基金项目:国家自然科学基金(U1805233,U1205123,41676158,41176116,40676083); 国家海洋公益性行业科研专项(201105027); 国家支撑计划项目(2013BAD10B03-2); 国家高技术研究发展计划重点项目(2007AA091406); 福建省科技重大专项(2017NZ0004); 福建产业技术创新重大平台(2014N2004); 福建省海洋经济发展补助资金项目(FJHJF-L-20
(厦门大学海洋与地球学院,近海海洋环境科学国家重点实验室,海洋生物制备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,福建省海洋生物资源开发利用协同创新中心,福建省海洋生物抗菌肽产业技术创新研究院,福建 厦门 361102)
(State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science,State-Province Joint Engineering Laboratory of Marine Bioproducts and Technology,Fujian Collaborative Innovation Center Exploitation and Utilization of Marine Biological Resources,Fujian Innovation Ins
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202010033
备注
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(U1805233,U1205123,41676158,41176116,40676083); 国家海洋公益性行业科研专项(201105027); 国家支撑计划项目(2013BAD10B03-2); 国家高技术研究发展计划重点项目(2007AA091406); 福建省科技重大专项(2017NZ0004); 福建产业技术创新重大平台(2014N2004); 福建省海洋经济发展补助资金项目(FJHJF-L-20
引言
我国是世界上最大的水产养殖国家,养殖量占世界总量的60%以上.水产养殖业长期过量使用抗生素导致的细菌耐药性增加、水产品中抗生素残留和养殖环境中抗生素污染等问题,已成为严重影响我国水产养殖业健康发展的重大科学问题.国际上瑞典、丹麦等国家于20世纪80—90年代就开始禁止饲料中添加抗生素,我国农业农村部于2019年发布194号公告[1]:自2020年起,我国饲料中全面禁止添加抗生素,减少滥用抗生素造成的危害,维护动物源食品安全和公共卫生安全.自1928年青霉素问世以来,抗生素的种类不断增加,至今已逾百种.除了临床使用外,1950年美国食品与药品管理局(FDA)首次批准抗生素可以作为饲料添加剂使用,此后抗生素被全面应用于动物养殖业,在预防和治疗动物传染性疾病、促进动物生长等方面发挥了重要作用.但由于抗生素在医疗卫生和农业生产等领域的滥用,大量抗生素迅速失去效力,原本对抗生素敏感的微生物对抗生素出现高度耐受,这种现象称为抗生素耐药性.抗生素耐药性给人类带来了新的风险,甚至成为威胁人类健康的一个公共健康问题.畜牧和水产养殖业中长期滥用抗生素也是导致细菌耐药性的重要原因.我国是抗生素生产和消费大国,仅在2013年我国就使用抗生素16.2万t,约占全球用量的一半,其中48%为人用,52%为兽用,据报道最终超过5万t抗生素被排放进入水土环境中[2].2018年我国抗生素原料药产量19.6万t,约占全球用量的一半,且超50%用于养殖业[3].此外,每年有数万吨抗生素被排放进入水土环境中.由于长时间不合理的使用以及缺乏严格的监管机制,抗生素耐药性问题十分严峻.我国现已成为世界上细菌耐药最严重的国家之一,同时也是世界上细菌耐药率增长最快的国家之一.
然而,近30多年来新型抗生素的开发很少,因此开发新型抗耐药性细菌感染、可替代抗生素的治疗药物已迫在眉睫.寻找抗生素的有效替代品,亦成为水产养殖业发展的迫切需求,而抗菌肽的研发与利用可为解决这一重要问题提供关键技术支撑.抗菌肽是一类广泛存在于自然界生物体中的小分子多肽,作为生物体先天性免疫防御系统的重要组成部分,在机体对抗外界病原微生物感染和自身免疫调节中发挥重要作用.天然抗菌肽通常由12~100个氨基酸组成,具有较好的热稳定性和水溶性,抗菌谱广,对革兰氏阳性(G+)和阴性(G-)细菌都有抗菌活性,对耐药性细菌也有较好的活性.
海洋拥有地球上约80%的生物资源,海洋无脊椎动物居多,面对海洋环境中多种病原微生物或有害物质等,无脊椎动物需要建立比脊椎动物更多样性的先天性免疫系统.海洋无脊椎动物拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)因其自身是开放系统且有多次蜕皮的脆弱发育阶段,易受微生物侵染,是开发高效且抗多种病原微生物的新型抗菌肽的重要来源,值得深入研究.
