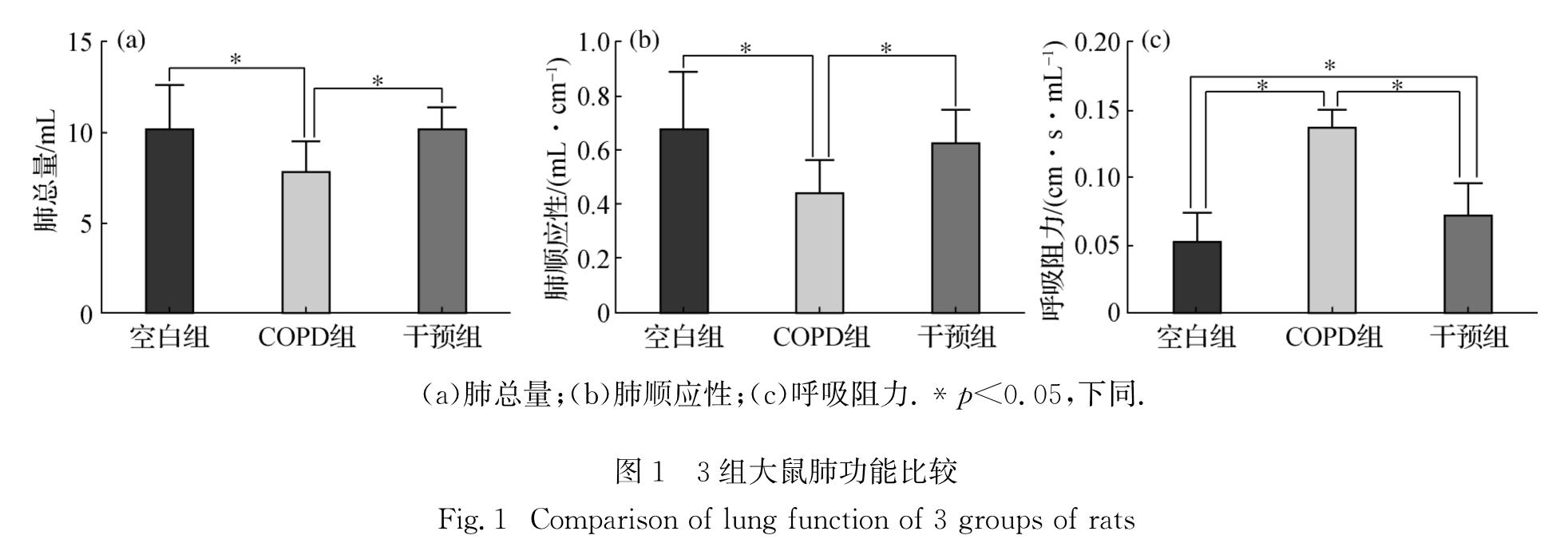
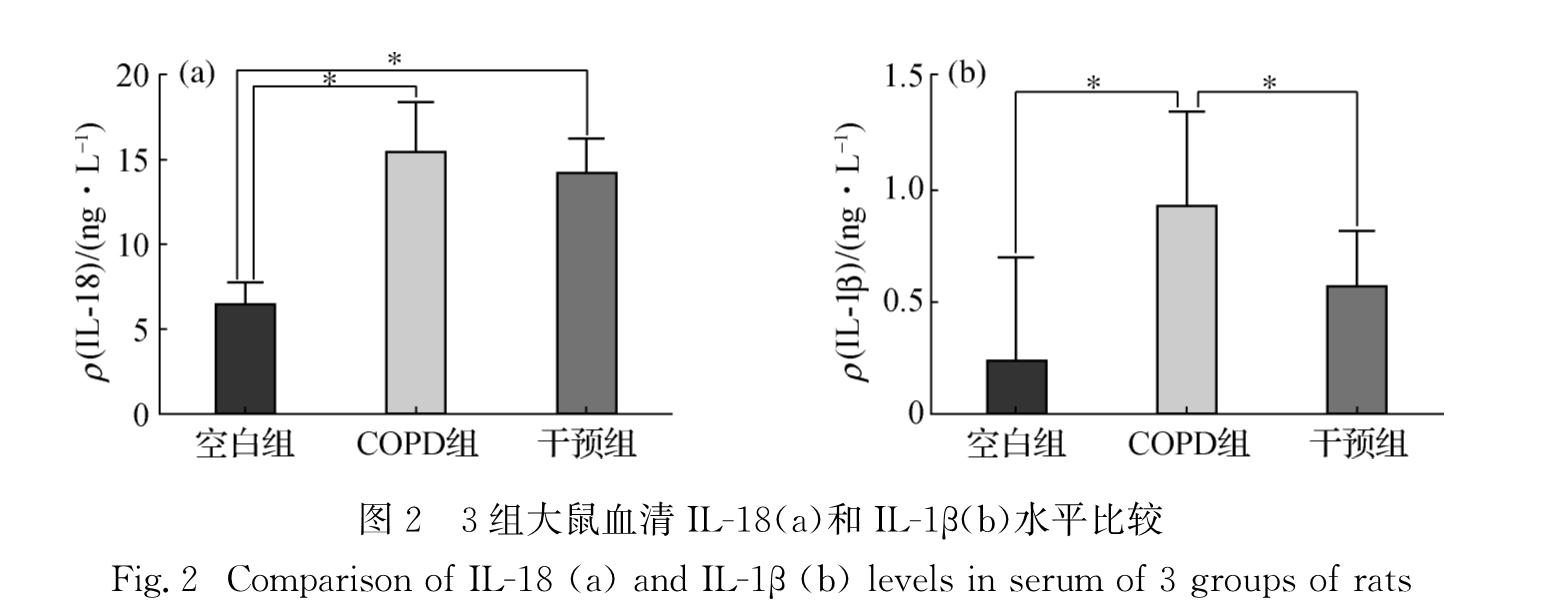
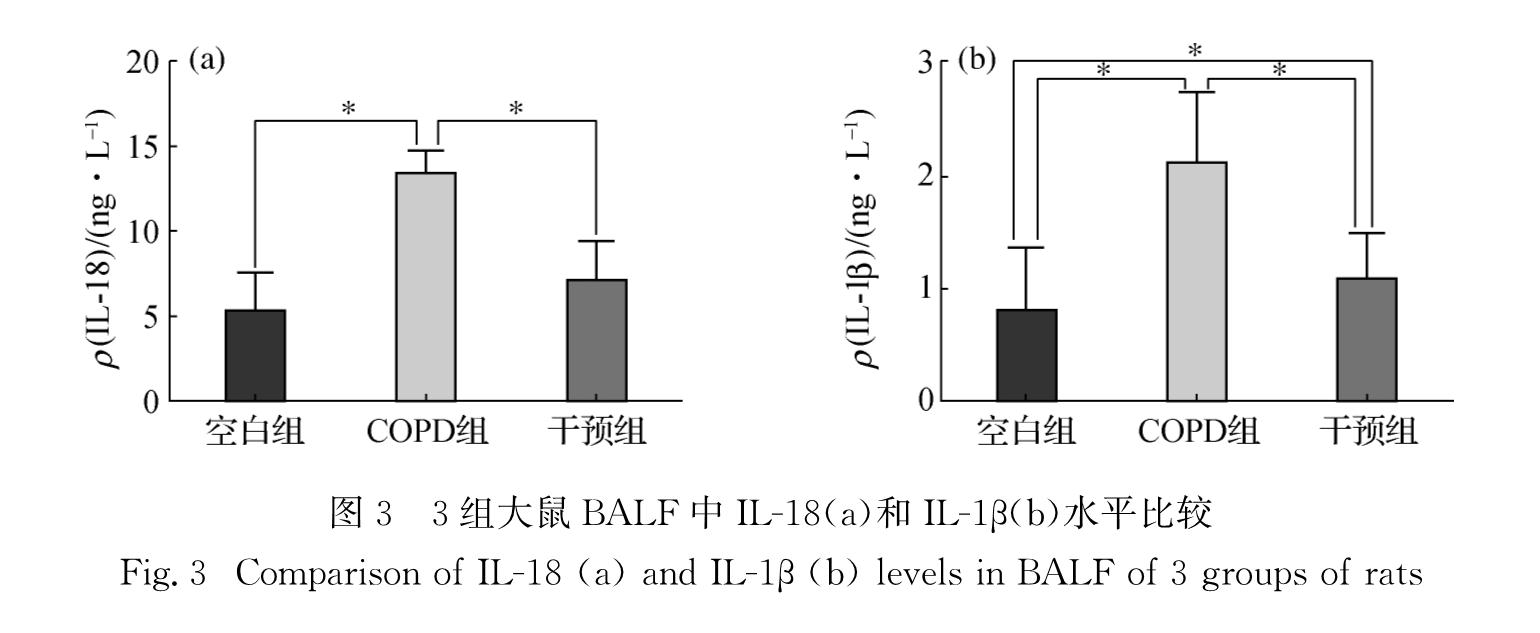
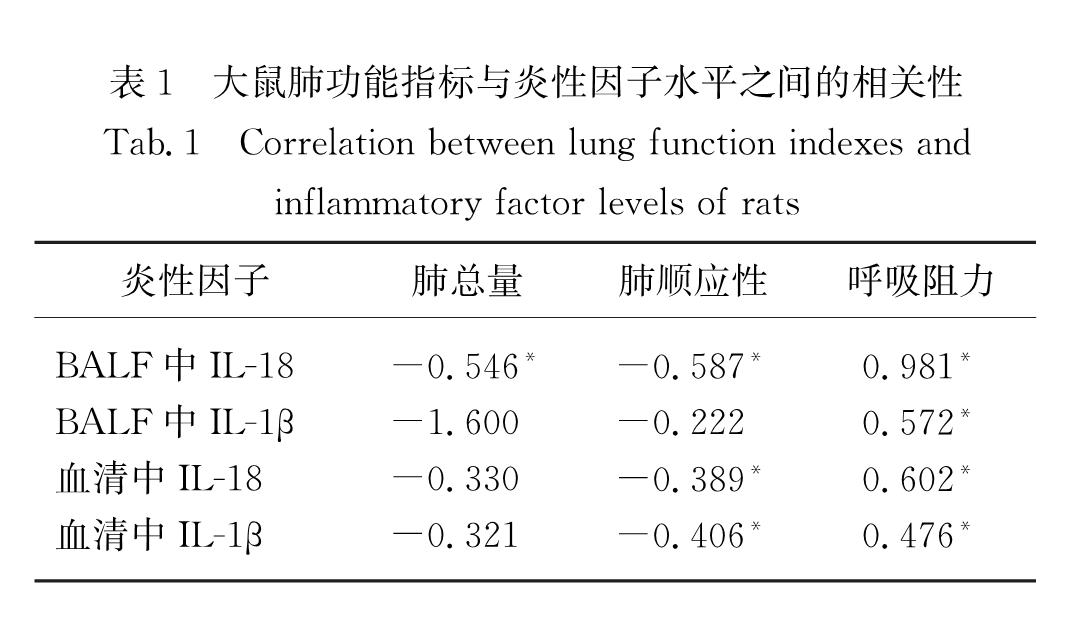
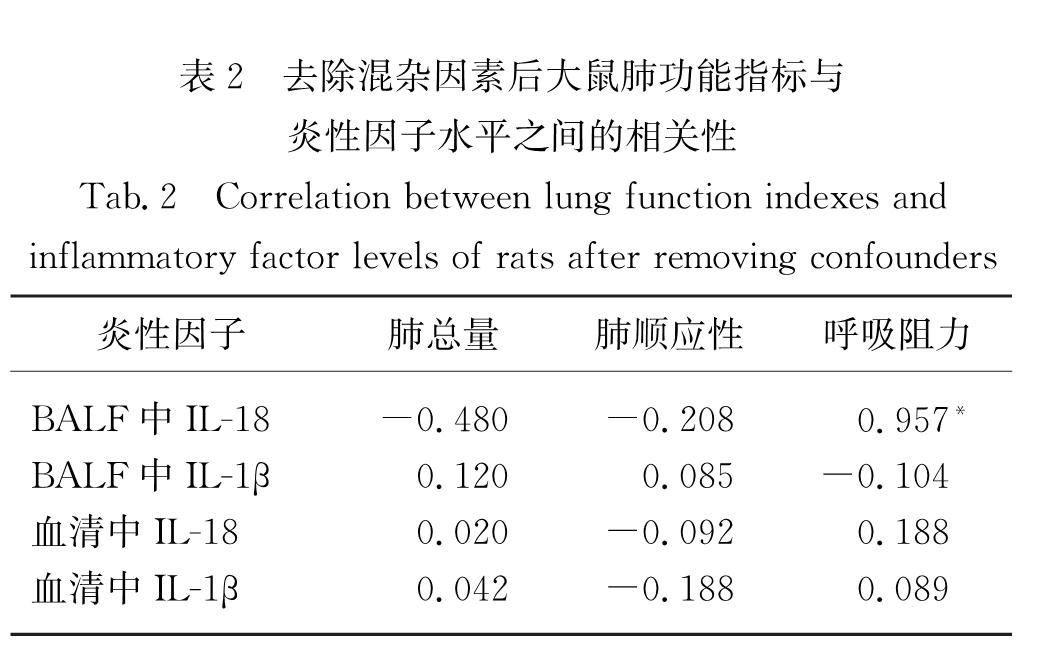
为了探讨核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎性小体在慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)发病中的作用,并分析白细胞介素-18(IL-18)及白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)在COPD大鼠体内分泌与肺功能的关系,按照随机原则将36只wistar大鼠平均分为空白组、COPD组及干预组,其中COPD组及干预组建造大鼠模型,干预组在造模的同时给予AC-YVAD-CMK抑制剂处理,造模结束后测定3组大鼠的呼吸阻力、肺总量、肺顺应性及血清、支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中IL-18和IL-1β的水平.结果显示:1)COPD组大鼠的肺总量和肺顺应性均低于干预组和空白组(p<0.05),呼吸阻力大小依次为COPD组>干预组>空白组(p<0.05); 2)COPD组大鼠血清中IL-1β水平高于空白组和干预组(p<0.05),COPD组和干预组大鼠血清中IL-18水平高于空白组(p<0.05); 3)COPD组大鼠BALF中 IL-18水平高于干预组和空白组(p<0.05),BALF中IL-1β水平大小依次为COPD组>干预组>空白组(p<0.05); 4)大鼠BALF中IL-18水平与其呼吸阻力呈显著正相关(p<0.05).