(School of Computer Science and Technology,Soochow University,Suzhou 215006,China)
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202011027
备注
引言
和统计机器翻译(statistical machine translation,SMT)[1]相比,神经机器翻译(neural machine translation,NMT)[2-4]仅用一个神经网络就可以实现源语言到目标语言的翻译, 省去了搭建特征工程的困扰,显著提高了机器翻译的质量.NMT模型通常由一个编码器和一个解码器构成,其中编码器将源端句子中的每个单词根据其上下文编码成含上下文信息的隐藏状态; 基于其隐藏状态,解码器按从左到右的顺序生成目标端单词.
神经网络本质是一种数据驱动的方法,大量的数据有利于神经网络学习到更合理的参数.特别是对于数据规模受限的小语种来说,通过增加训练数据带来的性能提升往往效果更加明显.因此,如何更多、更好地生成大量平行数据成为许多研究者日益关注的问题.
作为一种增加训练数据的常用方法,数据扩充技术已经被广泛应用于计算机视觉[5]和自然语言处理[6-8]领域.在计算机视觉领域,主要通过对图片进行翻转和随机剪裁操作实现图像数据的扩充.在自然语言处理领域,数据扩充的思路总体上主要分为两大类:1)句子级别数据扩充,从句子级别生成更多高质量的训练样本,提高模型的泛化能力.2)单词级别数据扩充,对句子中的单词进行随机交换、丢弃和替换等操作,得到更多带有噪声的数据,提高模型的鲁棒性.
作为一种句子级数据扩充的方法,反向翻译被应用在很多无监督机器翻译模型上,取得了不错的效果.Sennrich等[7]提出用反向翻译技术构造伪平行句对.该方法首先在已有平行语料的基础上训练一个反向翻译的模型,然后利用这个反向翻译模型来翻译提前收集到的大规模目标端单语语料,获得伪平行句对,最后将伪平行句对和人工标注平行句对合在一起进行模型训练.然而,反向翻译技术需要额外训练一个反向的翻译模型,这无疑会增大运算开销.此外,收集到的单语语料往往存在噪声,对带有噪声的语句进行反向翻译会进一步降低伪平行数据的质量,从而影响翻译模型的性能.He等[9]发现任何机器翻译任务都有一个对偶任务,能够使得翻译系统自动地从无标注数据中进行学习.原任务和对偶任务能够形成一个闭环,即使没有人类标注者的参与,也能够生成含信息量的反馈信号用以训练翻译模型.
在单词级别数据扩充方面,Iyyer等[6]在求解一句话的平均词向量前,随机去除文本中的某些单词.Artetxe等[8]设置一个固定长度的窗口,在窗口内随机和相邻的单词进行替换.Fadaee等[10]利用在大规模单语语料上训练得到语言模型,寻找可以被低频词汇替换的高频词汇,通过这种方法大大提高低频词的出现频率,缓解数据相对稀疏的问题.相较于直接替换为某个确定的单词,Gao等[11]提出一种融合多个单词信息的方法.该方法首先训练一个语言模型,把语言模型预测下一个单词的概率分布作为每个候选单词嵌入表示的权重,然后将线性组合词表中每个单词的嵌入表示作为要替换的单词.
为了解决数据缺乏导致的NMT泛化能力不足的问题,同时避免反向翻译技术中单独训练反向模型的开销,受预训练模型BERT(bidirectional encoder representations from Transformer)[12]启发,本研究提出了一种简单有效且可以对原始平行数据的目标端进行动态扩充的方法.该方法在每次加载目标端句子时按照一定策略对句子中单词进行随机噪声化,从而提高目标端语言模型对句子的表达能力.具体地,在加载一批数据时,随机选择目标端句子中的一些单词,并将其进行噪声化,然后约束编码器预测出被覆盖的单词.如果在整个训练过程中同样的一批数据被加载了n次,就等效于将训练数据扩充了n倍.通过约束编码器还原原始语句,可以使自身学到更深层的语言表征能力.
1 背景知识
1.1 NMTNMT由编码器和解码器构成,训练的目标是使模型参数在平行语料S={(x(s),y(s))}|S|s=1(|S|表示平行语料的句子数)上取得最大似然.近年来,国内外很多研究者提出的模型[3,13-14]均是基于编码器-解码器结构.由于Transformer[14]序列到序列模型在很多任务上都能取得较好的性能,本研究选择Transformer作为基准模型.值得注意的是,本方法与模型的内部结构无关,同样适用于其他序列到序列模型.