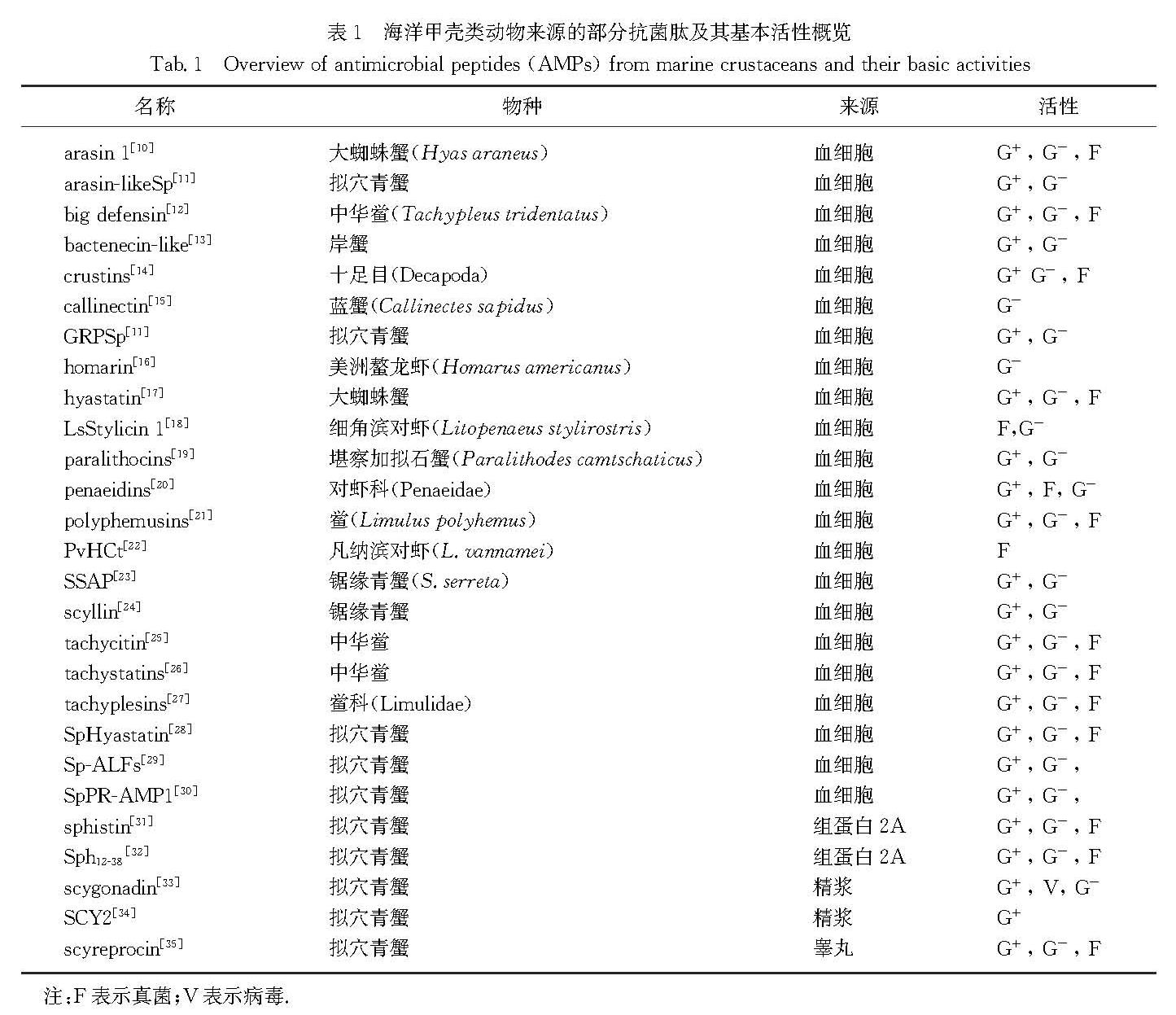
自1981年瑞典科学家从昆虫中分离获得首个抗菌肽天蚕素[4]以来,迄今人们在各种生物体中陆续发现了3 000多个抗菌肽或其类似物(APD数据库,http:∥aps.unmc.edu/AP/main.php).相对于陆地生物的抗菌肽,海洋动物的抗菌肽研究开始较晚,第一个蟹类抗菌肽是1996年Schnapp等[5]从岸蟹(Carcinus maenas)中分离得到的富含脯氨酸的甲壳动物抗菌肽.随后陆续从虾蟹类等中获得了一些抗菌肽,如鲎素(tachyplesins)[6]、抗脂多糖因子(ALFs)[6]、对虾素(penaeidins)[7]、甲壳素(crustins)[8]等.但迄今APD数据库显示的甲壳动物抗菌肽仅有60多种,与同是节肢动物的昆虫(300余种)相比,数量相对较少.大多数已报道的海洋甲壳动物来源抗菌肽具有良好的抗细菌(G+菌和G-菌)、抗病毒活性; 而具有抗真菌活性的海洋甲壳动物抗菌肽相对较少[9].目前,海洋甲壳类动物抗菌肽大多来源于十足目动物(表1).
表1 海洋甲壳类动物来源的部分抗菌肽及其基本活性概览
Tab.1 Overview of antimicrobial peptides(AMPs)from marine crustaceans and their basic activities由表1可见,目前海洋甲壳动物来源的抗菌肽大多鉴定自血淋巴系统,多具有广谱抗菌活性.近10年来,海洋甲壳动物的血淋巴系统被视为挖掘新型高效抗菌物质的良好资源.其中来源于拟穴青蟹的抗菌肽主要包括crustins和ALFs等.crustins是一类带信号肽的阳离子抗菌肽,N端有多结构域,C端有乳清酸性蛋白(WAP)结构域,分子质量为7.0 ~ 14.0 ku,具有抗菌、抗病毒、蛋白酶抑制活性和体液免疫调节等多种功能.在拟穴青蟹中有6个crustins已被报道[36-39]:根据不同的N端区域,CrusSp、SpCrus3、SpCrus4和SpCrus6被划分为Ⅰ型crustins(富含半胱氨酸),而SpCrus2和SpCrus5为Ⅱ型crustins(富含甘氨酸).这些crustins主要在鳃中表达,重组SpCrustins对G+菌有很强的抗菌活性,而对G-菌的抗菌活性较弱,且大多数可被细菌诱导上调表达; 所有SpCrustins都能特定结合G+菌、G-菌、真菌和微生物表面的碳水化合物成分,如脂多糖(LPS)、脂磷壁酸、肽聚糖和β-葡聚糖.ALFs是抗菌肽家族的另一主要类型,能够结合并中和G-菌的成分LPS,在拟穴青蟹中共发现7种ALFs:ALFSp[40]、ALFSp2[41]、Sp-ALF1和Sp-ALF2[42]、SpALF4[43]、SpALF5[44]和SpALF6[45].大部分SpALFs主要分布在血细胞中,哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)、副溶血性弧菌(V.parahaemolyticus)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)或LPS刺激均能显著诱导其上调表达; 重组SpALFs或含有LPS结合结构域的SpALFs衍生肽对G+菌和G-菌,甚至对酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)和白色念珠菌(Camdida albicans)都有很强的抗菌活性; 其中Sp-ALF1和Sp-ALF2重组蛋白可有效抑制白斑综合征病毒(WSSV)的复制,并对所选择的微生物和细菌碳水化合物组分表现出不同的结合活性[42].
