实语音识别错误,本文通过人工朗读NIST汉英实验测试集,并采用讯飞语音识别系统获取其语音识别结果进行统计分析,主要包括:1)语音识别错误的词性分析; 2)语音识别错误的类型分析; 3)语音识别错误对翻译性能的影响; 4)语音识别错误对其他词翻译的影响.得出的主要结论为:名词和动词出现语音识别错误的次数较多,人名最易出现语音识别错误; 同音异形字的语音识别错误出现次数最多; 长度较小的句子在翻译时受到语音识别错误影响的程度更加明显; 与语音识别错误词距离更近的词的翻译更易受到影响.
Objective : In actual simultaneous interpretation, speech recognition errors will affect the translation of other content during machine translation. Therefore, statistical analysis for the impact of speech recognition errors on translation performance is instructive for improving the robustness of machine translation. The main tasks of statistical analysis of speech recognition errors are: 1) part of speech analysis of errors; 2) analysis of the types of errors; 3) the effects of errors on translation performance; 4) the impacts of errors on the translation of other words.
Methods : The experiment is based on the Transformer model, the training set comes from the LDC corpus, and the validation set is the noise-free NIST06 data set. The analysis of the speech recognition results of the NIST02 and NIST03 datasets includes: calculating the part of speech percentage and type percentage of errors, comparing the translation performance of the test set with and without speech recognition errors, and analyzing other words which are easily affected by the errors based on the plane distance and the structural distance.
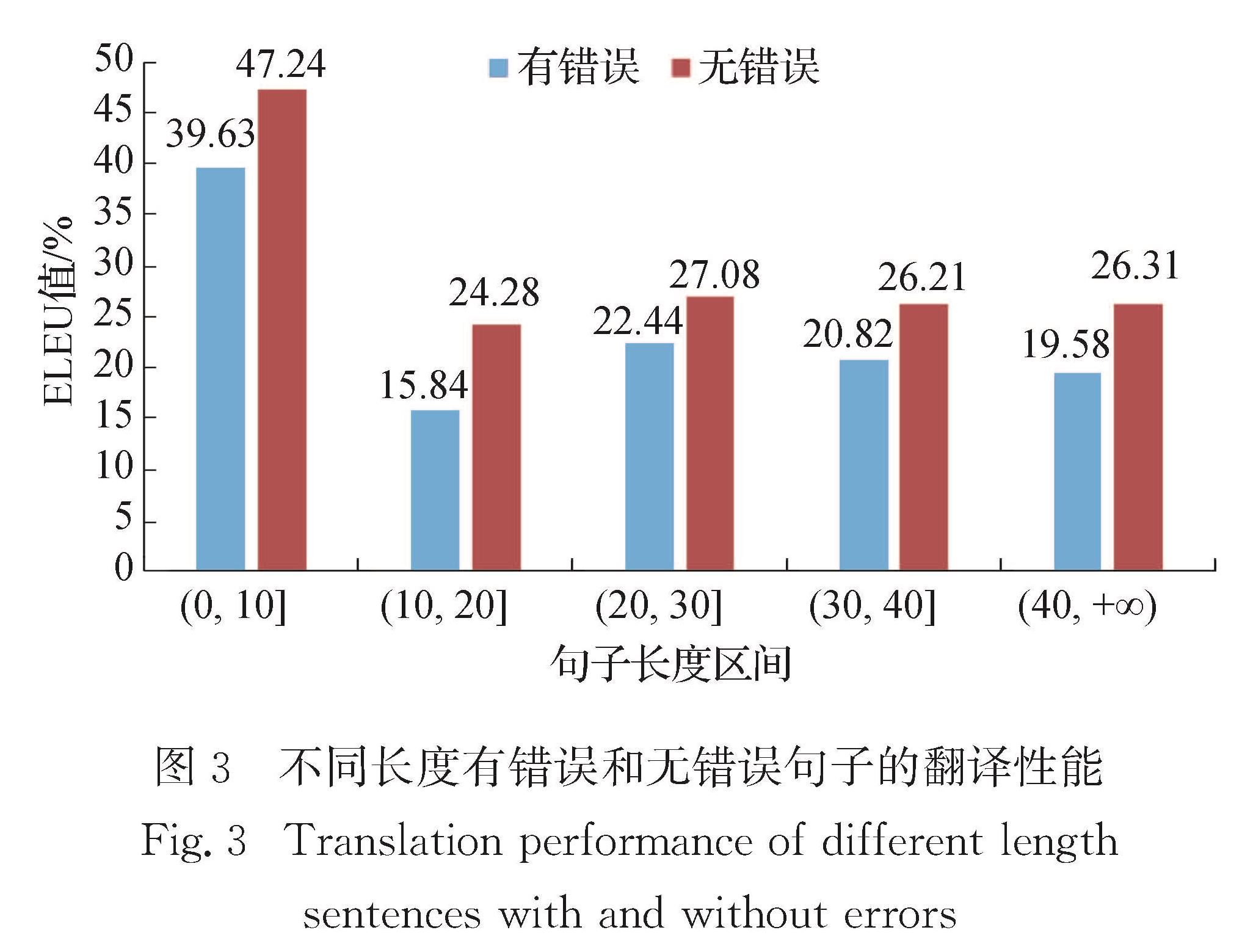
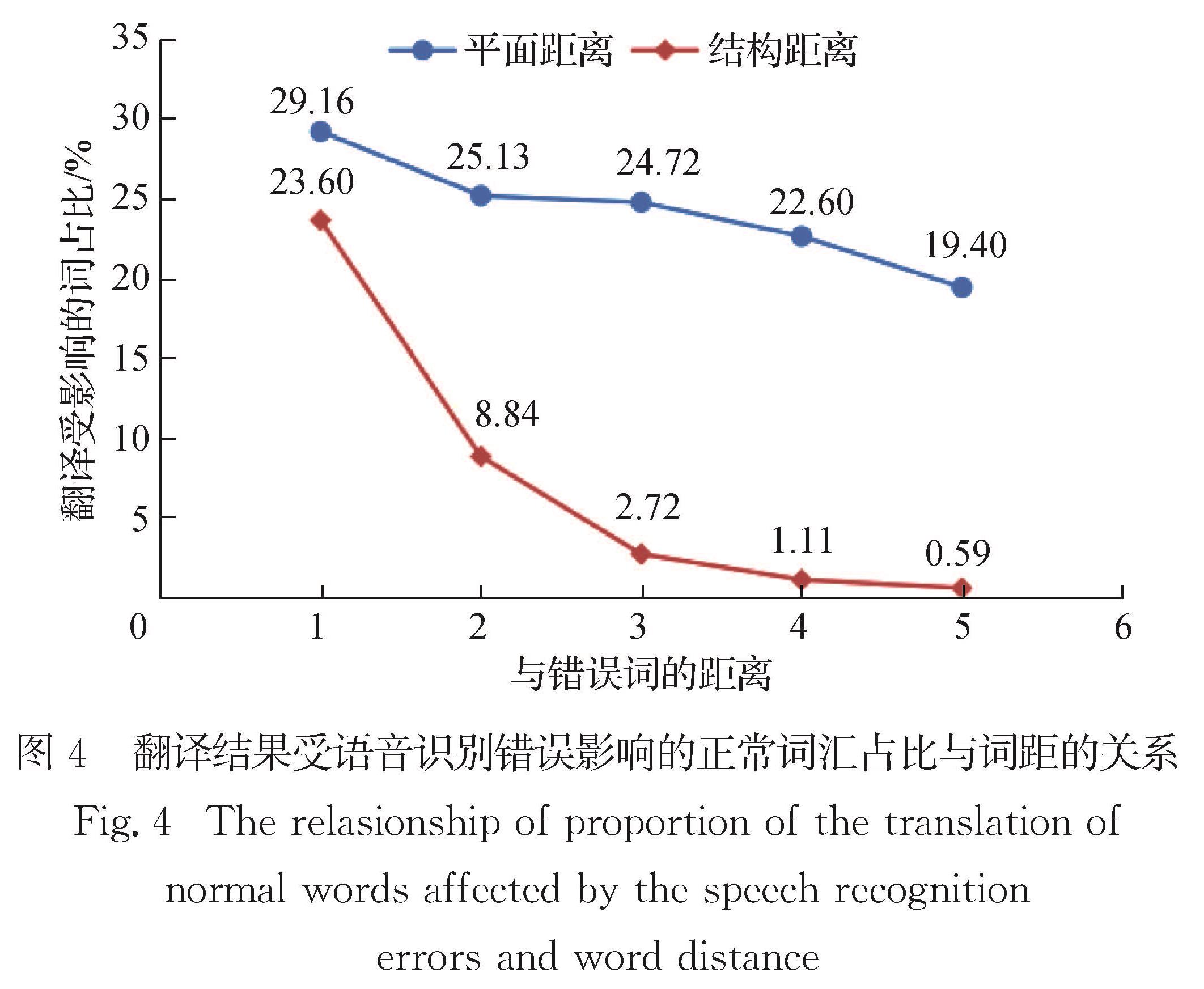
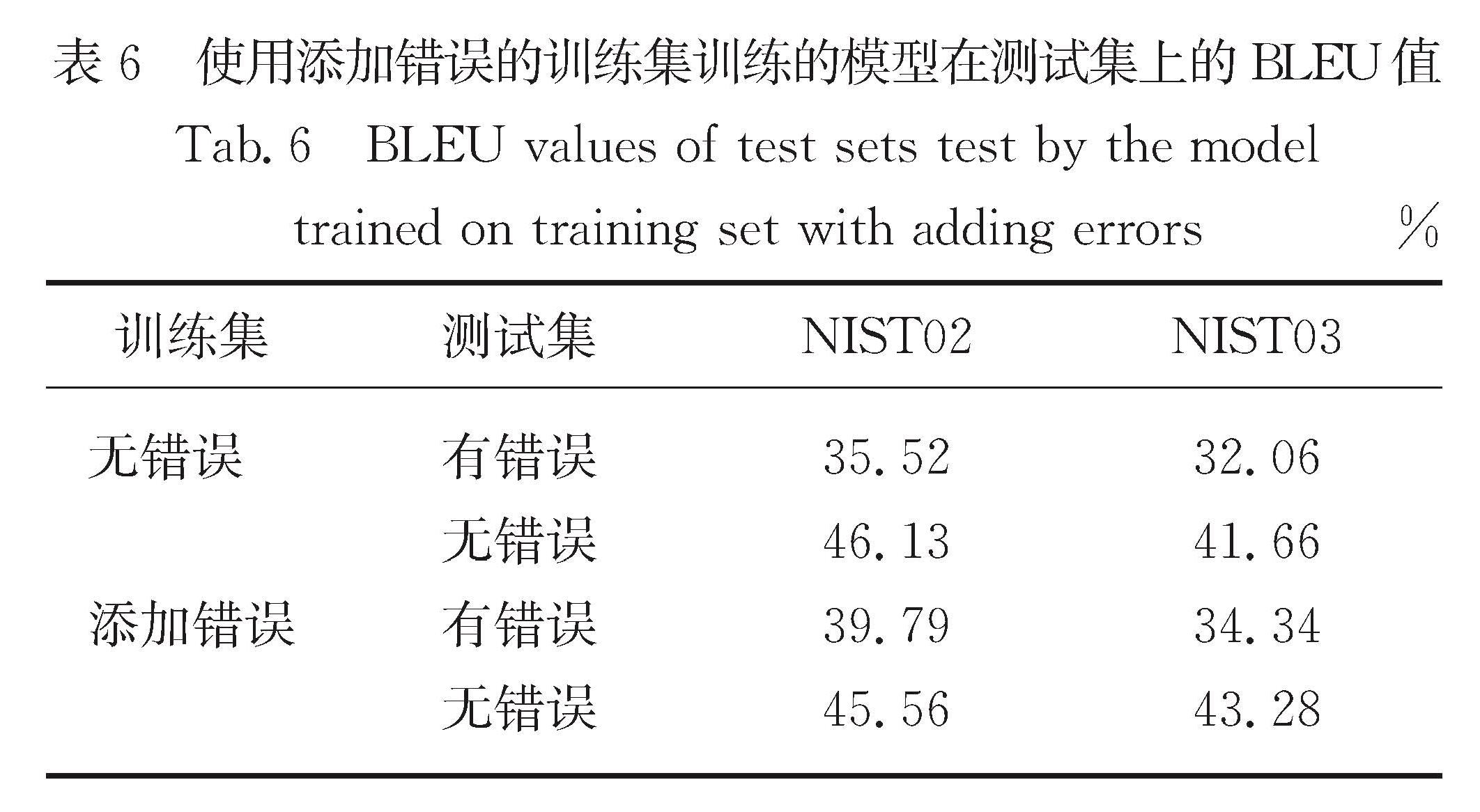
Results : Firstly, in all words, nouns and verbs have a high proportion of total and error. Names, numerals and pronouns whose proportion of errors is obviously larger than the total proportion are more prone to speech recognition errors. Among them, the names’ proportion of errors is far greater than the total proportion, indicating that the