NMT中的编码器首先将源句子集合x={x1,x2,…,xN}映射成词向量e(x)=[e(x1),e(x2),…,e(xN)],然后把这N个词向量编码成隐藏状态h.根据隐藏状态h和目标端句子T个词的集合y={y1,y2,…,yT},解码器从左到右逐个生成目标端单词的概率,得到y的概率:
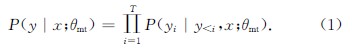
其中:θmt={θenc,θdec},为整个模型的参数; θenc和θdec分别为编码器的解码器的参数; y<i表示在预测第i个目标端单词时已经翻译得到的目标端单词.模型在训练集S上定义的损失函数为
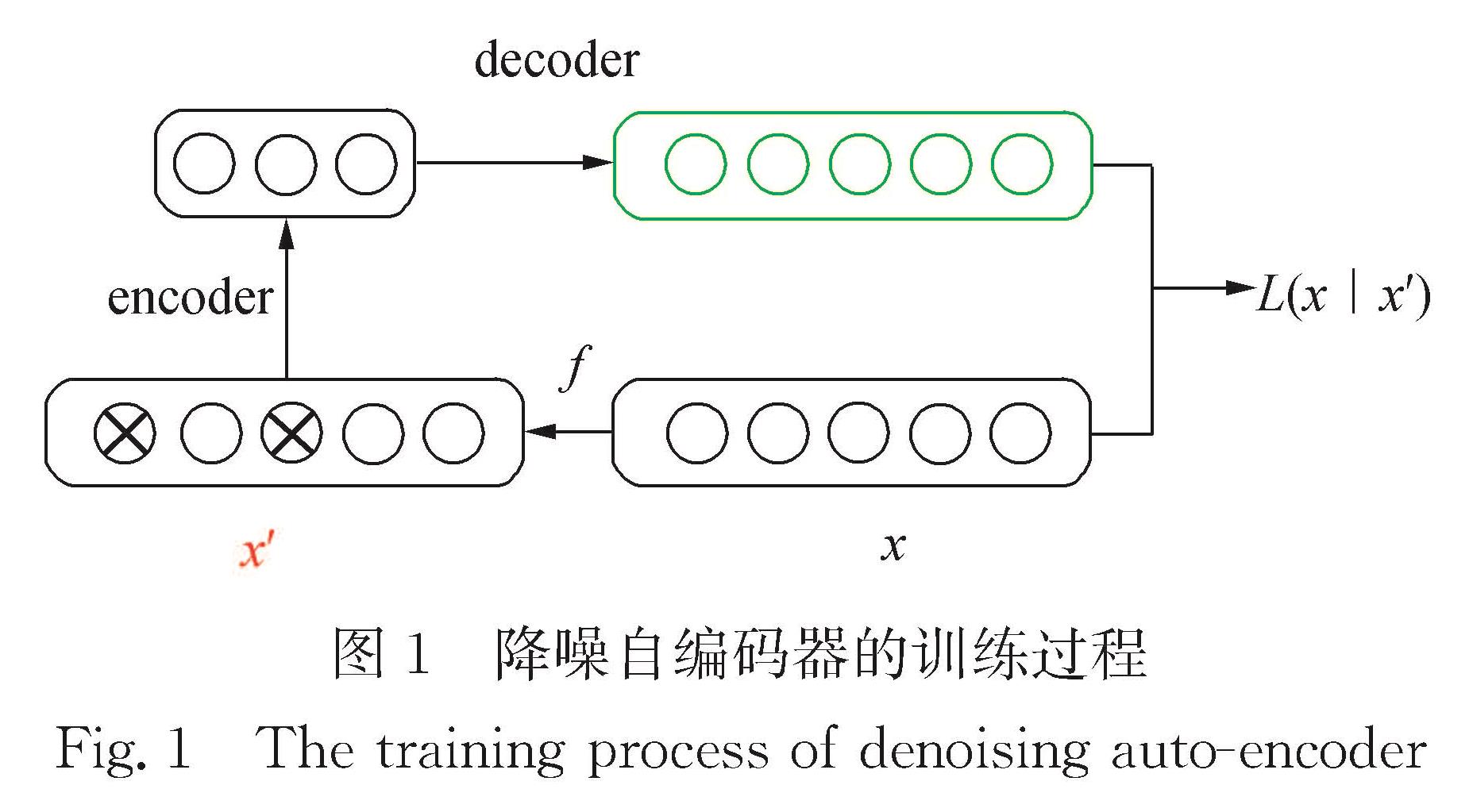
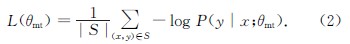 1.2 降噪自编码器
1.2 降噪自编码器和自编码器相比,降噪自编码器[15]可以学习叠加噪声的原始数据,而其学习到的特征和从未叠加噪声的数据学习到的特征几乎一致,因此降噪自编码器具有更强的鲁棒性; 同时降噪自编码器可以避免自编码器简单地保留原始输入数据的信息.
降噪自编码器的训练过程如图1所示,给定一个单词序列x={xi}ni=1,首先引入一个损坏过程f(x)得到带有噪声的单词序列x'={x'i}ni=1.通过最小化损失L(x|x')使得模型从带有噪声的x'重构干净数据点x,其中损失函数为
L(x|x')=-log Pdec(x|fen(x')).(3)
其中,fen(x')表示x'输入编码器后的输出,Pdec(x|fen(x'))表示编码器输入为x'时,解码器输出x的概率.