从拟穴青蟹中还分离到其他一些在血细胞中高表达的阳离子抗菌肽,包括SpHyastatin[28,46]、富含脯氨酸的SpPR-AMP1[47]、arasin-likeSp和GRPSp[46].其中SpPR-AMP1是一个富含脯氨酸的分子质量为6.5 ku的小分子抗菌肽,可被肽聚糖(PGN)诱导表达[22],重组或合成的SpPR-AMP1均能抑制G+菌Micrococcus luteus和G-菌V.harveyi的生长.arasin-likeSp和GRPSp的成熟肽分子质量分别为4.4 和3.0 ku,且都含有一个富含甘氨酸的区域和几个半胱氨酸残基; 它们也可以在细菌感染时被上调表达,且两种合成的肽都显示出对不同细菌的抗菌活性[46].此外,拟穴青蟹的一些免疫因子也具有抗菌活性,如:一种新型Ⅰ型溶菌酶Splys-Ⅰ在拟穴青蟹的肠道中高表达,虽然它缺乏典型的溶菌酶活性,但是能被细菌诱导上调,并能通过结合和黏附抑制细菌生长[48].另一种溶菌酶是最近从拟穴青蟹中分离得到的C型溶菌酶(SpLyzC),主要分布在肝胰脏和鳃中; 与Splys-Ⅰ类似,SpLyzC对细菌,特别是蟹类病原体副溶血性弧菌具有抗菌活性[49].
本课题组自2002年起一直聚焦我国水产养殖业抗生素污染的重大科学问题,以研发抗生素的有效替代品为目标,致力于海洋动物新型抗菌肽的研发与利用研究,先后从海洋鱼类、青蟹等分离鉴定出一系列新型抗菌肽.下文重点介绍几种拟穴青蟹(后文简称青蟹)新型抗菌肽的发现、研究及其应用,总结自2006年首次报道一种源于青蟹精浆的新型抗菌肽scygonadin后的系列研究成果及其进展.
1 源于青蟹精浆的新型抗菌肽scygonadin和SCY2的发现及其功能
1.1 新型抗菌肽scygonadin及其同源抗菌肽SCY2利用离子交换和反相层析技术,从我国重要海水养殖青蟹精浆中分离纯化得一个分子质量为10.8 ku的多肽,其具有显著抗菌活性; 通过基质辅助激光解析电离飞行时间质谱(MALDI-TOF MS)鉴定该多肽指纹图谱,Edman降解法测定其N端部分氨基酸序列,并经GenBank和Swiss-Prot等数据库检索分析证明为一种新的抗菌肽,命名为scygonadin[50-51].该新型抗菌肽scygonadin主要在成熟的雄性青蟹射精管中高表达,是迄今在甲壳动物中发现的首个阴离子抗菌肽,丰富了甲壳动物抗菌肽的理论; 后续研究发现scygonadin具有广谱抗菌活性,且能抑制WSSV感染青蟹[50-51].
随后克隆获得与scygonadin有65%序列相似度、分子质量10.0 ku、等电点4.84的另一个同源多肽,是一种主要抗G+菌的阴离子抗菌肽,命名为SCY2[34].两种抗菌肽都具有较强的抗微生物活性:scygonadin抗G+菌和G-菌,而SCY2主要抗G+菌.SCY2也能抑制WSSV感染青蟹,且在水产致病菌副溶血弧菌感染青蟹的情况下,能够提高青蟹的存活率,说明SCY2在青蟹抗病原微生物感染中可发挥重要的免疫作用[31].该发现丰富了甲壳动物抗菌肽在保证青蟹授精、精子输送和纳精囊中长期保存等生殖免疫方面的理论.
1.2 Scygonadin和SCY2基因的交配诱导表达特性及其受激素孕酮调控的机制本课题组前期研究发现Scygonadin和SCY2基因均在成熟雄性青蟹的射精管中高表达,且不受LPS、嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)和白色念珠菌等直接刺激诱导表达[50-51].Scygonadin和SCY2基因均在青蟹繁殖季节表达量最高,且在雄性青蟹中交配前的表达量高于交配后,推测其可能在交配时受到体内激素水平或其他物质的调节; 深入研究不同激素对两基因表达模式的影响发现,Scygonadin和SCY2基因的表达模式与青蟹性腺成熟规律一致,而性类固醇激素的周年变化也与青蟹性腺成熟时期相吻合,说明性类固醇激素可能参与青蟹性成熟的调节过程[50-51].进一步在细胞培养中用多种激素验证发现,激素孕酮可显著诱导SCY2基因的表达,且加入孕酮受体抑制剂后,SCY2基因的表达被显著抑制; 而以LPS刺激的细胞中SCY2的表达与对照类似,都无显著变化,说明SCY2是由激素孕酮而非LPS刺激诱导,推测SCY2的表达可能受孕酮信号调控[34].此外,交配后雄性射精管中高表达的两种抗菌肽的转录本减少,而雌性纳精囊中两种抗菌肽的转录本显著增多,表明两种抗菌肽可能随交配后的雄性精液共同转移至雌蟹体内[34],表明新发现的scygonadin和SCY2两种抗菌肽功能与青蟹生殖免疫相关.上述两种抗菌肽在青蟹性成熟时经交配诱导高表达,且其表达受激素孕酮调控,在精子转运、纳精囊储存和授精过程中发挥保护作用,具有生殖免疫功能,为进一步探究激素在青蟹体内生殖免疫中的调控机制奠定了基础.
