(厦门大学化学化工学院,固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室,福建 厦门 361005)
(State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces,College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361005,China)
stereoselective hydroxylation; dioxygen activation; quantum mechanics; molecular mechanics; peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenese; dopamine β-monooxygenasedoi:10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202006016
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202006010
备注
铜是生物体中含量第二多的过渡金属元素.含铜酶的数量和种类众多,在生物体中分布广泛,其普遍参与氧气的传输以及活化、电子转移、底物氧化等重要代谢过程.双铜单加氧酶肽基甘氨酸α羟基化酶(PHM)和多巴胺β单加氧酶(DβM)通过对相应底物C—H键立体选择性羟基化,合成生理学重要的激素和神经递质.尽管对这两种双铜单加氧酶已进行了大量研究,但是针对氧气活化机制以及底物羟基化的中间体仍有很多争议.本文主要总结双铜单加氧酶PHM和DβM中氧气活化以及底物羟基化机理的理论研究进展,并与实验数据进行比较.
Copper is the second most abundant transition metal element in organisms.Copper-containing enzymes are widely distributed in organisms.Most of them are involved in critical metabolic processes,including dioxygen transport and activation,electron transfer and substrate oxidation.The binuclear copper-containing enzymes,peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenese(PHM)and dopamine β-monooxygenase(DβM),accomplish the biosynthesis of physiologically important hormones and neurotransmitters by the stereoselective hydroxylation of C—H bond in corresponding substrates.Despite of extensive experimental and computational studies,the mechanisms of dioxygen activation and nature of the active species for substrate hydroxylation are still controversial.Herein,we review the recent progress in the computational study of oxygen activation and substrate hydroxylation by binuclear copper monooxygenases PHM and DβM,and gauge the computed mechanism with experimental data.
引言
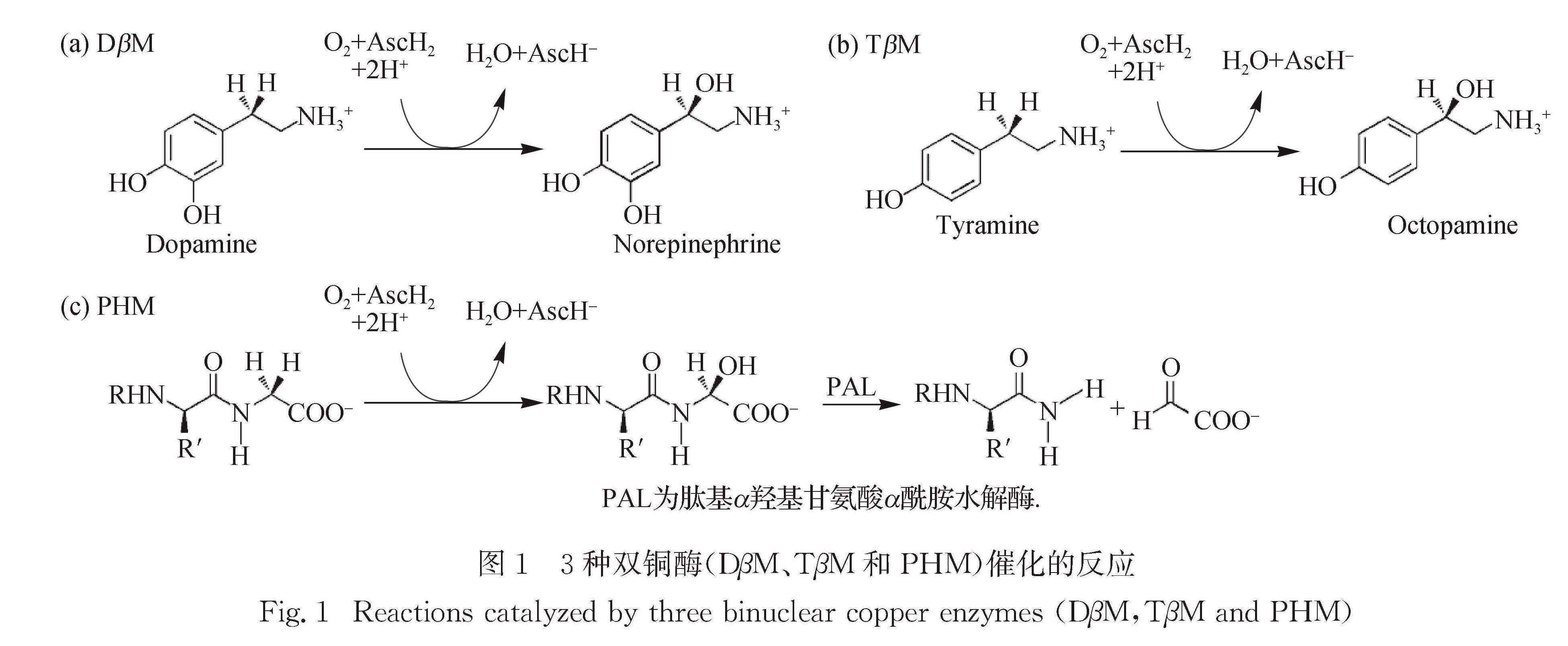
氧气是一种绿色、易得且动力学很稳定的氧化剂[1-8].自然界为有效利用氧气,进化出了大量可活化氧气的金属酶,它们可驱动大量氧化反应[1-16],包括芳香化合物的羟基化、C—C键的裂解和形成以及极具挑战的C—H键官能化.在这些反应中,铜辅因子在氧气还原过程中起着重要作用[3-4,14-15,17-18].铜氧化合物是铜酶催化反应的重要中间体,在铜酶反应机理研究和合成化学方面备受关注[19].双铜酶是一类重要铜蛋白,包括肽基甘氨酸α羟基化酶(PHM)[17,20-37]、多巴胺β单加氧酶(DβM)[19,22,38-55]和酪胺β单加氧酶(TβM)[56-61].这3种酶通过对相应底物的C—H键立体选择性羟基化,合成生理学重要的激素和神经递质,如图1所示[14].
DβM是在哺乳动物肾上腺神经分泌小泡中发现的一种糖蛋白,在多巴胺合成路径中催化多巴胺转化为去甲肾上腺素[41-42],其活性在调节多巴胺和肾上腺素生理上至关重要.人体DβM缺陷会导致患者不能合成肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素,进而引起严重的低血压[43].此外,对小鼠的研究发现DβM缺陷会引起胚胎在子宫中死亡,表明DβM对于胚胎发育也是不可或缺的[44].目前已开发DβM的抑制剂可限制去甲肾上腺素的量而作为降血压药[45-46].DβM能羟基化一系列与多巴胺类似的苯乙胺[47],也能催化不同非天然氧化反应,包括硫氧化[50]、硒氧化[49]和烯烃环氧化[51].DβM已经从大量哺乳动物中分离得到,研究最多的是牛[52]和雄性SD大鼠[53].DβM同时存在可溶型[54]和膜结合蛋白型[39],其中可溶型DβM有二体和四体结构,分别由2或4个相同的73 ku 亚基组成[55]; 膜结合蛋白型的DβM为四体结构,由2个可溶的 73 ku 亚基和另2个不同的77 ku亚基构成.
TβM催化羟基化酪胺为章鱼胺.章鱼胺是一种重要的神经递质,与一系列生理过程有关,包括神经肌肉传递、行为发育和排卵[57-58].TβM是DβM的同源物,39%序列一致,55%序列相似[62].TβM已从美国螯龙虾(Homarus americanus)[59]、烟草飞蛾(Manduca sexta)[60]和黑腹果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster)[61]中分离得到,其中由果蝇获得的重组TβM在溶剂中以大量约69 ku的单体和少量二体形式存在[61].然而人们对生物体内的TβM却了解很少.图1 3种双铜酶(DβM、TβM和PHM)催化的反应
Fig.1 Reactions catalyzed by three binuclear copper enzymes(DβM,TβM and PHM)PHM的序列32%和DβM相同,是肽基甘氨酸α酰胺单加氧酶(PAM)的一部分; PAM的功能为水解酰胺化肽激素,也可进行一些其他单加氧反应,包括硫氧化、氮脱甲基化和氧脱甲基化[22,28].肽酰胺反应分两步:第一步为PHM羟基化肽基甘氨酸α碳; 第二步为PAL水解酰胺键得到活性氮端肽激素.由于超过一半肽激素活化都需要α酰胺化,所以这一过程极其重要.目前PAM已从很多哺乳动物中分离获得[28,37,63-64],敲除该基因可导致酰胺化肽的缺乏,进而引起死亡[64].从SD大鼠的PAM重组蛋白中分离得到一种35 ku的蛋白PHMcc,仅表现PHM活性[36],在动力学、晶体学和光谱学方面应用广泛.