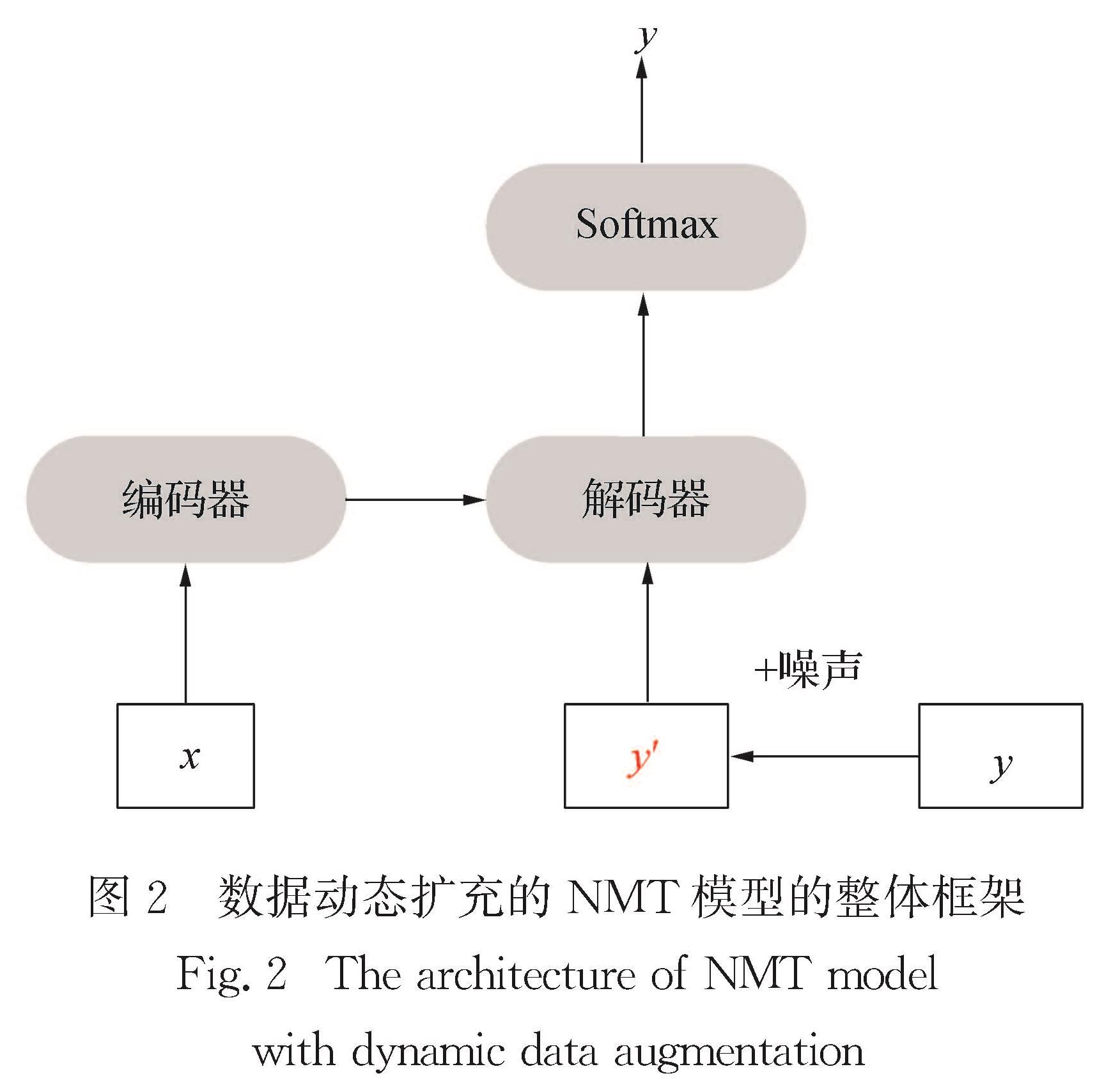
2 目标端动态数据扩充方法
对于NMT,扩充训练数据的方法除了需要大规模的单语语料外,往往还需要训练一个辅助的模型.而对于资源缺乏的语言来说,引入质量较低的单语语料往往会损害翻译模型的质量.针对上述问题,本研究提出一种在不引入外部语料的情况下实现数据动态扩充的方法.该方法首先对输入的目标端语句按照一定策略随机进行噪声化,然后利用编码器将受损的句子还原,以提高编码器对目标单词的预测能力,实现翻译性能的整体提升.如图2所示,和基础的NMT系统相比,本方法仅增加了一个随机添加噪声的模块,对于模型的其余部分并没有改动,可以方便应用于其他序列到序列模型.