由上述结果可知:COPD模型大鼠的肺总量、肺顺应性降低而呼吸阻力升高,体内IL-18和IL-1β水平升高,且BALF中IL-18水平与大鼠呼吸阻力呈正相关性,提示IL-18参与了COPD炎症反应; 阻断NLRP3炎性小体中caspase-1活化可以改善COPD模型大鼠肺功能并降低IL-18和IL-1β水平,提示NLRP3炎性小体可能参与了大鼠COPD的发病过程.
To investigate the pathogenesis of leotide-binding oligomerization domain-1ike receptors family pyrin domain containing 3(NLRP3)inflammasome of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD)as well as to explore the relationship between the secretion of IL-18,IL-1β in COPD rats and lung function, we randomized 36 wistar rats into three groups:the control group, the COPD group and the intervention group,and built the COPD rat models.The intervention group was given AC-YVAD-CMK inhibitor at the same time as building. Respiratory resistance(Rrs), total lung capacity(TLC),lung compliance(Crs),IL-18 and IL-1β levels in serum and broncho-alveolar lavage fluid(BALF)were determined after building.Results showed as following:1)The TLC and Crs of COPD group were lower than those in the intervention group and the control group(p<0.05),and the decreasing order in the levels of Rrs were the COPD group,the intervention group and the control group(p<0.05).2)IL-1β level in serum of rats in the COPD group were higher than that in the control group and the intervention group,and the IL-18 level in serum of the COPD group and the intervention group was higher than that in the control group(p<0.05).3)The IL-18 level in BALF of the COPD group was higher than that in the intervention group and the control group.The IL-1β level in BALF of the three groups was the greatest in the COPD group,followed by the intervention group and then the control group,and all of difference were significant(p<0.05).4)Rrs showed significant positive correlation with the IL-18 level in BALF.Taken together,the TLC and Crs decreased in the COPD model rats,but Rrs,IL-18 and IL-1β levels increased,and the IL-18 level in BLAF of rats was correlated with the Rrs,which indicated that IL-18 was involved in the inflammatory response in COPD.Moreover,the lung function might be improved, and IL-18 and IL-1β levels might decreased in COPD rats by inhibition of caspase-1 activation in NLRP3 inflammasome,which indicated that NLRP3 inflammasome was involved in the pathogenesis of COPD rats.