1 非耦合双铜单加氧酶的结构
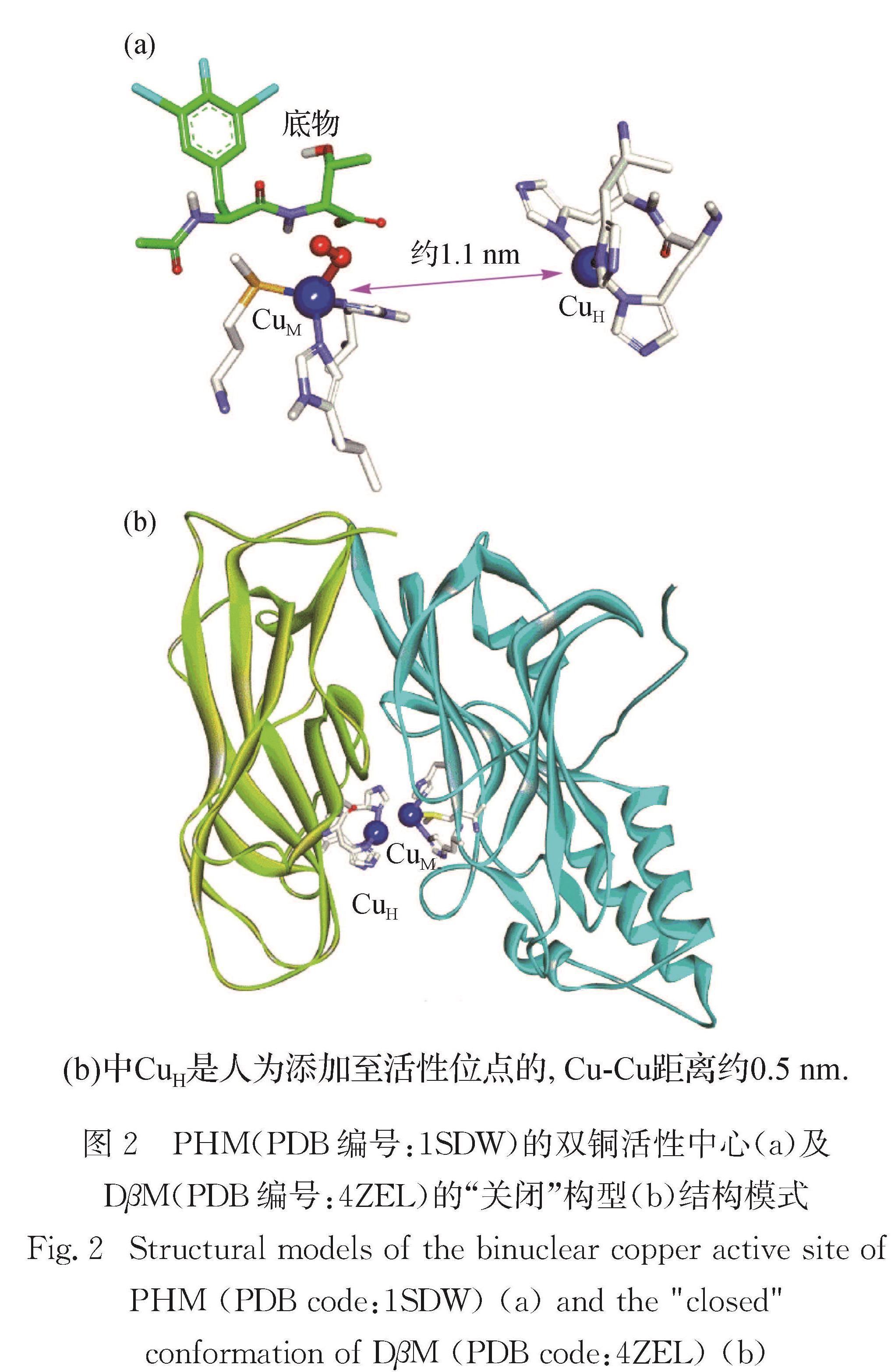
PHM、DβM和TβM结构相似,包含2个相距约1.1 nm的铜辅因子CuM和CuH,CuM与1个甲硫氨酸残基和2个组氨酸残基配位,而CuH与3个组氨酸残基配位[14,20,27,33-34,65-68].这些酶中的2个铜位点间距很远且没有桥联配体,因此被称为“非耦合”双铜单加氧酶[14,17].CuM位点负责氧气的配位和活化,以及底物的羟基化反应; 而CuH位点是电子载体,为氧气催化活化提供额外电子[14,17,69-71].此外,也有报道铜辅基对PHM的结构稳定有重要意义[72].
目前已经解析了大量PHM和DβM的晶体结构,对研究酶的构效关系有重要意义.Amel团队测定了PHM的四级结构[20,73],包含与CuM端基配位的超氧残基和位于CuM附近的N-乙酰基(二碘酪氨酸)-D-苏氨酸(IYT)底物,如图2(a)所示.在该结构中,2个铜原子间距约1.1 nm,其间充满溶剂,呈现“开放”构型,有利于协同底物抗坏血酸(AscH-)的进入并还原Cu(Ⅱ)为Cu(Ⅰ).近期解析得到DβM的二体晶体结构[40],发现该二体结构同时包含“开放”和“关闭”构型单体各1个.“开放”构型单体中2个铜原子距离约1.4 nm,与PHM类似; 而“关闭”构型单体比较少见,2个铜原子距离约为0.5 nm,如图2(b)所示.因此,DβM可能通过“开放”构型进行底物输运、铜的还原以及产物释放,而含有2个耦合铜原子的“关闭”构型才是真正的反应活性中心[40].
2 非耦合双铜单加氧酶的动力学研究
动力学和动力学同位素效应实验已广泛用于研究PHM和DβM中氧气的活化以及C—H键羟基化机理.PHM和DβM动力学性质类似,因此推测反应机理也类似[17].针对PHM和DβM,已进行了大量稳态动力学和同位素效应的实验研究[19].
在大量抗坏血酸的条件下,酶能被充分还原,相应实验测定了翻转数(kcat)和催化效率(kcat/KM)[17].研究发现马尿酸为PHM能催化的最小底物,而其他一些较大的肽基甘氨酸(如Tyr-Val-Gly)也可作为底物,以马尿酸作为底物时KM约1.7 mmol/L,而以Tyr-Val-Gly作为底物时KM约0.01 mmol/L[74].实验推测可能是因为马尿酸与蛋白质较弱的相互作用而导致KM较大.PHM羟基化马尿酸的翻转数为39.1 s-1,总反应能垒推算约71 kJ/mol[75].DβM羟基化多巴胺时KM约0.49 mmol/L,翻转数为12.7 s-1,底物与酶的活性满足Michaelis-Menten稳态动力学; 在氧化Tyr-Val-Gly,还原剂为抗坏血酸时,KM为0.25 mmol/L,且提高抗坏血酸的浓度,反应速率和底物的KM都会升高[76].即使在还原剂显著过量的条件下,解析的PHM晶体结构中也未发现抗坏血酸的结合[20,68,77].然而与PHM不同的是,DβM的翻转速率会随还原剂抗坏血酸的增加而下降[78].
底物的同位素效应研究对于理解整个反应具有重要意义.实验观测得一级氘代同位素效应对PHM和DβM分别为1.56[79-81]和1.00[82]; 同时,C—H键羟基化的“内禀”同位素效应对PHM和DβM分别为10.6[83]和10.9[80,84],并估算出PHM羟基化马尿酸的C—H键反应能垒焓约54 kJ/mol,反应能垒吉布斯自由能约58 kJ/mol.此外,实验发现18O取代底物的动力学同位素效应较氘代底物高[82-83],由此推测O—O键活化可能与C—H键活化是可逆耦合的.通过电子顺磁共振(EPR)冷冻淬火研究发现DβM中铜辅因子还原的一级速率为250 s-1,表明酶还原不是决速步骤[71,85].预还原的DβM可在空气中氧化,在底物存在下EPR测量得酶的氧化速率为82 s-1[71],表明:1)无底物时酶与氧气的反应速率比有底物时慢1 000倍,即底物加速氧气还原; 2)酶的再氧化不是反应决速步骤.在PHM中,通过分析底物和氧气结合到酶活性区域的速率与氧气浓度的关系,表明底物先于氧气进入活性区域[83]; 然而实验数据分析表明DβM和TβM中底物和氧气的结合为随机机理[56,86].