2.1 构建噪声输入和降噪自编码器类似,本研究首先构造带有噪声的目标输入.假设给定目标序列输入y={yi}ni=1,对每个序列15%的单词进行随机覆盖得到y'={y'i}ni=1,并保证每句话覆盖的最大单词数不超过20,对于同一个句子可以同时使用以下3种策略得到噪声序列:1)以80%的概率用[MASK]替换随机选中的单词; 2)以10%的概率用词表中的任意一个单词替换选中的单词; 3)以10%的概率保持选中的单词不变.
with dynamic data augmentation假设目标端的输入序列为: 中国 消费者 信心 支持 中国 经济 增长.在构造带有噪声的输入序列时分别选择第二、第五和最后一个单词(消费者、中国、增长)进行以上3种策略的替换,示例如表1所示.
采用以上3种策略后,得到的最终噪声输入为:中国[MASK] 信心 支持 世界 经济 增长.
2.2 重构目标句子在得到含有噪声的目标序列y'={y'i}ni=1之后,解码器需要结合编码器的输出将y'还原为y.与BERT相比,不同之处在于:本方法不仅预测出被覆盖的单词,而是重构整个目标端序列.
解码端重构目标序列的过程可以认为是最大化条件概率P(y|h,y'; θdec),如式(4)所示.
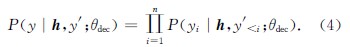
通过解码器递归地从左至右逐一生成目标词,最终得到完整的译文y={yi}ni=1.因此,模型在每个伪平行句对(x,y')定义的损失函数为
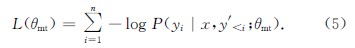
3 实验结果与分析
4 结 论
本研究针对NMT面临训练语料不足的问题,提出了一种新的数据扩充方法.该方法在每次加载一批训练数据时,通过不同的覆盖、替换等操作随机修改句子中的单词,得到新的目标句子,然后和源端语句构成新的平行句对,对翻译模型进行训练; 通过约束解码器重构原始目标语句,提高模型对抗噪声的能力.
在英德和中英翻译的实验结果表明,本研究提出的动态数据扩充技术可以有效提高NMT模型的鲁棒性,相对于基准系统BLEU值分别提高了0.69和0.66 个百分点.
然而,该方法也存在一个缺点,即随机将一些单词替换为其他单词可能会损坏句子的语义信息,甚至会完全颠倒句子的语义信息.因此,在未来的工作中,将考虑加入句子的句法信息,在扩充数据的同时尽可能保持句子的本来信息,进一步提升机器翻译的质量.
本研究对训练数据的源语句和目标语句分别进行静态和动态扩充,使用multi-bleu.perl(https:∥github.com/moses-smt/mosesdecoder/blob/master/scripts/generic/multi-bleu.perl)脚本评测翻译性能.
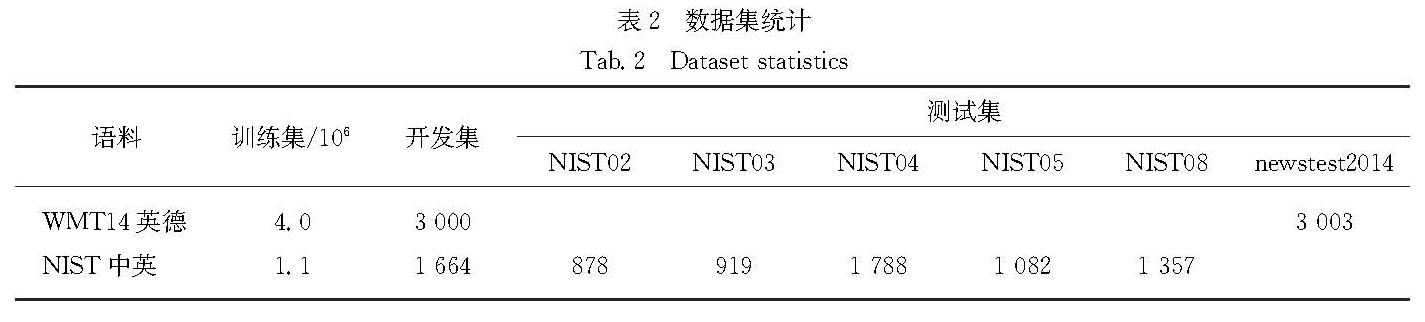
3.1 语料说明为了验证本研究提出的动态数据扩充技术,分别在WMT14英德(http:∥www.statmt.org/wmt14/translation-task.html)和NIST中英(https:∥www.nist.gov/srd)双语平行语料上实验.
1)WMT14英德翻译:训练集共包含450万英语到德语平行语料,由Europarl v7、Common Crawl Corpus和News Commentary数据集构成.此外,实验使用newstest2013和newstest2014分别作为开发集和测试集.