1.3 SCY2互作蛋白scyreprocin的显著抗细菌和抗真菌活性在研究拟穴青蟹抗菌肽SCY2的过程中,通过酵母双杂交技术,从雄性拟穴青蟹性腺中鉴定得一个与SCY2存在相互作用的蛋白,发现其核酸序列、氨基酸序列与现有的开放数据库中序列无任何相似性,命名为scyreprocin[35].通过基因工程表达技术获得抗菌肽scyreprocin的原核表达产物(rScyreprocin),该表达产物具有广谱抗菌活性,能够以较低的效应浓度(<10 μmol/L)有效抑制及杀灭病原细菌(包括G+菌和G-菌)和真菌、显著抑制霉菌孢子的萌发、抑制并清除真菌生物膜的形成,且rScyreprocin对多株分离自临床样本的多重耐药性菌亦表现出较强的抑杀活性; rScyreprocin针对不同的微生物具有不同的抑杀菌作用机制,能够直接作用于细菌及真菌表面,使微生物细胞膜通透性发生改变,膜结构破损,细胞内容物泄露而导致微生物死亡,还能够诱导真菌细胞发生凋亡效应,通过诱导凋亡及破坏细胞膜结构双重方式杀伤真菌; rScyreprocin与SCY2无协同抗菌活性,然而rScyreprocin与SCY2联合使用时对真菌生物膜表现出一定的联合抑制效应[35].
rScyreprocin具有良好的体内抗菌活性.在海水青鳉(Oryzias melastigma)注射半致死剂量的哈维氏弧菌2 h后,再注射不同浓度的rScyreprocin、SCY2及rScyreprocin+SCY2,结果显示[35]:仅注射哈维氏弧菌的海水青鳉24 h内存活率仅有40%; 而在rScyreprocin注射组中,随着剂量上升,海水青鳉存活率可达60%~80%,且1 μg/尾的注射剂量可达到与8 μg/尾注射剂量相同的保护效果,均能将海水青鳉的存活率提升至80%,表明高浓度rScyreprocin注射对海水青鳉存活无影响,且可在病原菌哈维氏弧菌感染下提高其存活率.此外,SCY2本身虽然不能显著提高哈维氏弧菌感染下海水青鳉的存活率,但是将其与rScyreprocin共同使用时,可在减少rScyreprocin用量的情况下达到更好的保护效果,说明该抗菌肽在受试靶动物抵御病原微生物过程中可发挥重要的免疫作用.因此,该抗菌肽在抗菌药物及抑菌防霉剂方面具有应用潜力.
2 源于血淋巴系统的两种新型抗菌肽sphistin和SpHyastatin的发现及其功能
2.1 sphistin的体内外抗菌活性本课题组在前期研究中发现了几种源于血淋巴系统的新型抗菌肽,如SpHyastatin[28]和sphistin[31]等.sphistin源于青蟹血液中组蛋白2A的N-端38个氨基酸,研究发现[31]:其具有很强的抗G+菌、G-菌及酵母菌等活性; 通过扫描电镜观察到用sphistin处理的大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)表面有细胞内容物渗出,证明sphistin处理能够提高大肠杆菌的细胞膜通透性; 用双光子共聚焦显微镜进一步观察到sphistin能够结合到金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和毕赤酵母(Pichia pastoris)的细胞膜上,但不能进入细胞质,可见其抗菌机制很可能是通过吸附到细菌细胞膜表面,导致细胞膜通透性增加而产生抗菌作用.sphistin对多种细菌具有很强的抑杀活性,最小抑制浓度(MIC)为1.5~3 μmol/L,对金黄色葡萄球菌的MIC<1.5 μmol/L,对水产致病菌嗜水气单胞菌的MIC<1.5 μmol/L; 此外,sphistin还具有较强的抗真菌作用,对肿瘤细胞亦表现出显著抑制作用.
对sphistin的结构域分析发现,其截短肽Sph12-38同样具有广谱的抗菌活性[32]:对金黄色葡萄球菌、谷氨酸棒状杆菌(Corynebacterium glutamicum)、溶壁微球菌(Micrococcus lysodeikticus)、枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)、荧光假单胞菌(Pseudomonas fluorescens)、嗜水气单胞菌、温和气单胞菌(Aeromones sobria)等均具有很强的抑杀作用,MIC<3 μmol/L; 杀菌动力学曲线表明,Sph12-38对温和气单胞菌的杀灭率可在6 h内达到100%.体内抗菌试验研究发现Sph12-38对感染了温和气单胞菌的海水青鳉具有良好的免疫保护作用[32]:将Sph12-38与温和气单胞菌混合后共注射海水青鳉,与单独注射温和气单胞菌的海水青鳉相比,在注射后7 d内,海水青鳉存活率有明显提高,证明Sph12-38可以在温和气单胞菌感染时提高海水青鳉的存活率; 此外,在注射后48 h内,共注射的海水青鳉肝脏内免疫基因表达量相对于健康的海水青鳉显著上调,而相对于单独注射温和气单胞菌的海水青鳉则显著下调,表明Sph12-38对温和气单胞菌感染海水青鳉引起的炎症反应具有缓解作用.
2.2 SpHyastatin的体内外抗菌活性及其调控机制从本课题组前期建立的血细胞cDNA文库筛选获得抗菌肽SpHyastatin[28]:其具有较强的抗微生物活性,其真核表达产物对嗜水气单胞菌、荧光假单胞菌以及真菌等均显示较强的抑杀作用; SpHyastatin在血淋巴细胞中表达量最高,在青蟹的大眼幼体、仔蟹(10~20 mg)、仔蟹(40 g)和成蟹(300 g)4个阶段发育过程中始终保持高水平表达,暗示该抗菌肽可能在青蟹整个发育过程中发挥免疫作用.