3 非耦合双铜单加氧酶的机理研究
目前PHM和DβM的反应机理特别是氧气活化和底物羟基化过程仍不够清晰,而TβM的各项研究较少,故下文主要讨论PHM和DβM的反应机理.
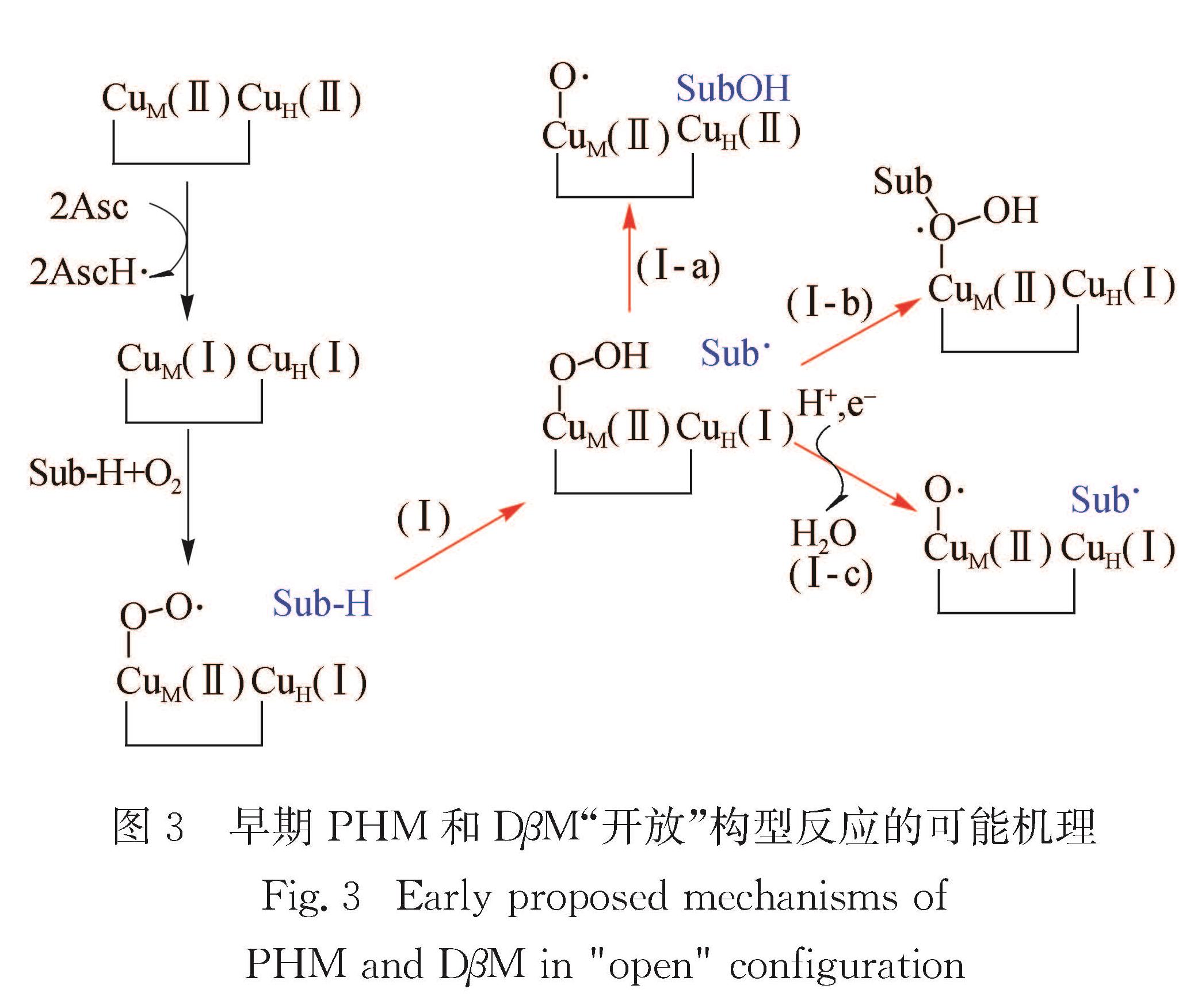
3.1 早期PHM和DβM“开放”构型反应机理图3总结了基于早期实验和理论研究得到的双铜单加氧酶的可能机理.一般认为2个Cu(Ⅱ)开始先被抗坏血酸还原为Cu(Ⅰ),然后氧气结合到CuM(Ⅰ),形成铜超氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·[14,87-88].目前实验上还没有获得这几种酶的铜超氧物种中间体的光谱表征结果.然而,晶体学研究已经捕捉到铜超氧物种的结构[20],并且该物种在模型化合物中被广泛表征[14-15,17-19,22,89-126].关于后续反应机理有很多的可能路径被提出,但还没有完全令人满意的结果.一般认为羟基化反应首先需要从甘氨酸上进行提取发生反应[22,35,127-128]; 接下来的反应是羟基回弹,但其机理尚不明确[68,128-130].由于羟基回弹可能并不是反应的决速步骤,相关实验证据很难获得,但理论计算普遍认同羟基回弹机理[128-129].
整个反应除氧气外还需要消耗2个质子和2个电子,而质子电子的输入可能会进一步生成各式各样的氧物种.由于酶中质子电子转移研究的复杂性,有关C—H键提取的活性物种一直备受争议.Bauman等[126]根据氧气和双氧水在体系中的交换,提出反应中会存在1个CuM(Ⅰ)—O2的等价中间体.第1个提出的中间体为Cu(Ⅱ)—OOH物种[71,80],然而其模型化合物的实验研究发现该物种不能进行C—H键提取,计算得反应能垒超过160 kJ/mol[131],表明Cu(Ⅱ)—OOH可能不是活性物种.Prigge等[20]根据晶体结构提出Cu(Ⅱ)M—O22-为反应的活性物种; Rudzka等[73]获得了体系与双氧水配位但没有底物的晶体结构,也提出CuM(Ⅱ)—O22-为可能的氢提取活性物种.理论计算发现基态为二重态,氢提取反应能垒超过120 kJ/mol,而从水分子提取质子的能垒仅约20 kJ/mol[38,131].早期密度泛函理论(DFT)计算表明侧基铜超氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·为氢提取反应的活性中间体[128],而模型化合物的DFT研究提出端基铜超氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·为氢提取活性物种[89],但是给出的自由能能垒约93 kJ/mol[89].Crespo等[129]考虑到蛋白质环境的因素时,使用QM/MM(quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics)计算发现CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·进行氢提取反应能垒约88 kJ/mol,高于实验推测的约58 kJ/mol.
铜超氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·之前被广泛认为是氢提取的活性物种.从底物提取氢原子后,后续反应可能有3种不同历程,如图3所示.第1种反应历程(Ⅰ-a):CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH物种的远端氧进攻底物自由基,形成羟基化产物和铜氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O·,这一反应路径由Solomon等[14]和Chen等[128]早期提出,估算的自由能垒相对于Cu(Ⅰ)和O2为116 kJ/mol; 第2种反应历程(Ⅰ-b):底物自由基进攻CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH物种的近端氧,伴随O—O键的断裂,形成中间体CuM(Ⅱ)(OH)(·OSub),这一反应路径自由能垒为99.6 kJ/mol[89]; 第3种反应历程(Ⅰ-c):CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH物种的远端氧通过质子耦合的电子转移,发生O—O键断裂,生成一分子水和铜氧物种CuM(Ⅱ)—O·,这一过程是热力学不利的,自由能变化为36.4 kJ/mol[89].相关Metadynamics模拟结果表明Cu(Ⅱ)—OOH物种通过质子耦合的电子转移发生O—O键断裂,在热力学和动力学层面都是不利的[132],因此可以排除第3种反应历程.