2)NIST中英翻译:训练语料使用的是语言数据联盟(Linguistic Data Consortium,LDC)提供的125万对中英双语平行语料.实验使用NIST06作为开发集,NIST02、NIST03、NIST04、NIST05和NIST08作为测试集.
实验去除两个语言对中训练集长度大于90的平行句对,并使用字节对编码(byte pair encoding,BPE)[16]将单词切分成更小的单元.其中,对英德翻译,在英德语料上联合BPE处理并设置操作次数为3; 对中英翻译,分别在中文和英文端使用BPE处理并设置操作数为3和2.处理后的各数据集样本数如表2所示.
3.2 实验设置本实验使用开源OpenNMT[17]实现的Transformer(https:∥github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-py)和Bahdanau等[3]提出的RNNSearch模型作为基准模型.在预处理时,共享英德的源端与目标端词表,词表大小为33 663; 中英语料不进行词表共享,得到的中英文词表大小分别为30 587和19 877.
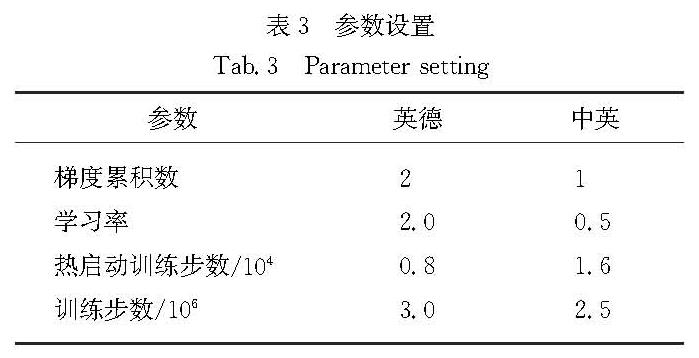
1)Transformer模型设置.训练时,英德和中英模型设置相同的参数主要有:编码器与解码器的层数均为6层,多头注意力机制均为8个头,批处理大小为4 096,词向量、编码器和解码器的隐藏层维度均为512,前馈神经网络的维度为2 048,失活率[18]为0.1.使用Glorot方法初始化模型参数,其他参数均使用默认配置.表3给出了英德和中英实验不同的参数设置.
实验模型分别在一块GTX 1080Ti显卡上训练.在网络训练过程中,采用Adam算法进行参数更新,其参数β1为0.9,β2为0.998,为10-9,训练过程中每隔5×103步保存一次模型.在测试过程中,使用束搜索算法生成最终译文,束搜索的大小设置为5,长度惩罚因子α为0.6,选择开发集性能最高的模型作为实验最终模型.
2)RNNSearch模型设置.英德和中英模型采用相同的实验设置,具体为:编码器和解码器的维度为1 000,批处理大小为80,设置源端目标端最长单词序列为50,失活率[18]为0.3,训练过程中学习率为0.000 5,梯度裁剪的大小为1.实验模型分别在一块GTX 1080Ti显卡上训练6轮.在测试过程中,使用束搜索算法生成最终译文,设置束搜索的大小为10,在开发集上选择性能最高的模型作为实验的测试模型.
3.3 实验结果及分析为了验证本研究提出的动态数据扩充技术的有效性,分别在Transformer和RNNSearch基准模型上进行以下几组实验的对比分析:在Transformer模型上对目标端序列静态扩充(tgt-SA),即对同样一批数据即使加载多次也采取同样的覆盖方式; 在加载一批数据时对源端句子(src-DA)和目标端句子进行动态扩充(tgt-DA),即对同样一批数据每次加载都采用不同的覆盖方式.由于本研究主要为验证目标端动态数据扩充方法技术的有效性,所以在RNNSearch模型上仅对比tgt-DA和RNNSearch基准模型的性能.