体内试验研究结果显示[28]:青蟹感染副溶血弧菌后,注射SpHyastatin可较显著地提高青蟹的存活率; 用SpHyastatin表达产物单独注射青蟹1 h后再经副溶血弧菌感染192 h,亦可显著提高青蟹的存活率; 此外,SpHyastatin表达产物与副溶血弧菌共注射青蟹120 h,可延迟青蟹的死亡,青蟹的半数致死时间可从10 h延迟到30 h,表明SpHyastatin具有免疫保护作用.在细菌感染下SpHyastatin的存在会影响其他免疫基因的表达水平.青蟹注射副溶血弧菌后,其Toll通路相关基因(Spaetzle、SpToll、Cactus、Dorsal和Relish)、抗氧化酶相关基因(SOD、CAT和GPx)及溶菌酶基因的表达水平均显著升高; 而SpHyastatin与副溶血弧菌共注射后,青蟹中上述基因的表达会显著降低.
通过基因步移技术扩增获得576 bp的SpHyastatin基因上游调控序列,分析发现核因子κB(NF-κB)结合位点是SpHyastatin基因启动子区域的关键转录调控元件; 进而利用双荧光素酶报告系统及鲤鱼上皮瘤细胞EPC和人宫颈癌细胞Hela研究其转录调控机制,发现SpHyastatin基因5' 侧翼-107~-69 bp区域存在假定NF-κB结合位点,而NF-κB结合位点的三碱基突变和缺失突变重组子的转录活性显著下降,表明该元件对SpHyastatin基因的转录起正调控作用; 此外,LPS可显著增强SpHyastatin基因启动子的转录活性,但对NF-κB结合位点突变的重组子无明显诱导作用,提示LPS可能通过NF-κB结合位点调控SpHyastatin基因的转录[52].上述研究结果有助于深入研究LPS或病原微生物刺激引起抗菌肽基因的表达变化机制.
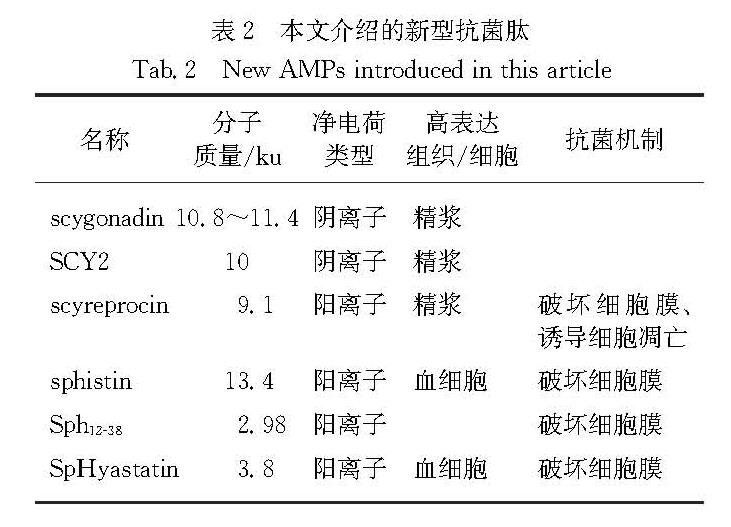
上述6种新型抗菌肽的特性及其抗菌机制总结于表2.
3 新型抗菌肽与抗生素的协同抗菌作用
多年来人们一直在探索减少抗生素用量的方法或寻找新的抗菌试剂.抗菌肽是理想的候选药物,其可以单独使用,也可以与传统抗生素联合使用杀灭病原体和多重耐药性细菌.本课题组利用临床病原菌铜绿假单胞菌(P.aeruginosa)评价了拟穴青蟹抗菌肽sphistin和Sph12-38联合8种临床常用抗生素的抗菌效果[53].
体外抗菌实验显示:利福平和阿奇霉素对铜绿假单胞菌的MIC分别为2.5和180 μg/mL; 而抗菌肽sphistin和Sph12-38对铜绿假单胞菌的MIC分别为24和12 μmol/L.当抗生素利福平和阿奇霉素联合sphistin和Sph12-38使用时,1/4×MIC的sphistin+1/10×MIC的阿奇霉素(分级抑制浓度指数(FICI)=0.350)和1/16×MIC的sphistin+1/4×MIC的利福平(FICI=0.313)均能有效杀灭铜绿假单胞菌; 1/8×MIC的Sph12-38+1/10×MIC的阿奇霉素(FICI=0.225)和1/8×MIC的Sph12-38+1/4×MIC的利福平(FICI=0.375)同样能有效杀灭铜绿假单胞菌.可见抗生素利福平和阿奇霉素与抗菌肽sphistin和Sph12-38联合使用对铜绿假单胞菌均具有协同抗菌作用,其机制可能是sphistin和Sph12-38与铜绿假单胞菌外膜的LPS结合,使得细菌细胞膜的通透性增加,促进细胞对利福平和阿奇霉素的摄取,从而杀灭细菌.
体内抗菌试验结果显示:在小鼠背部人为制造的2 cm×2 cm伤口(深及真皮层)使用铜绿假单胞菌涂抹2 h后,分别将利福平、阿奇霉素、Sph12-38、Sph12-38+利福平以及Sph12-38+阿奇霉素经皮下注射到小鼠背部感染伤口中,与伤口只注射生理盐水的小鼠(对照组)相比,注射了Sph12-38+利福平和Sph12-38+阿奇霉素的小鼠伤口愈合时间显著缩短,由对照组的7~8 d缩短至4~5 d,表明两种抗生素与抗菌肽Sph12-38协同使用时,能够显著促进感染了铜绿假单胞菌的小鼠伤口愈合,并且使愈合时间明显缩短3 d.
综上所述,抗菌肽sphistin和Sph12-38与抗生素利福平和阿奇霉素联合使用对铜绿假单胞菌具有显著的协同抗菌作用,与单独使用抗生素进行治疗相比,抗生素与抗菌肽的联合使用能够显著降低抗生素的用量.由于阿奇霉素和利福平都不是临床上治疗铜绿假单胞菌感染时优先使用的药物,所以将抗菌肽与这两种抗生素联合使用在一定程度上扩展了它们的应用范围.