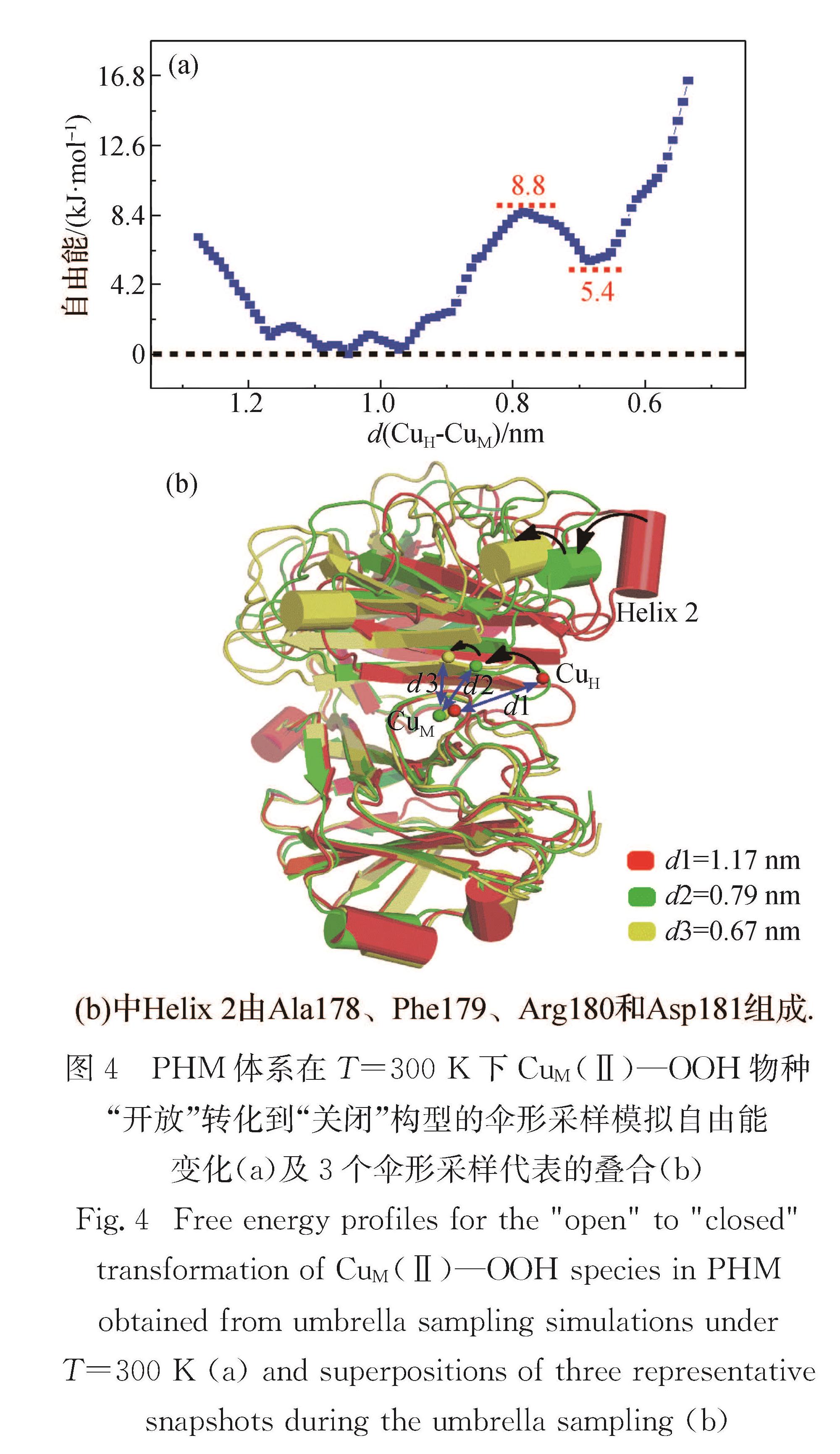
CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种除可能对目标底物进行氢提取外,也可能对协同底物抗坏血酸进行氢提取.在多糖单加氧裂解酶(LPMO)的研究中,Wang等[132]发现CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种很容易从抗坏血酸夺取活泼氢原子生成CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH中间体.由于抗坏血酸是一种高效的氢原子供体[133],比从底物提取氢原子容易很多.近期Wu等[134]计算了PHM中CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种分别从底物和抗坏血酸提取氢原子的反应过渡态,结果显示从抗坏血酸羟基提取氢原子的反应能垒为42.7 kJ/mol,而从底物马尿酸C—H键提取氢原子的反应能垒高达109.2 kJ/mol,这与之前DFT计算相符[89].CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种从抗坏血酸提取氢原子首先生成CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH中间体.进一步计算发现该中间体通过远端氧提取底物C—H键上氢原子的反应能垒超过188.4 kJ/mol,且不能得到稳定产物; 而通过近端氧提取底物C—H键的氢原子生成CuM(Ⅰ)—H2O2的反应能垒超过167.4 kJ/mol[134].以上结果显示“开放”构型CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH对底物C—H键羟基化无反应活性,因此排除其作为活性中间体的可能性.3.2 “开放”到“关闭”的构型转化晶体学研究发现DβM可同时包含“开放”和“关闭”构型单体.“关闭”构型单体中2个耦合的铜原子可能作为反应活性中心,而“开放”构型可能负责底物进入、铜的还原和产物释放等[14,17,69-71].Wu等[134]通过伞形采样研究了300 K下CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH物种由“开放”转化到“关闭”构型的自由能变化(图4(a)),计算结果显示这一构型转化动力学很容易发生,反应自由能垒约8.8 kJ/mol,自由能变化为5.4 kJ/mol.如图4(b)所示:
在这一转化过程中,2个铜原子的距离缩短到0.67 nm,与DβM“关闭”构型(约0.5 nm)类似; 此外,2个铜原子距离的缩短主要由CuH区域中Helix 2的靠近造成,而CuM的位置在整个伞形采样中基本无变化,这也间接支持结构灵活的CuH位点可能参与O—O键的活化.图4 PHM体系在T=300 K下Cu M (Ⅱ)—OOH物种“开放”转化到“关闭”构型的伞形采样模拟自由能变化(a)及3个伞形采样代表的叠合(b)
Fig.4 Free energy profiles for the "open" to "closed" transformation of CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH species in PHM obtained from umbrella sampling simulations under T=300 K(a)and superpositions of three representative snapshots during the umbrella sampling(b)4 “耦合”双铜单加氧酶的催化循环机理
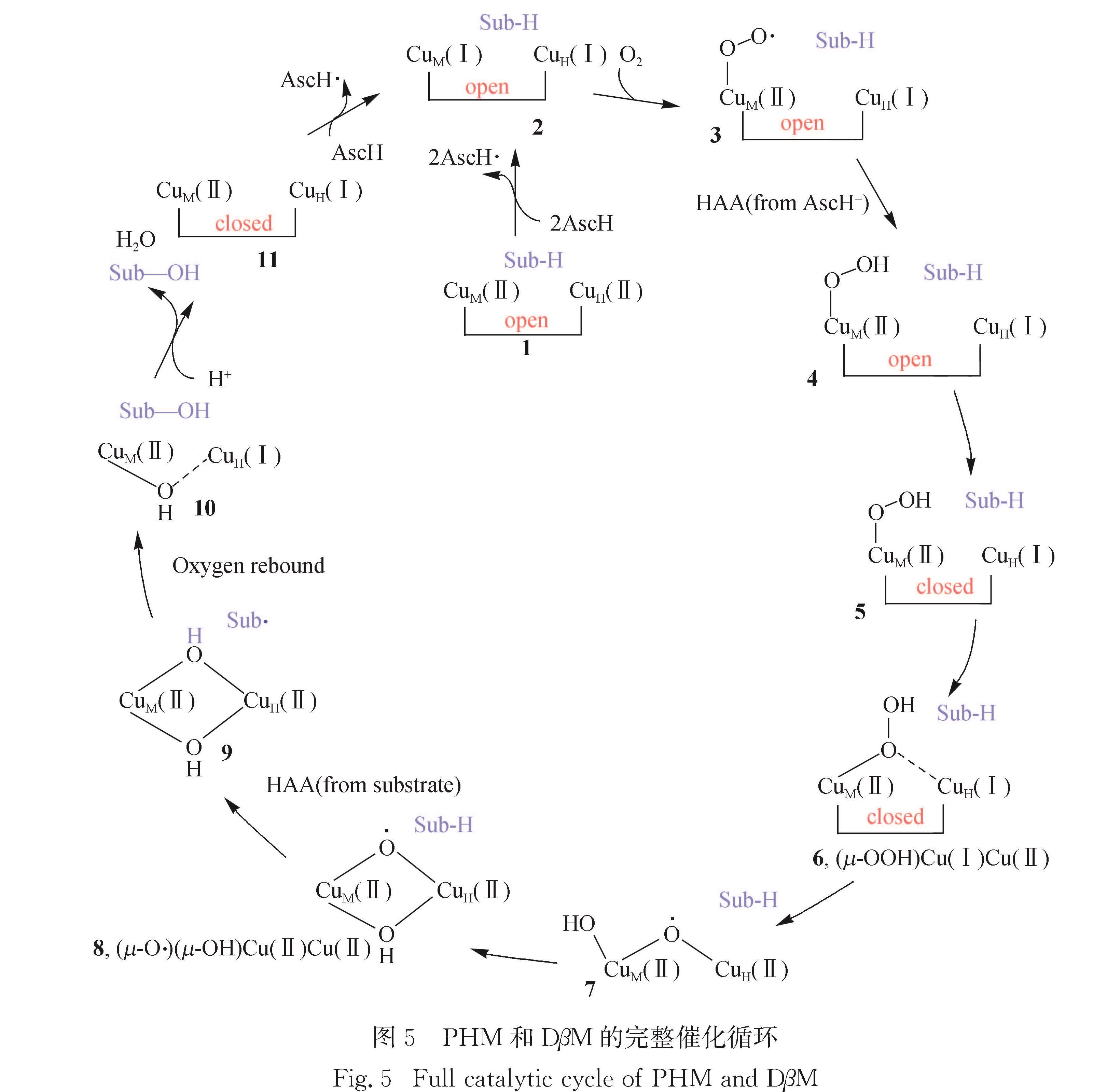
前文中提到“开放”构型下CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH中O—O键无法被进一步活化,另外伞形采样计算发现“开放”构型下CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH很容易转化为“关闭”构型下的CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH.量子力学进一步计算发现“关闭”构型中OOH基团通过桥式同时配位到CuM和CuH时最稳定,记为(μ-OOH)Cu(Ⅰ)Cu(Ⅱ).图5给出了PHM和DβM的完整催化循环机理,可以看出:从(μ-OOH)Cu(Ⅰ)Cu(Ⅱ),即6出发反应首先通过OOH的O—O键均裂生成中间体7; 接着OH迁移到CuH形成(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ)中间体8,这一过程的反应能垒为59.9 kJ/mol; 而(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ)直接提取底物氢原子的能垒高达85.0 kJ/mol,远高于实验能垒(约58.0 kJ/mol),因此(μ-O·)(μ-OH)CuM(Ⅱ)CuH(Ⅱ)不是氢提取活性物种.前一步生成的(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ)中间体的OH基团能够进一步配位在CuH上,形成(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ),能垒仅为27.6 kJ/mol.CuM—S在此转化过程中键长明显增加,表明CuM—S是柔性的,与实验观测相符,这表明弱的CuM—S键有利于O—O键断裂,否则四配位构型的CuM不利于OH进一步配位,从而阻碍O—O键断裂.(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ)可从底物提取氢原子形成底物自由基和(μ-OH)2Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ),该反应能垒仅为41.45 kJ/mol,与实验推测相符.氢提取反应同位素效应,动力学同位素实验(KIE)值测算为12.1,与实验观测的10.9相符[134].后续经过羟基回弹即得到产物,这一步反应的KIE值k(18OH)/k(OH)和k(18OD)/K(OD)分别为1.3和1.5.最后产物释放,吸收质子脱水完成催化循环.此外,实验观测还发现PHM的M314H突变体活性降低的情况[135-136],计算结果显示M314H突变体O—O键断裂的能垒为72.85 kJ/mol,比野生型O—O键断裂的能垒高约12.0 kJ/mol,与实验观测相符.这可能是因为野生型酶中柔性的CuM—S有利于OH配位到CuM上.
5 总结与展望
本文总结了现阶段双铜单加氧酶PHM和DβM催化机理的理论研究进展,讨论了氧气活化过程中各种可能的中间体以及对底物羟基化的反应活性,包括CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·、CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH、CuM(Ⅱ)—O·和(μ-O·)(HO)CuM(Ⅱ)CuH(Ⅱ).根据计算的反应能垒和实验的推估值,提出最有可能的活性物种为(μ-O·)(HO)CuM(Ⅱ)CuH(Ⅱ).同时,给出与实验相符的PHM和DβM的完整反应机理为:1)静息态的2个Cu(Ⅱ)由抗坏血酸还原为Cu(Ⅰ),氧气结合到CuM,形成相应CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种; 2)CuM(Ⅱ)—O2·物种提取抗坏血酸氢原子形成CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH; 3)CuH移动靠近CuM,CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH构型由“开放”转化到“关闭”; 4)“关闭”型CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH异构化为(μ-OOH)Cu(Ⅰ)Cu(Ⅱ); 5)O—O键断裂,OH迁移生成氢提取活性物种(μ-O·)(μ-OH)Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ); 6)氢提取反应生成底物自由基和(μ-OH)2Cu(Ⅱ)Cu(Ⅱ); 7)羟基回弹得到产物; 8)底物释放,质子化脱水,完成催化循环.以上机理研究揭示了氧气活化机制以及底物羟基化活性物种,也为进一步开发基于双铜单加氧酶的生物合成反应提供了理论基础.