speech parts of names are most prone to speech recognition errors. Secondly, the main types of speech recognition errors include homophones, names, near tone special-shaped characters, more words and less words, among which homophones account for the largest proportion of errors, and much higher than the second proportion of names. Thirdly, sentences shorter than 20 words are more affected by speech recognition errors, and the BLEU value is 7~9 percentage points lower than that of sentences without errors. However, sentences longer than 20 words are slightly less affected by speech recognition errors, and the BLEU value is 4~7 percentage points lower than that of sentences without errors. Fourthly, both plane distance and structural distance are negatively correlated with the proportion of normal words affected by errors during translation; with the increase of distance, the effect of structural distance on translation decreases more obviously than that of plane distance; from the perspective of structural distance, the influence of errors on other words is generally lower than that of plane distance. Finally, the model developed by the error-added training set performs better on the test set with speech recognition errors than the model developed by the error-free training set. For the NIST02 test set with errors, the BLEU value increased by about 4 percentage points. For NIST03 test set with errors, the BLEU value increased by about 2 percentage points.
Conclusions : 1) Nouns, verbs and other content words have more speech recognition errors, and names are most prone to speech recognition errors. 2) Homophones have the most speech recognition errors, which reflects that the recognition results of homophones are not accurate enough. 3) Shorter sentences are more influenced by speech recognition errors during translation. 