4 新型抗菌肽的基因工程表达及应用
4.1 抗菌肽的原核与真核基因工程表达抗菌肽在生物体内含量较低,直接从动物组织分离纯化成本高,难以满足功能研究或规模化生产应用的需求; 其结构特殊(如含有多个二硫键等),利用化学方法合成抗菌肽也受到一定局限.为此,本课题组利用基因工程技术构建了含有不同新型青蟹抗菌肽基因的多个原核或真核高效表达载体,获得了scygonadin、SCY2和scyreprocin等多个抗菌肽的表达产物,且抗菌实验结果表明所表达的抗菌肽具有广谱抗菌活性[34-35,50-51,54-55].在此基础上,与企业合作建立了海洋动物抗菌肽的毕赤酵母规模化发酵工艺,使抗菌肽实现了稳定高表达,可满足产业化要求.
此外,本课题组利用基因工程表达技术获得了稳定表达抗菌肽Scy-hepc融合基因的转基因小球藻(Chlorella)[56]:用嗜水气单胞菌分别感染黑鲷(Sparus macrocephalus)和龙胆石斑鱼(Epinephelus fuscoguttatus(♀)×E.lanceolatus(♂))后,以灌胃方式分别喂食转抗菌肽Scy-hepc融合基因的小球藻和野生型小球藻,发现喂食转抗菌肽基因小球藻的黑鲷和龙胆石斑鱼的存活率均显著高于喂食野生型小球藻的对照组,其中嗜水气单胞菌感染的龙胆石斑鱼36 h后存活率比对照组高30%,嗜水气单胞菌感染的黑鲷72 h后存活率比对照组高50%,说明转抗菌肽Scy-hepc基因的小球藻对受试靶动物具有较强的免疫保护作用.
4.2 新型抗菌肽基因工程产品的示范应用目前,两种海洋动物抗菌肽产品分别在国家资质检测机构完成了产品的小鼠经口急性毒性试验、三致试验和大鼠慢性毒性试验等,证明其安全、无毒副作用; 进一步按照国家农业部相关要求,在海水养殖鱼类完成了抗菌肽的中间试验和环境释放试验.基于此,大黄鱼抗菌肽和青蟹抗菌肽的基因工程产品分别于2015和2016年获得国家农业部批准的生产应用安全证书(农基安办证书(2015)第036号和农基安证字(2016)第018号),其中大黄鱼抗菌肽是我国迄今获批的首个海洋动物抗菌肽生产应用的安全证书,表明新型海洋动物抗菌肽正式获准进入示范应用阶段.
获得生产应用安全证书的海洋动物抗菌肽产品具有抗菌效果好、不易产生耐药性、无残留等特点,2017年3月起已先后在福建省和浙江省等7个养殖场的石斑鱼、大黄鱼、鲈鱼和对虾等养殖品种上进行示范应用,并取得了显著效果,不仅能显著促进养殖动物的生长,还能显著提高机体免疫力和抗病能力.
5 总结与展望
本文阐述了目前抗生素耐药性的现状以及海洋甲壳类抗菌肽的研究进展,并重点介绍了拟穴青蟹中新型抗菌肽的发现及其应用,总结了本课题组自2006年首次报道了一种源于青蟹精浆的新型抗菌肽scygonadin后的系列研究成果及其进展.
海洋孕育着地球上超过半数的物种,其物种丰度、多样性大大超过陆地.尽管目前已知的抗菌肽中来源于海洋动物的相比于陆地生物的尚少,但科学家们已经逐渐注意到海洋这个潜在的天然活性物质宝库.海洋生物为抵御病原感染、逃避猎食者及捕食猎物而进化产生不同的活性分子,为我们提供了数目庞大的具有分子结构多样性的活性物质.然而,海洋甲壳类动物的基因注释存在一定困难,成为限制挖掘其活性蛋白(如抗菌肽等)的主要因素.随着越来越多海洋甲壳类动物基因组的测序及发表,将会有更多包括抗菌肽在内的活性蛋白(如抗氧化蛋白、凝集素、模式识别受体和蛋白酶等)被逐步挖掘并应用于实际生产中.
此外,随着抗生素在我国养殖产业饲料中的禁用,抗生素有效替代品的研发已成为保障我国养殖业健康发展的重大需求; 随着全球性抗生素耐药性问题的出现,人们的健康安全受到极大的威胁,研发可有效抗耐药性细菌、真菌的药物或活性物质也势在必行,这是当代和未来的挑战也是机遇.源于海洋生物的抗菌肽的发现与利用,在未来的养殖业、食品、饲料和人类健康等方面将发挥不可替代的重要作用,也具有重大的开发和利用价值.
- [1] 中华人民共和国农业农村部.中华人民共和国农业农村部公告第194号[EB/OL].[2020-10-10].http:∥www.xmsyj.moa.gov.cn/zcjd/201907/t20190710_6320678.htm.
- [2] ZHANG Q Q,YING G G,PAN C G,et al.Compre-hensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China:source analysis,multimedia modeling,and linkage to bacterial resistance[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(11):6772-6782.
- [4] STEINER H,HULTMARK D,ENGSTRÖM A,et al.Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity[J].Journal of Immunology,2009,182(11):6635-6637.
- [5] SCHNAPP D,KEMP G D,SMITH V J.Purification and characterization of a proline-rich antibacterial peptide,with sequence similarity to bactenecin-7,from the haemocytes of the shore crab,Carcinus maenas[J].Eur J Biochem,1996,240(3):532-539.
- [6] ZANJANI N T,MIRANDA-SAKSENA M,CUNNINGHAM A L,et al.Antimicrobial peptides of marine crustaceans:the potential and challenges of developing therapeutic agents[J].Current Medicinal Chemistry,2018,25(19):2245-2259.