- [1] PAU M Y M,LIPSCOMB J D,SOLOMON E I.Substrate activation for O2 reactions by oxidized metal centers in biology[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2007,104(47):18355-18362.
- [2] KOVALEVA E G,LIPSCOMB J D.Versatility of biological non-heme Fe(Ⅱ)centers in oxygen activation reactions[J].Nature Chemical Biology,2008,4(3):186-193.
- [3] MEIER K K,JONES S M,KAPER T,et al.Oxygen activation by Cu LPMOs in recalcitrant carbohydrate polysaccharide conversion to monomer sugars[J].Chemical Reviews,2018,118(5):2593-2635.
- [4] WIKSTRÖM M,KRAB K,SHARMA V.Oxygen activation and energy conservation by cytochrome C oxidase[J].Chemical Reviews,2018,118(5):2469-2490.
- [5] BOLLINGER J M,Jr,KREBS C.Enzymatic C—H activation by metal-superoxo intermediates[J].Current Opinion in Chemical Biology,2007,11(2):151-158.
- [6] COSTAS M,MEHN M P,JENSEN M P,et al.Dioxygen activation at mononuclear nonheme iron active sites:enzymes,models,and intermediates[J].Chemical Reviews,2004,104(2):939-986.
- [7] JASNIEWSKI A J,QUE L,Jr.Dioxygen activation by nonheme diiron enzymes:diverse dioxygen adducts,high-valent intermediates,and related model complexes[J].Chemical Reviews,2018,118(5):2554-2592.
- [8] HUANG X Y,GROVES J T.Oxygen activation and radical transformations in heme proteins and metalloporphyrins[J].Chemical Reviews,2018,118(5):2491-2553.
- [9] GUO M,CORONA T,RAY K,et al.Heme and nonheme high-valent iron and manganese oxo cores in biological and abiological oxidation reactions[J].ACS Central Science,2019,5(1):13-28.
- [10] CIANO L,DAVIES G J,TOLMAN W B,et al.Bracing copper for the catalytic oxidation of C—H bonds[J].Nature Catalysis,2018,1(8):571-577.
- [11] WANG B T,CAO Z X,ROVIRA C,et al.Fenton-derived OH radicals enable the MPnS enzyme to convert 2-hydroxyethylphosphonate to methylphosphonate:insights from ab initio QM/MM MD simulations[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(23):9284-9291.
- [12] GUENGERICH F P,YOSHIMOTO F K.Formation and cleavage of C—C bonds by enzymatic oxidation-reduction reactions[J].Chemical Reviews,2018,118(14):6573-6655.
- [13] SHAIK S,COHEN S,WANG Y,et al.P450 enzymes:their structure,reactivity,and selectivity modeled by QM/MM calculations[J].Chemical Reviews,2010,110(2):949-1017.
- [14] SOLOMON E I,HEPPNER D E,JOHNSTON E M,et al.Copper active sites in biology[J].Chemical Reviews,2014,114(7):3659-3853.
- [15] TRAMMELL R,RAJABIMOGHADAM K,GARCIA-BOSCH I.Copper-promoted functionalization of organic molecules:from biologically relevant Cu/O2 model systems to organometallic transformations[J].Chemical Reviews,2019,119(4):2954-3031.
- [16] CITEK C,HERRES-PAWLIS S,STACK T D P.Low temperature syntheses and reactivity of Cu2O2 active-site models[J].Accounts of Chemical Research,2015,48(8):2424-2433.
- [17] KLINMAN J P.Mechanisms whereby mononuclear copper proteins functionalize organic substrates[J].Chemical Reviews,1996,96(7):2541-2562.
- [18] WHITTAKER J W.Free radical catalysis by galactose oxidase[J].Chemical Reviews,2003,103(6):2347-2364.
- [19] KLINMAN J P.The copper-enzyme family of dopamine β-monooxygenase and peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase:resolving the chemical pathway for substrate hydroxylation[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2006,281(6):3013-3016.
- [20] PRIGGE S T,EIPPER B A,MAINS R E,et al.Dioxy-gen binds end-on to mononuclear copper in a precata-lytic enzyme complex[J].Science,2004,304(5672):864-867.
- [21] BELL J,ASH D E,SNYDER L M,et al.Structural and functional investigations on the role of zinc in bifunc-tional rat peptidylglycine α-amidating enzyme[J].Biochemistry,1997,36(51):16239-16246.