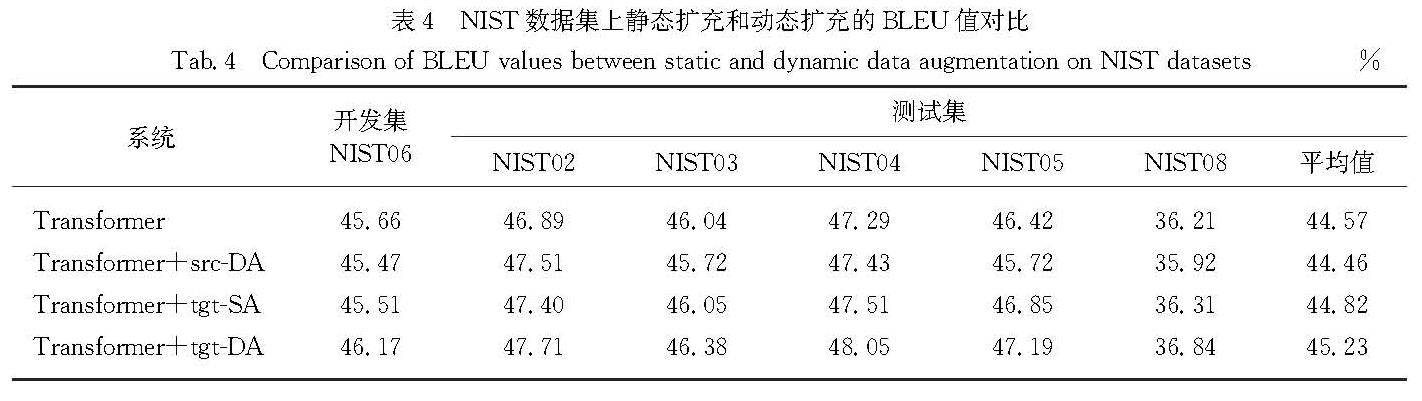
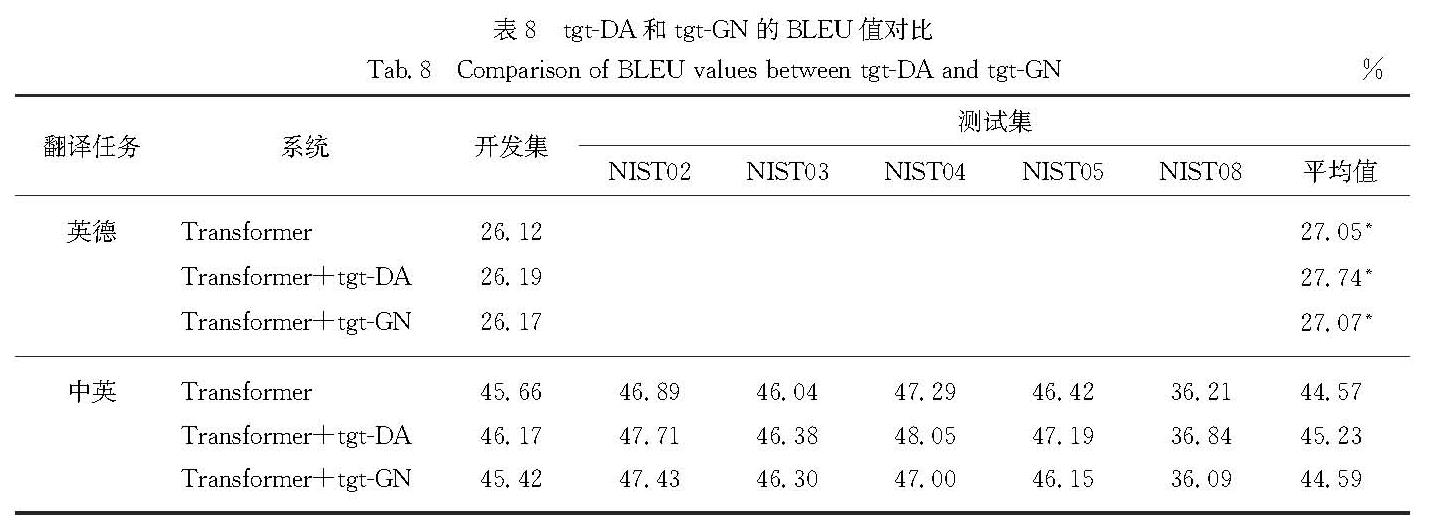
3.3.1 Transformer中英翻译对所提出的方法,本研究在中英数据集上分别进行3组实验:静态扩充的方法仅用于目标端(tgt-SA)、动态扩充的方法分别作用于源端和目标端句子(src-DA,tgt-DA).表4给出了中英翻译的实验结果,可以看出:相较于基本的Transformer系统,单纯对目标端输入序列静态扩充会带来双语互译评估(BLEU)值的微弱提升(0.25个百分点),而对目标序列动态扩充的方法可以在NIST02~NIST08数据集上取得持续的提升,BLEU值平均提高0.66个百分点.这验证了动态数据扩充技术的有效性.然而将动态扩充的方法作用于源端语句时,BLEU值反而降低了0.11个百分点.
由表中数据可以得出以下结论:
1)在中英翻译实验上:对于目标单词序列,静态扩充方法和动态扩充方法都会提高编码器预测单词的能力; 并且动态扩充技术增加了目标句子的多样性,比静态扩充可以带来更高质量的翻译译文.
2)对源语言动态扩充时,编码器得到的隐藏层状态会丢失部分语义信息,因此不仅不会提升模型的翻译性能反而会降低译文质量.