- [7] DESTOUMIEUX D,MUNOZ M,BULET P,et al.Penaeidins,a family of antimicrobial peptides from penaeid shrimp(Crustacea,Decapoda)[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2000,57(8/9):1260-1271.
- [8] VARGAS-ALBORES F,MARTÍNEZ-PORCHAS M.Crustins are distinctive members of the WAP-containing protein superfamily:an improved classification approach[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2017,76:9-17.
- [9] WANG G,LI X,WANG Z.APD3:the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2016,44(D1):D1087-D1093.
- [10] STENSVA·G K,HAUG T,SPERSTAD S V,et al.Arasin 1,a proline-arginine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from the spider crab,Hyas araneus[J].Developmental & Comparative Immunology,2008,32(3):275-285.
- [11] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPARYUP P,TASSANAKAJON A.Two novel antimicrobial peptides,arasin-likeSp and GRPSp,from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain, exhibit the activity against some crustacean pathogenic bacteria[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol,2011,30(2):706-712.
- [12] SAITO T,KAWABATA S I,SHIGENAGA T,et al.A novel big defensin identified in horseshoe crab hemocytes:isolation,amino acid sequence,and antibacterial activity[J].The Journal of Biochemistry,1995,117(5):1131-1137.
- [13] SCHNAPP D,KEMP G D,SMITH V J.Purification and characterization of a proline-rich antibacterial peptide,with sequence similarity to bactenecin-7,from the haemocytes of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas[J].European Journal of Biochemistry,1996,240(3):532-539.
- [14] SMITH V J,FERNANDES J M O,KEMP G D,et al.Crustins:enigmatic WAP domain-containing antibacterial proteins from crustaceans[J].Developmental & Compa-rative Immunology,2008,32(7):758-772.
- [15] KHOO L,ROBINETTE D W,NOGA E J.Callinectin,an antibacterial peptide from blue crab,Callinectes sapidus,hemocytes[J].Marine Biotechnology,1999,1(1):44-51.
- [16] BATTISON A L,SUMMERFIELD R,PATRZYKAT A.Isolation and characterisation of two antimicrobial peptides from haemocytes of the American lobster Homarus americanus[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2008,25(1/2):181-187.
- [17] SPERSTAD S V,HAUG T,VASSKOG T,et al.Hyastatin,a glycine-rich multi-domain antimicrobial peptide isolated from the spider crab(Hyas araneus)hemocytes[J].Molecular Immunology,2009,46(13):2604-2612.
- [18] ROLLAND J L,ABDELOUAHAB M,DUPONT J,et al.Stylicins,a new family of antimicrobial peptides from the Pacific blue shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris[J].Molecular Immunology,2010,47(6):1269-1277.
- [19] MOE M K,HAUG T,SYDNES M O,et al.Paralithocins,antimicrobial peptides with unusual disulfide connectivity from the red king crab,Paralithodes camtschaticus[J].Journal of Natural Products,2018,81(1):140-150.
- [20] DESTOUMIEUX D,MUÑOZ M,COSSEAU C,et al.Penaeidins,antimicrobial peptides with chitin-binding activity,are produced and stored in shrimp granulocytes and released after microbial challenge[J].Journal of Cell Science,2000,113(Pt3):461-469.
- [21] MIYATA T,TOKUNAGA F,YONEYA T,et al.Antimicrobial peptides,isolated from horseshoe crab hemocytes,tachyplesin Ⅱ,and polyphemusins Ⅰ and Ⅱ:chemical structures and biological activity[J].The Journal of Biochemistry,1989,106(4):663-668.
- [22] ESCAMILLA-TREVIÑO L L,SHEN H,HERNANDEZ T,et al.Early lignin pathway enzymes and routes to chlorogenic acid in switchgrass(Panicum virgatum L.)[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2014,84(4/5):565-576.
- [23] YEDERY R D,REDDY K V R.Purification and characterization of antibacterial proteins from granular hemocytes of Indian mud crab,Scylla serrata[J].Acta Biochimica Polonica,2009,56(1):71-82.
- [24] MAJUMDER M,CHATTOPADHYAY T,GUHA A K,et al.Inhibition of bacterial respiration by a low-molecular weight lectin,scyllin,from Scylla serrata crab hemolymph[J].Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics,1997,34(1/2):87-89.
- [25] KAWABATA S I,NAGAYAMA R,HIRATA M,et al.Tachycitin,a small granular component in horseshoe crab hemocytes,is an antimicrobial protein with chitin-binding activity[J].The Journal of Biochemistry,1996,120(6):1253-1260.
- [26] OSAKI T,OMOTEZAKO M,NAGAYAMA R,et al.Horseshoe crab hemocyte-derived antimicrobial polypeptides,tachystatins,with sequence similarity to spider neurotoxins[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1999,274(37):26172-26178.
- [27] NAKAMURA T,FURUNAKA H,MIYATA T,et al.Tachyplesin,a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab(Tachypleus tridentatus).Isolation and chemical structure[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1988,263(32):16709-16713.
- [28] SHAN Z,ZHU K X,PENG H,et al.The new antimicrobial peptide SpHyastatin from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain with multiple antimicrobial mechanisms and high effect on bacterial infection[J].Front Microbiol,2016,7(67):1140.
- [29] LIU H P,CHEN R Y,ZHANG Q X,et al.Characteri-zation of two isoforms of antiliopolysacchride factors(Sp-ALFs)from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2012,33(1):1-10.
- [30] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPHAIPHAN P,CHAROENSAPSRI W,et al.Characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of SpPR-AMP1,a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain[J].Developmental & Comparative Immunology,2017,74:209-216.
- [31] CHEN B,FAN D Q,ZHU K X,et al.Mechanism study on a new antimicrobial peptide Sphistin derived from the N-terminus of crab histone H2A identified in haemo-lymphs of Scylla paramamosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2015,47(2):833-846.