- [22] PRIGGE S T,MAINS R E,EIPPER B A,et al.New insights into copper monooxygenases and peptide amida-tion:structure,mechanism and function[J].Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2000,57(8/9):1236-1259.
- [23] SALDISE L,MARTÍNEZ A,MONTUENGA L M,et al.Distribution of peptidyl-glycine α-amidating mono-oxygenase(PAM)enzymes in normal human lung and in lung epithelial tumors[J].Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry,1996,44(1):3-12.
- [24] MART NEZ A,TRESTON A M.Where does amidation take place?[J].Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,1996,123(2):113-117.
- [25] KULATHILA R,CONSALVO A P,FITZPATRICK P F,et al.Bifunctional peptidylglcine α-amidating enzyme requires two copper atoms for maximum activity[J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,1994,311(1):191-195.
- [26] EIPPER B A,QUON A S W,MAINS R E,et al.The catalytic core of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase:investigation by site-directed muta-genesis,Cu X-ray absorption spectroscopy,and electron paramagnetic resonance[J].Biochemistry,1995,34(9):2857-2865.
- [27] CHEN P,BELL J,EIPPER B A,et al.Oxygen activation by the noncoupled binuclear copper site in peptidyl-glycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase.Spectroscopic definition of the resting sites and the putative CuM(Ⅱ)—OOH intermediate[J].Biochemistry,2004,43(19):5735-5747.
- [28] PERKINS S N,HUSTEN E J,EIPPER B A.The 108-kDa peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase precur-sor contains two separable enzymatic activities involved in peptide amidation[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,1990,171(3):926-932.
- [29] BOUSQUET-MOORE D,MAINS R E,EIPPER B A.Peptidylgycine α-amidating monooxygenase and copper:a gene-nutrient interaction critical to nervous system function[J].Journal of Neuroscience Research,2010,88(12):2535-2545.
- [30] JIANG N,KOLHEKAR A S,JACOBS P S,et al.PHM is required for normal developmental transitions and for biosynthesis of secretory peptides in Drosophila[J].Developmental Biology,2000,226(1):118-136.
- [31] CZYZYK T A,NING Y,HSU M S,et al.Deletion of peptide amidation enzymatic activity leads to edema and embryonic lethality in the mouse[J].Developmental Biology,2005,287(2):301-313.
- [32] EIPPER B A,PERKINS S N,HUSTEN E J,et al.Peptidyl-α-hydroxyglycine α-amidating lyase.Purification,characterization,and expression.[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1991,266(12):7827-7833.
- [33] JARON S,BLACKBURN N J.Characterization of a half-apo derivative of peptidylglycine monooxygenase.Insight into the reactivity of each active site copper[J].Biochemistry,2001,40(23):6867-6875.
- [34] PRIGGE S T,KOLHEKAR A S,EIPPER B A,et al.Amidation of bioactive peptides:the structure of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase[J].Science,1997,278(5341):1300-1305.
- [35] KATOPODIS A G,MAY S W.Novel substrates and inhibitors of peptidylglycine.α-amidating monooxy-genase[J].Biochemistry,1990,29(19):4541-4548.
- [36] KOLHEKAR A S,KEUTMANN H T,MAINS R E,et al.Peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase:active site residues,disulfide linkages,and a two-domain model of the catalytic core[J].Biochemistry,1997,36(36):10901-10909.
- [37] MAINS R E,EIPPER B A.Secretion and regulation of two biosynthetic enzyme activities,peptidyl-glycine α-amidating monooxygenase and a carboxypeptidase,by mouse pituitary corticotropic tumor cells[J].Endocri-nology,1984,115(5):1683-1690.
- [38] EVANS J P,AHN K,KLINMAN J P.Evidence that dioxygen and substrate activation are tightly coupled in dopamine β-monooxygenase:implications for the reactive oxygen species[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2003,278(50):49691-49698.
- [39] SLATER E P,ZAREMBA S,HOGUE-ANGELETTI R A.Purification of membrane-bound dopamine β-mono-oxygenase from chromaffin granules:relation to soluble dopamine β-monooxygenase[J].Archives of Biochemis-try and Biophysics,1981,211(1):288-296.
- [40] VENDELBOE T V,HARRIS P,ZHAO Y,et al.The crystal structure of human dopamine β -hydroxylase at 2.9 Å resolution[J].Science Advances,2016,2(4):e1500980.
- [41] WINKLER H,APPS D K,FISCHER-COLBRIE R.The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules:established facts and unresolved topics[J].Neuro-science,1986,18(2):261-290.
- [42] REEDY B J,BLACKBURN N J.Preparation and chara-cterization of half-apo dopamine-β-hydroxylase by selec-tive removal of CuA.Identification of a sulfur ligand at the dioxygen binding site by EXAFS and FTIR spectro-scopy[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1994,116(5):1924-1931.
- [43] GARY T,ROBERTSON D.Lessons learned from dopa-mine β-hydroxylase deficiency in humans[J].Physi-ology,1994,9(1):35-39.
- [44] THOMAS S A,MATSUMOTO A M,PALMITER R D.Noradrenaline is essential for mouse fetal develop-ment[J].Nature,1995,374(6523):643-646.
- [45] HIDAKA H.Fusaric(5-butylpicolinic)acid,an inhibitor of dopamine β -hydroxylase,affects serotonin and nora-drenaline[J].Nature,1971,231(5297):54-55.
- [46] FULLER R W,HO P P K,MATSUMOTO C,et al.New inhibitors of dopamine β -hydroxylase[J].Advances in Enzyme Regulation,1977,15:267-281.
- [47] BELIAEV A,FERREIRA H,LEARMONTH D A,et al.Dopamine β -monooxygenase:mechanism,substrates and inhibitors[J].Current Enzyme Inhibition,2009,5(1):27-43.
- [48] COLOMBO G,RAJASHEKHAR B,GIEDROC D P,et al.Alternate substrates of dopamine β -hydroxylase.Ⅰ.Kinetic investigations of benzyl cyanides as substrates and inhibitors[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1984,259(3):1593-1600.
- [49] MAY S W,HERMAN H H,ROBERTS S F,et al.Ascorbate depletion as a consequence of product recycling during dopamine β-monooxygenase catalyzed selenoxidation[J].Biochemistry,1987,26(6):1626-1633.
- [50] MAY S W,PHILLIPS R R S.Asymmetric sulfoxidation by dopamine β-hydroxylase,an oxygenase heretofore considered specific for methylene hydroxylation[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1980,102(18):5981-5983.
- [51] PADGETTE S R,WIMALASENA K,HERMAN H H,et al.Olefin oxygenation and N-dealkylation by dopamine β-monooxygenase:catalysis and mechanism-based inhibi-tion[J].Biochemistry,1985,24(21):5826-5839.
- [52] FRIEDMAN S,KAUFMAN S.3,4-dihydroxyphenyle-thylamine β-hydroxylase:physical properties,copper content,and role of copper in the catalytic acttivity[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1965,240(12):4763-4773.
- [53] WEINSHILBOUM R,AXELROD J.Serum dopamine-β -hydroxylase activity[J].Circulation Research,1971,28(3):307-315.
- [54] FISCHER-COLBRIE R,SCHOBER M.Isolation and cha-racterization of chromogranins A,B,and C from bovine chromaffin granules and a rat pheochromocytoma[J].Journal of Neurochemistry,1987,48(1):262-270.
- [55] KLINMAN J P,KRUEGER M,BRENNER M,et al.Evidence for two copper atoms/subunit in dopamine β-monooxygenase catalysis[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1984,259(6):3399-3402.
- [56] HESS C R,MCGUIRL M M,KLINMAN J P.Mecha-nism of the insect enzyme,tyramine β-monooxygenase,reveals differences from the mammalian enzyme,dopa-mine β-monooxygenase[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2008,283(6):3042-3049.
- [57] ROEDER T.Tyramine and octopamine:ruling behavior and metabolism[J].Annual Review of Entomology,2005,50(1):447-477.
- [58] MONASTIRIOTI M.Distinct octopamine cell population residing in the CNS abdominal ganglion controls ovulation in Drosophila melanogaster[J].Developmental Biology,2003,264(1):38-49.
- [59] WALLACE B G.The biosynthesis of octopamine-charac-terization of lobster tyramine β-hydroxylase[J].Journal of Neurochemistry,2006,26(4):761-770.
- [60] LEHMAN H K,MURGIUC C M,HILDEBRAND J G.Characterization and developmental regulation of tyramine-β-hydroxylase in the CNS of the moth,Manduca sexta[J].Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2000,30(5):377-386.