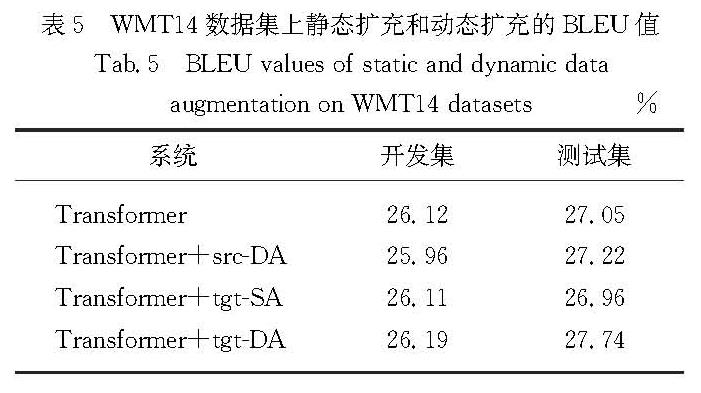
3.3.2 Transformer英德翻译表5给出了英德翻译实验结果,可以看出:Transformer基准系统在测试集上的BLEU值为27.05%,对目标端语句进行静态扩充时,BLEU值为26.96%,BLEU值不仅没有提升反而降低了0.09个百分点; 然而对于目标端语句进行动态扩充可以获得显著的性能提升,BLEU值为27.74%,提高了0.69 个百分点.
表4 NIST数据集上静态扩充和动态扩充的BLEU值对比
Tab.4 Comparison of BLEU values between static and dynamic data augmentation on NIST datasets表5 WMT14数据集上静态扩充和动态扩充的BLEU值
Tab.5 BLEU values of static and dynamic data augmentation on WMT14 datasets根据表5的实验结果,在英德翻译系统上可以得到如下结论:
1)对目标端语句进行静态数据扩充可能会损害模型的翻译性能.然而在中英翻译实验上,静态数据扩充能够获得有限提升.由此可见,静态数据扩充方法带来的翻译性能可能会受到语系的影响.
2)本研究提出的动态扩充的方法应用于源端语句和目标端语句时都会提升模型的翻译性能,并且应用于目标端时提升的效果更为明显.
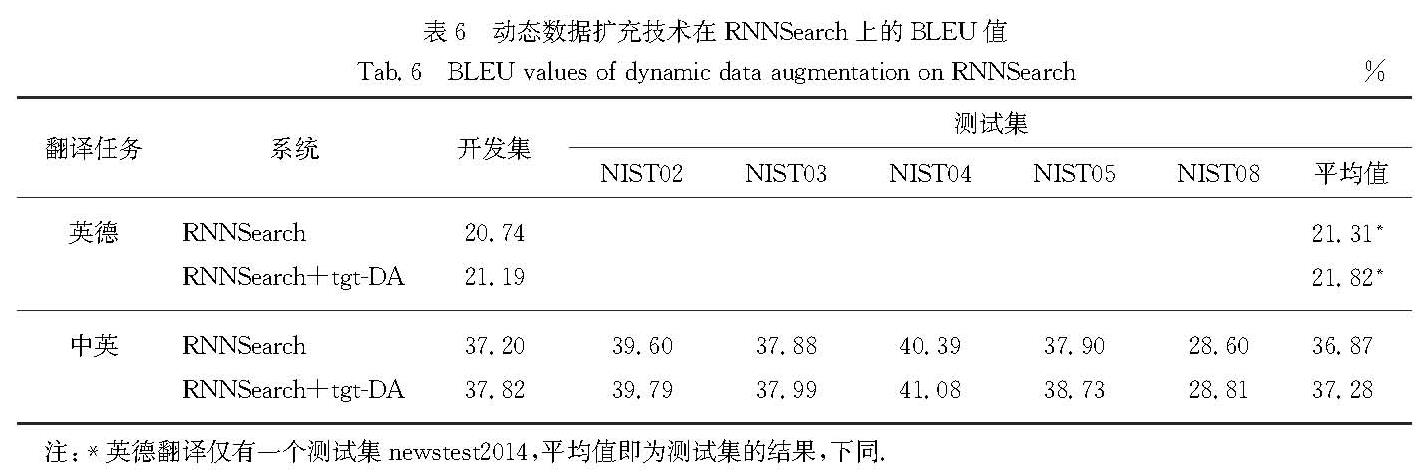
3.3.3 RNNSearch动态数据扩充为了进一步论证本研究提出方法的有效性,将目标端动态数据扩充技术应用在RNNSearch[3]机器翻译模型上.表6给出了RNNSearch模型上的中英和英德实验结果,可以看出:动态数据扩充方法在英德翻译任务上提高了0.51个百分点,在中英翻译任务上平均提高了0.41个百分点.由此可以得出无论是在当前的主流翻译模型Transformer上,还是在RNNSearch上,本研究提出的动态数据扩充方法虽然简单,但是都能够带来翻译性能的提高.