- [32] MA X W,HOU L,CHEN B,et al.A truncated Sph12-38 with potent antimicrobial activity showing resistance against bacterial challenge in Oryzias melastigma[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2017,67:561-570.
- [33] HUANG W S,WANG K J,YANG M,et al.Purification and part characterization of a novel antibacterial protein Scygonadin,isolated from the seminal plasma of mud crab,Scylla serrata(Forskål,1775)[J].Journal of Experimental Marine Biology & Ecology,2006,339(1):37-42.
- [34] QIAO K,XU W F,CHEN H Y,et al.A new antimi-crobial peptide SCY2 identified in Scylla paramamosain exerting a potential role of reproductive immunity[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2016,51:251-262.
- [35] YANG Y,CHEN F,CHEN H Y,et al.A novel antimi-crobial peptide scyreprocin from mud crab Scylla paramamosain showing potent antifungal and anti-biofilm activity[J].Front Microbiol,2020,11:1589.
- [36] DU Z Q,WANG Y,MA H Y,et al.A new crustin homologue(SpCrus6)involved in the antimicrobial and antiviral innate immunity in mud crab,Scylla paramamo-sain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2019,84:733-743.
- [37] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPARYUP P,TASSANAKAJON A,et al.Molecular cloning and characterization of crustin from mud crab Scylla paramamosain[J].Mol Biol Rep,2009,36(5):841-850.
- [38] WANG H,ZHANG J X,WANG Y,et al.Newly identified type Ⅱ crustin(SpCrus2)in Scylla paramamo-sain contains a distinct cysteine distribution pattern exhibiting broad antimicrobial activity[J].Develop-mental and Comparative Immunology,2018,84:1-13.
- [39] WANG Y,ZHANG X W,WANG H,et al.SpCrus3 and SpCrus4 share high similarity in mud crab(Scylla paramamosain)exhibiting different antibacterial activities[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2018,82:139-151.
- [40] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPARYUP P,TASSANAKAJON A,et al.Antilipopolysaccharide factor(ALF)of mud crab Scylla paramamosain:molecular cloning,genomic organization and the antimicrobial activity of its synthetic LPS binding domain[J].Molecular Immunology,2007,44(12):3195-3203.
- [41] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPARYUP P,TASSANAKAJON A.Molecular cloning,genomic organization and antibacterial activity of a second isoform of antilipopolysaccharide factor(ALF)from the mud crab,Scylla paramamosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2011,30(1):58-66.
- [42] LIU H P,CHEN R Y,ZHANG Q X,et al.Characteri-zation of two isoforms of antiliopolysacchride factors(Sp-ALFs)from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2012,33(1):1-10.
- [43] ZHU L,LAN J F,HUANG Y Q,et al.SpALF4:a newly identified anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2014,36(1):172-180.
- [44] SUN W W,WAN W S,ZHU S,et al.Characterization of a novel anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform(SpALF5)in mud crab,Scylla paramamosain[J].Molecular Immunology,2015,64(2):262-275.
- [45] HOU Z G,WANG Y,HUI K,et al.A novel anti-lipopolysaccharide factor SpALF6 in mud crab Scylla paramamosain exhibiting different antimicrobial activity from its single amino acid mutant[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2017,72:44-56.
- [46] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPARYUP P,TASSANAKAJON A.Two novel antimicrobial peptides,arasin-likeSp and GRPSp,from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain,exhibit the activity against some crustacean pathogenic bacteria[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2011,30(2):706-712.
- [47] IMJONGJIRAK C,AMPHAIPHAN P,CHAROENSAPSRI W,et al.Characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of SpPR-AMP1,a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2017,74:209-216.
- [48] ZHOU J,ZHAO S,FANG W H,et al.Newly identified invertebrate-type lysozyme(Splys-Ⅰ)in mud crab(Scylla paramamosain)exhibiting muramidase-deficient antimicrobial activity[J].Developmental and Compara-tive Immunology,2017,74:154-166.
- [49] XIE J W,CHENG C H,MA H L,et al.Molecular characterization,expression and antimicrobial activities of a c-type lysozyme from the mud crab,Scylla parama-mosain[J].Developmental and Comparative Immuno-logy,2019,98:54-64.
- [50] WANG K J,HUANG W S,YANG M,et al.A male-specific expression gene,encodes a novel anionic antimicrobial peptide,scygonadin,in Scylla serrata[J].Mol Immunol,2007,44(8):1961-1968.
- [51] XU W F,QIAO K,HUANG S P,et al.Quantitative gene expression and in situ localization of scygonadin potentially associated with reproductive immunity in tissues of male and female mud crabs,Scylla parama-mosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2011,31(2):243-251.
- [52] SHAN Z G,ZHU K X,CHEN F Y,et al.In vivo activity and the transcriptional regulatory mechanism of the antimicrobial peptide SpHyastatin in Scylla para-mamosain[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2016,59:155-165.
- [53] LIU J,CHEN F Y,WANG X F,et al.The synergistic effect of mud crab antimicrobial peptides Sphistin and Sph12-38 with antibiotics azithromycin and rifampicin enhances bactericidal activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J].Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology,2020,10:572849.
- [54] PENG H,YANG M,HUANG W S,et al.Soluble expression and purification of a crab antimicrobial peptide scygonadin in different expression plasmids and analysis of its antimicrobial activity[J].Protein Expr Purif,2010,70(1):109-115.
- [55] PENG H,LIU H P,CHEN B,et al.Optimized production of scygonadin in Pichia pastoris and analysis of its antimicrobial and antiviral activities[J].Protein Expr Purif,2012,82(1):37-44.
- [56] HE Y B,PENG H,LIU J,et al.Chlorella sp.transgenic with Scy-hepc enhancing the survival of Sparus macro-cephalus and hybrid grouper challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2018,73:22-29.