- [61] GRAY E E,SMALL S N,MCGUIRL M A.Expression and characterization of recombinant tyramine β-monooxy-genase from Drosophila:a monomeric copper-containing hydroxylase[J].Protein Expression and Purification,2006,47(1):162-170.
- [62] MONASTIRIOTI M,LINN C E,Jr,WHITE K.Charac-terization of Drosophila tyramine β-hydroxylase gene and isolation of mutant flies lacking octopamine[J].The Journal of Neuroscience,1996,16(12):3900-3911.
- [63] GLEMBOTSKI C C.Further characterization of the pep-tidyl α-amidating enzyme in rat anterior pituitary secre-tory granules[J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,1985,241(2):673-683.
- [64] KOLHEKAR A S,ROBERTS M S,JIANG N,et al.Neuropeptide amidation in Drosophila:separate genes encode the two enzymes catalyzing amidation[J].The Journal of Neuroscience,1997,17(4):1363-1376.
- [65] BOSWELL J S,REEDY B J,KULATHILA R,et al.Structural investigations on the coordination environment of the active-site copper centers of recombinant bifunctional peptidylglycine α-amidating enzyme[J].Biochemistry,1996,35(38):12241-12250.
- [66] SIEBERT X,EIPPER B A,MAINS R E,et al.The cata-lytic copper of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating mono-oxygenase also plays a critical structural role[J].Biophysical Journal,2005,89(5):3312-3319.
- [67] CHUFÁN E E,PRIGGE S T,SIEBERT X,et al.Differential reactivity between two copper sites in pepti-dylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(44):15565-15572.
- [68] PRIGGE S T,KOLHEKAR A S,EIPPER B A,et al.Substrate-mediated electron transfer in peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase[J].Nature Structural Biology,1999,6(10):976-983.
- [69] DE LA LANDE A,MARTÍ S,PARISEL O,et al.Long distance electron-transfer mechanism in peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase:a perfect fitting for a water bridge[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2007,129(38):11700-11707.
- [70] MELIÁ C,FERRER S,R∨EZÁC∨ J,et al.Investigation of the hydroxylation mechanism of noncoupled copper oxygenases by ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J].Chemistry:A European Journal,2013,19(51):17328-17337.
- [71] BRENNER M C,KLINMAN J P.Correlation of copper valency with product formation in single turnovers of dopamine β-monooxygenase[J].Biochemistry,1989,28(11):4664-4670.
- [72] MAHESHWARI S,SHIMOKAWA C,RUDZKA K,et al.Effects of copper occupancy on the conformational landscape of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating mono-oxygenase[J].Communications Biology,2018,1(1):74.
- [73] RUDZKA K,MORENO D M,EIPPER B,et al.Co-ordination of peroxide to the CuM center of peptidyl-glycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase(PHM):structural and computational study[J].Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry,2013,18(2):223-232.
- [74] MCINTYRE N R,LOWE E W,Jr,BELOF J L,et al.Evidence for substrate preorganization in the peptidyl-glycine α-amidating monooxygenase reaction describing the contribution of ground state structure to hydrogen tunneling[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(46):16393-16402.
- [75] TAKAHASHI K,ONAMI T,NOGUCHI M.Kinetic isotope effects of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating mono-oxygenase reaction[J].Biochemical Journal,1998,336(1):131-137.
- [76] MAINS R E,GLEMBOTSKI C C,EIPPER B A.Peptide α-amidation activity in mouse anterior pituitary AtT-20 cell granules:properties and secretion[J].Endocrino-logy,1984,114(5):1522-1530.
- [77] METZ S,KASTNER J,SOKOL A A,et al.C hem S hell:a modular software package for QM/MM simula-tions[J].Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews:Computational Molecular Science,2014,4(2):101-110.
- [78] STEWART L C,KLINMAN J P.Cooperativity in the dopamine β-monooxygenase reaction.Evidence for ascorbate regulation of enzyme activity[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1991,266(18):11537-11543.
- [79] FRANCISCO W A,BLACKBURN N J,KLINMAN J P.Oxygen and hydrogen isotope effects in an active site tyrosine to phenylalanine mutant of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase:mechanistic implications[J].Biochemistry,2003,42(7):1813-1819.
- [80] MILLER S M,KLINMAN J P.Secondary isotope effects and structure-reactivity correlations in the dopamine β-monooxygenase reaction:evidence for a chemical mechanism[J].Biochemistry,1985,24(9):2114-2127.
- [81] AHN N,KLINMAN J P.Mechanism of modulation of dopamine β-monooxygenase by pH and fumarate as deduced from initial rate and primary deuterium isotope effect studies[J].Biochemistry,1983,22(13):3096-3106.
- [82] TIAN G C,BERRY J A,KLINMAN J P.Oxygen-18 kinetic isotope effects in the dopamine β-monooxygenase reaction:evidence for a new chemical mechanism in non-heme metallomonooxygenases[J].Biochemistry,1994,33(1):226-234.
- [83] FRANCISCO W A,MERKLER D J,BLACKBURN N J,et al.Kinetic mechanism and intrinsic isotope effects for the peptidylglycine α-amidating enzyme reaction[J].Biochemistry,1998,37(22):8244-8252.
- [84] MILLER S M,KLINMAN J P.Magnitude of intrinsic isotope effects in the dopamine β-monooxygenase reaction[J].Biochemistry,1983,22(13):3091-3096.
- [85] BRENNER M C,MURRAY C J,KLINMAN J P.Rapid freeze and chemical-quench studies of dopamine β-monooxygenase:comparison of pre-steady-state and steady-state parameters[J].Biochemistry,1989,28(11):4656-4664.
- [86] GOLDSTEIN M,JOH T H,GARVEY T Q.Kinetic studies of the enzymic dopamine β-hydroxylation reaction[J].Biochemistry,1968,7(8):2724-2730.
- [87] FREEMAN J C,VILLAFRANCA J J,MERKLER D J.Redox cycling of enzyme-bound copper during peptide amidation[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1993,115(11):4923-4924.
- [88] EIPPER B A,MAINS R E,GLEMBOTSKI C C.Iden-tification in pituitary tissue of a peptide α-amidation activity that acts on glycine-extended peptides and requires molecular oxygen,copper,and ascorbic acid[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,1983,80(16):5144-5148.
- [89] COWLEY R E,CIRERA J,QAYYUM M F,et al.Structure of the reduced copper active site in prepro-cessed galactose oxidase:ligand tuning for one-electron O2 activation in cofactor biogenesis[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2016,138(40):13219-13229.
- [90] ITOH S.Developing mononuclear copper-active-oxygen complexes relevant to reactive intermediates of biological oxidation reactions[J].Accounts of Chemical Research,2015,48(7):2066-2074.
- [91] MAITI D,FRY H C,WOERTINK J S,et al.A 1:1 copper-dioxygen adduct is an end-on bound superoxo copper(Ⅱ)complex which undergoes oxygenation rea-ctions with phenols[J].Journal of the American Che-mical Society,2007,129(2):264-265.
- [92] LEE J Y,PETERSON R L,OHKUBO K,et al.Mecha-nistic insights into the oxidation of substituted phenols via hydrogen atom abstraction by a cupric-superoxo complex[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2014,136(28):9925-9937.
- [93] KIM S,LEE J Y,COWLEY R E,et al.A N3S(thioe-ther)-ligated Cu(Ⅱ)-superoxo with enhanced reactivity[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2015,137(8):2796-2799.
- [94] BHADRA M,LEE J Y C,COWLEY R E,et al.Intramo-lecular hydrogen bonding enhances stability and reacti-vity of mononuclear cupric superoxide complexes[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2018,140(29):9042-9045.
- [95] SOLOMON E I,GINSBACH J W,HEPPNER D E,et al.Copper dioxygen(bio)inorganic chemistry[J].Faraday Discussions,2011,148:11-39.
- [96] YAMAGUCHI S,KUMAGAI A,NAGATOMO S,et al.Synthesis,characterization,and thermal stability of new mononuclear hydrogenperoxocopper(Ⅱ)complexes with N3O-type tripodal ligands bearing hydrogen-bonding interaction sites[J].Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan,2005,78(1):116-124.
- [97] YAMAGUCHI S,WADA A,FUNAHASHI Y,et al.Thermal stability and absorption spectroscopic behavior of(μ-peroxo)dicopper complexes regulated with intra-molecular hydrogen bonding interactions[J].European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2003,2003(24):4378-4386.