4) Whether it is the plane distance of the errors in the segmented sentence or the structural distance related to the dependency relationship of the errors, the proportion of other words affected by the translation is basically negatively correlated with the distance. 5) During the training of translation model, the model trained by using the training set with errors added has better translation performance on the test sets with speech recognition errors.
Methods : The experiment is based on the Transformer model, the training set comes from the LDC corpus, and the validation set is the noise-free NIST06 data set. The analysis of the speech recognition results of the NIST02 and NIST03 datasets includes: calculating the part of speech percentage and type percentage of errors, comparing the translation performance of the test set with and without speech recognition errors, and analyzing other words which are easily affected by the errors based on the plane distance and the structural distance.
Results : Firstly, in all words, nouns and verbs have a high proportion of total and error. Names, numerals and pronouns whose proportion of errors is obviously larger than the total proportion are more prone to speech recognition errors. Among them, the names’ proportion of errors is far greater than the total proportion, indicating that the speech parts of names are most prone to speech recognition errors. Secondly, the main types of speech recognition errors include homophones, names, near tone special-shaped characters, more words and less words, among which homophones account for the largest proportion of errors, and much higher than the second proportion of names. Thirdly, sentences shorter than 20 words are more affected by speech recognition errors, and the BLEU value is 7~9 percentage points lower than that of sentences without errors. However, sentences longer than 20 words are slightly less affected by speech recognition errors, and the BLEU value is 4~7 percentage points lower than that of sentences without errors. Fourthly, both plane distance and structural distance are negatively correlated with the proportion of normal words affected by errors during translation; with the increase of distance, the effect of structural distance on translation decreases more obviously than that of plane distance; from the perspective of structural distance, the influence of errors on other words is generally lower than that of plane distance. Finally, the model developed by the error-added training set performs better on the test set with speech recognition errors than the model developed by the error-free training set. For the NIST02 test set with errors, the BLEU value increased by about 4 percentage points. For NIST03 test set with errors, the BLEU value increased by about 2 percentage points.
Conclusions : 1) Nouns, verbs and other content words have more speech recognition errors, and names are most prone to speech recognition errors. 2) Homophones have the most speech recognition errors, which reflects that the recognition results of homophones are not accurate enough. 3) Shorter sentences are more influenced by speech recognition errors during translation. 4) Whether it is the plane distance of the errors in the segmented sentence or the structural distance related to the dependency relationship of the errors, the proportion of other words affected by the translation is basically negatively correlated with the distance. 5) During the training of translation model, the model trained by using the training set with errors added has better translation performance on the test sets with speech recognition errors.