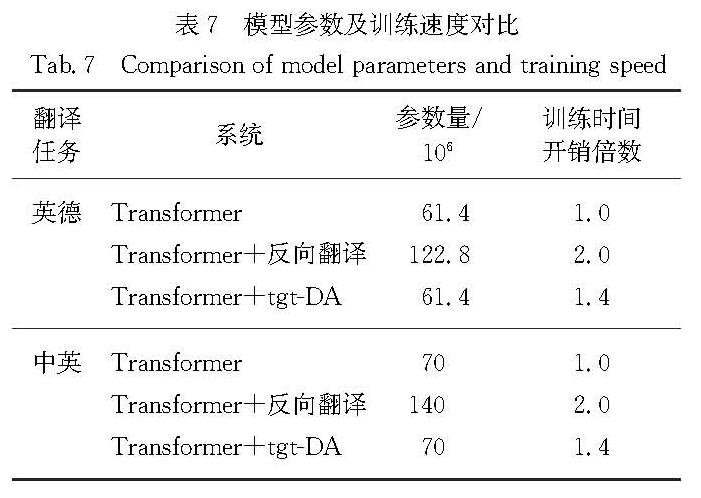
3.3.4 计算开销对比本研究提出的目标端语句动态扩充方法不需要改变模型的基本结构,因此并没有引入额外的模型参数,和基线系统相比训练产生的额外开销仅花费在构造目标端噪声输入上; 当使用反向翻译技术时,在模型参数和训练数据不变的情况下需要额外训练一个反向的模型,因此参数量和训练时间开销均为基线系统的2.0倍,如表7所示.
3.3.5 添加噪声分析由于本研究提出的动态数据扩充方法是对目标端序列进行修改,所以可以视为一种添加噪声的方法.为了探究动态数据扩充方法和对单词进行噪声化方法的关系,本研究使用Transformer翻译模型在英德和中英数据集上做如下对比实验:对目标端句子进
行动态扩充(tgt-DA)和对目标端句子中每个单词的词嵌入表示添加均值为0、方差为0.01的高斯噪声(tgt-GN).
表8给出了在Transformer模型上不同添加噪声方法的实验结果,可以看出:对目标端单词的词嵌入表示添加噪声时相较于基准系统可以带来微弱的性能提升,英德和中英翻译任务上BLEU值都提高了0.02 个百分点.虽然本研究提出的动态数据扩充方法也可以看作是一种动态添加噪声的方法,但是在英德和中英翻译任务上能够带来更多提升,BLEU值分别提高了0.69 和0.66个百分点.
- [1] KOEHN P,OCH F J,MARCU D.Statistical phrase-based translation[C]∥Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Human Language Technology.Edmonton:ACL,2003:48-54.
- [2] SUTSKEVER I,VINYALS O,LE Q V.Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1409.3215.pdf.
- [3] BAHDANAU D,CHO K H,BENGIO Y.Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1409.0473.pdf.
- [4] KALCHBRENNER N,BLUNSOM P.Recurrent continuous translation models[C]∥Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing.Seattle:ACL,2013:1700-1709.
- [5] KRIZHEVSKY A,SUTSKEVER I,HINTON G E.ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J].Communications of the ACM,2017,60(6):84-90.
- [6] IYYER M,MANJUNATHA V,BOYD-GRABER J,et al.Deep unordered composition rivals syntactic methods for text classification[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing.Beijing:ACL,2015:1681-1691.
- [7] SENNRICH R,HADDOW B,BIRCH A.Improving neural machine translation models with monolingual data[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Associa-tion for Computational Linguistics.Berlin:ACL,2016:86-96.
- [8] ARTETXE M,LABAKA G,AGIRRE E,et al.Unsuper-vised neural machine translation[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1710.11041.pdf.
- [9] HE D,XIA Y C,QIN T,et al.Dual learning for machine translation[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1611.00179.pdf.
- [10] FADAEE M,BISAZZA A,MONZ C.Data augmentation for low-resource neural machine translation[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Vancouver:ACL,2017:567-573.
- [11] GAO F,ZHU J H,WU L J,et al.Soft contextual data augmentation for neural machine translation[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Florence:ACL,2019:5539-5544.
- [12] GEHRING J,AULI M,GRANGIER D,et al.Convo-lutional sequence to sequence learning[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1705.03122v3.pdf.
- [13] DEVLIN J,CHANG M W,LEE K,et al.BERT:pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805v2.pdf.
- [14] VASWANI A,SHAZEER N,PARMAR N,et al.Attention is all you need[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762v5.pdf.
- [15] VINCENT P,LAROCHELLE H,BENGIO Y,et al.Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning.Helsinki:ACM,2008:1096-1103.
- [16] SENNRICH R,HADDOW B,BIRCH A.Neural machine translation of rare words with subword units[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Berlin:ACL,2016:1715-1725.
- [17] KLEIN G,KIM Y,DENG Y T,et al.OpenNMT:Open-source toolkit for neural machine translation[EB/OL].[2020-11-13].https:∥arxiv.org/pdf/1701.02810.pdf.
- [18] SRIVASTAVA N,HINTON G,KRIZHEVSKY A,et al.Dropout:a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2014,15(1):1929-1958.