- [98] MANN S I,HEINISCH T,WARD T R,et al.Peroxide activation regulated by hydrogen bonds within artificial Cu proteins[J].Journal of the American Chemical Socie-ty,2017,139(48):17289-17292.
- [99] DAHL E W,DONG H T,SZYMCZAK N K.Phenyla-mino derivatives of tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine:hydrogen-bonded peroxodicopper complexes[J].Chemical Commu-nications,2018,54(8):892-895.
- [100] LIU J J,DIAZ D E,QUIST D A,et al.Copper(Ⅰ)-dioxygen adducts and copper enzyme mechanisms[J].Israel Journal of Chemistry,2016,56(9/10):738-755.
- [101] ELWELL C E,GAGNON N L,NEISEN B D,et al.Copper-oxygen complexes revisited:structures,spectro-scopy,and reactivity[J].Chemical Reviews,2017,117(3):2059-2107.
- [102] MIRICA L M,OTTENWAELDER X,STACK T D P.Structure and spectroscopy of copper-dioxygen comple-xes[J].Chemical Reviews,2004,104(2):1013-1046.
- [103] LEWIS E A,TOLMAN W B.Reactivity of dioxygen-copper systems[J].Chemical Reviews,2004,104(2):1047-1076.
- [104] ZHU S L,MACMILLAN D W C.Enantioselective copper-catalyzed construction of aryl pyrroloindolines via an arylation-cyclization cascade[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2012,134(26):10815-10818.
- [105] ROSS M O,ROSENZWEIG A C.A tale of two methane monooxygenases[J].Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry,2017,22(2/3):307-319.
- [106] FUJISAWA K,TANAKA M,MORO-OKA Y,et al.A monomeric side-on superoxocopper(Ⅱ)complex:Cu(O2)(HB(3-tBu-5-iPrpz)3)[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1994,116(26):12079-12080.
- [107] ABOELELLA N W,LEWIS E A,REYNOLDS A M,et al.Snapshots of dioxygen activation by copper:the structure of a 1:1 Cu/O2 adduct and its use in syntheses of asymmetric bis(μ-oxo)complexes[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2002,124(36):10660-10661.
- [108] KUNISHITA A,KUBO M,SUGIMOTO H,et al.Mononuclear copper(Ⅱ)-superoxo complexes that mimic the structure and reactivity of the active centers of PHM and DβM[J].Journal of the American Che-mical Society,2009,131(8):2788-2789.
- [109] KUNISHITA A,ERTEM M Z,OKUBO Y,et al.Active site models for the CuA site of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase and dopamine β-monooxygenase[J].Inorganic Chemistry,2012,51(17):9465-9480.
- [110] KIM S,GINSBACH J W,LEE J Y,et al.Amine oxidative N-dealkylation via cupric hydroperoxide Cu—OOH homolytic cleavage followed by site-specific Fenton chemistry[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2015,137(8):2867-2874.
- [111] SÁNCHEZ-EGUÍA B N,FLORES-ALAMO M,ORIO M,et al.Side-on cupric-superoxo triplet complexes as competent agents for H-abstraction relevant to the active site of PHM[J].Chemical Communications,2015,51(55):11134-11137.
- [112] WÜRTELE C,GAOUTCHENOVA E,HARMS K,et al.Crystallographic characterization of a synthetic 1:1 end-on copper dioxygen adduct complex[J].Angewan-dte Chemie International Edition,2006,45(23):3867-3869.
- [113] TYEKLAR Z,JACOBSON R R,WEI N,et al.Rever-sible reaction of dioxygen(and carbon monoxide)with a copper(Ⅰ)complex.X-ray structures of relevant mo-nonuclear Cu(Ⅰ)precursor adducts and the trans-(μ-1,2-peroxo)dicopper(Ⅱ)product[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1993,115(7):2677-2689.
- [114] DONOGHUE P J,GUPTA A K,BOYCE D W,et al.An anionic,tetragonal copper(Ⅱ)superoxide complex[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(45):15869-15871.
- [115] PETERSON R L,HIMES R A,KOTANI H,et al.Cupric superoxo-mediated intermolecular C—H activa-tion chemistry[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2011,133(6):1702-1705.
- [116] LANCI M P,SMIRNOV V V,CRAMER C J,et al.Isotopic probing of molecular oxygen activation at copper(Ⅰ)sites[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2007,129(47):14697-14709.
- [117] PETERSON R L,GINSBACH J W,COWLEY R E,et al.Stepwise protonation and electron-transfer reduction of a primary copper-dioxygen adduct[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2013,135(44):16454-16467.
- [118] SARANGI R,ABOELELLA N,FUJISAWA K,et al.X-ray absorption edge spectroscopy and computational studies on LCuO2 species:superoxide-Cu(Ⅱ)versus peroxide-Cu(Ⅲ)bonding[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2006,128(25):8286-8296.
- [119] ABOELELLA N W,GHERMAN B F,HILL L M R,et al.Effects of thioether substituents on the O2 reactivity of β-diketiminate-Cu(Ⅰ)complexes:probing the role of the methionine ligand in copper monooxygenases[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2006,128(10):3445-3458.
- [120] KJAERGAARD C H,QAYYUM M F,WONG S D,et al.Spectroscopic and computational insight into the activation of O2 by the mononuclear Cu center in poly-saccharide monooxygenases[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2014,111(24):8797-8802.
- [121] WADA A,HARATA M,HASEGAWA K,et al.Struc-tural and spectroscopic characterization of a mono-nuclear hydroperoxo-copper(Ⅱ)complex with tripodal pyridylamine ligands[J].Angewandte Chemie Interna-tional Edition,1998,37(6):798-799.
- [122] BAILEY W D,DHAR D,CRAMBLITT A C,et al.Mechanistic dichotomy in proton-coupled electron-transfer reactions of phenols with a copper superoxide complex[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(13):5470-5480.
- [123] HEDEG RDÅ E D,RYDE U.Targeting the reactive intermediate in polysaccharide monooxygenases[J].Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry,2017,22(7):1029-1037.
- [124] HEDEG RDÅ E D,RYDE U.Molecular mechanism of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases[J].Chemical Science,2018,9(15):3866-3880.
- [125] CALDARARU O,OKSANEN E,RYDE U,et al.Mechanism of hydrogen peroxide formation by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase[J].Chemical Science,2019,10(2):576-586.
- [126] BAUMAN A T,YUKL E T,ALKEVICH K,et al.The hydrogen peroxide reactivity of peptidylglycine mono-oxygenase supports a Cu(Ⅱ)-superoxo catalytic in-termediate[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2006,281(7):4190-4198.
- [127] BRADBURY A F,MISTRY J,ROOS B A,et al.4-phenyl-3-butenoic acid,an in vivo inhibitor of pepti-dylglycine hydroxylase(peptide amidating enzyme)[J].European Journal of Biochemistry,1990,189(2):363-368.
- [128] CHEN P,SOLOMON E I.O2 activation by binuclear Cu sites:noncoupled versus exchange coupled reaction mechanisms[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2004,101(36):13105-13110.
- [129] CRESPO A,MARTÍ M A,ROITBERG A E,et al.The catalytic mechanism of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase investigated by computer simulation[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2006,128(39):12817-12828.
- [130] KAMACHI T,KIHARA N,SHIOTA Y,et al.Com-putational exploration of the catalytic mechanism of dopamine β-monooxygenase:modeling of its mono-nuclear copper active sites[J].Inorganic Chemistry,2005,44(12):4226-4236.
- [131] ABAD E,ROMMEL J B,KÄESTNER J.Reaction mechanism of the bicopper enzyme peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2014,289(20):13726-13738.
- [132] WANG B J,WALTON P H,ROVIRA C.Molecular mechanisms of oxygen activation and hydrogen pero-xide formation in lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases[J].ACS Catalysis,2019,9(6):4958-4969.
- [133] WARREN J J,MAYER J M.Tuning of the thermo-chemical and kinetic properties of ascorbate by its local environment:solution chemistry and biochemical impli-cations[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(22):7784-7793.
- [134] WU P,FAN F F,SONG J S,et al.Theory demons-trated a "coupled" mechanism for O2 activation and substrate hydroxylation by binuclear copper monooxy-genases[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(50):19776-19789.
- [135] BAUMAN A T,BROERS B A,KLINE C D,et al.A copper-methionine interaction controls the pH-dependent activation of peptidylglycine monooxygenase[J].Bio-chemistry,2011,50(50):10819-10828.
- [136] KLINE C D,BLACKBURN N J.Substrate-induced car-bon monoxide reactivity suggests multiple enzyme conformations at the catalytic copper m-center of pepti-dylglycine monooxygenase[J].Biochemistry,2016,55(48):6652-6661.