(厦门大学 环境与生态学院,近海海洋环境科学国家重点实验室,福建省海陆界面生态环境重点实验室,福建 厦门 361102)
(State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science,Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Coastal Ecology and Environmental Studies,College of the Environment & Ecology,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361102,China)
South China Sea; South East Asian Time-series Study station; pico-phytoplankton; C:Chl-a
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201805036
备注
浮游植物的碳生物量和叶绿素a浓度比值(简记为C:Chl-a)是海洋生物地球化学过程中的关键基础参数,在自然环境下有极大的变化.通过收集和整理近年来南海的东南亚时间序列观测(the South East Asian Time-series Study,SEATS)站的现场调查资料,对比分析了超微型浮游植物中三大类群的变化及其总C:Chl-a的垂直分布.叶绿素a浓度通过高效液相色谱分析获得,碳生物量依据文献报道的同纬度海区的C:Chl-a计算或基于流式细胞技术分析细胞丰度与体积后经换算得到.结果显示基于这两种方法计算得到的超微型浮游植物三大类群的碳生物量之间均存在极显著正相关(n=41,p<0.001),其中聚球藻(Synechococcus)基于高效液相色谱分析获得的碳生物量有一定的高估,而原绿球藻(Prochlorocoecus)和超微型真核藻类(pico-eukaryotes)的数据结果则基本一致,这种差异可能与聚球藻的光适应机制有关.通过计算南海SEATS站全粒径浮游植物的C:Chl-a,发现其呈现随深度递减的变化趋势,但相对于同纬度海区整体上偏小,进而讨论了南海SEATS站浮游植物时空分布模式和C:Chl-a变化的原因.
Carbon to chlorophyll-a(C:Chl-a)ratio is the most critical phytoplankton parameter in marine biogeochemical processes,but highly uncertain in the natural environment.Here,we took the South East Asian Time-series Study(SEATS)station located in the northern South China Sea basin with relatively stable environmental conditions as our study area.By compiling the observational data collected in recent years,we compared and analyzed the carbon biomass of three major pico-phytoplankton groups estimated from high performance liquid chromatography-chemical taxonomy(HPLC-CHEMTAX)analysis and flow cytometry(FCM)based cell abundances as well as cellular bio-volumes.The carbon biomass estimated from the two approaches all exhibited highly positive correlations of the three major picophytoplankton groups(n=41,p<0.001).According to the quantitative results,the carbon biomass of Synechococcus estimated by HPLC-CHEMTAX analysis has a certain overestimation,while the carbon biomass of Prochlorococcus and pico-eukaryotes are basically consistent with the results based on FCM.This may result from the light adaptation mechanism of Synechococcus.We calculated the phytoplankton total C:Chl-a in full size categories at SEATS in the South China Sea,and found that the C:Chl-a decreased with depth,and the overall value was relatively small compared with other marine ecosystems located at the same latitude.This paper systematically discussed the distributional pattern of phytoplankton community at the SEATSstation both spatially and temporally,and the likely reasons for the variations in C:Chl-a.
引言
浮游植物是海洋生态系统中最主要的初级生产者,对全球气候变化起到非常重要的调控作用[1].浮游植物叶绿素a是初级生产过程的核心,因此很多研究以叶绿素a作为浮游植物生物量的指标.然而,浮游植物的碳生物量和叶绿素a浓度(质量浓度,下同)比值(简记为C:Chl-a)和全球气候变化(特别是碳循环)的关系更密切.大量研究结果证实,不同浮游植物类群对总叶绿素a浓度和对总碳生物量的贡献不同,更不能等同于对总初级生产力的贡献[2-3].最近Behrenfeld等[4]指出全球气候变化研究,特别是和碳循环相关的生物地球化学研究,需要使用浮游植物的碳生物量来评估浮游植物的生物量变化,而非叶绿素a浓度.
尽管浮游植物的叶绿素a浓度和碳的固定有直接关系,但是因为浮游植物种类之间的差异以及光和营养盐等环境因子的影响,在现场测得的叶绿素a浓度和碳生物量之间并没有确定的数学关系,这导致C: Chl-a有很大的不确定性.自1960年Strickland[5]命名C:Chl-a为F比值开始,国际上已有大量的研究工作围绕此展开[3,6-9],然而大部分的现场研究工作仍集中在北大西洋和赤道太平洋海区.目前已知C:Chl-a从实验室到现场在2个数量级之间变化(从几到几百); 同时,现场海区的叶绿素a浓度与碳生物量之间还常观测到非线性关系[9].对于一些研究资料较少的边缘海,因其复杂的环境特征和时空变化而很难参考其他海区已报道的经验比值[10].
我国南海是世界上最大的边缘海之一,在季节尺度上其上层海水的生物地球化学过程主要受东亚季风影响[11].作为联合全球海洋通量研究(joint global ocean flux study,JGOFS)的时间序列计划的一部分,由我国台湾地区学者在1999年发起并建立了位于南海的东南亚时间序列观测(the South East Asian Time-series Study,SEATS)站[11].SEATS站处于南海北部海盆区(18° N,116° E),水深3 846 m,表层水温相对较高且季节变化较小,受周围主要河流影响较小,具有典型的低纬度边缘海寡营养海盆特征[11].近年来,通过流式细胞技术(flow cytometry,FCM)和高效液相色谱法结合光合色素化学分类法(HPLC-CHEMTAX),对南海浮游植物的时空分布格局和调控机制有了较深入的了解.已有研究结果显示南海近岸水域的浮游植物优势类群为粒径较大的硅藻,海盆区表层的优势类群为原绿球藻(Prochlorococcus)和聚球藻(Synechococcus),次表层为定鞭藻(haptophytes)和青绿藻(prasinophytes)[12-13].Liu等[14]运用FCM对南海SEATS站的超微型浮游植物(细胞粒径小于2 μm)细胞丰度的季节变化做了定量研究,发现原绿球藻是丰度最高的浮游植物且最高丰度出现在夏季,而聚球藻和超微型真核藻类(pico-eukaryotes)的丰度在一年中大部分时间都比原绿球藻低1~2个数量级.Chen等[15]研究了南海北部(包括SEATS站)超微型浮游植物在不同季节细胞丰度的垂直分布规律、细胞大小以及C:Chl-a,其结果显示超微型真核藻类细胞丰度的垂直分布规律为在夏季形成次表层叶绿素a极大值(deep chlorophyll maximum,DCM)层,且最大丰度出现的深度随营养盐跃层深度的变化而变化.Xiao等[12]分析了2004—2015年间20个现场观测航次采集的5 338个光合色素样品,并结合温度、盐度和营养盐等理化因子建立了主要浮游植物类群的实际生态位均值和宽度模型.
在国内,碳生物量的研究还不多见.Sun等[16]较早开展了将浮游植物丰度转换为碳生物量的相关研究,通过对浮游植物形状进行分析、归类,建立了不同浮游植物的体积换算模型,再利用体积与碳生物量之间的转换系数,由浮游植物种类组成和丰度的结果计算各主要类群对碳生物量的贡献.这大大降低了直接从叶绿素a或分粒级叶绿素a通过C:Chl-a简单计算所得碳生物量结果的不确定性.Chang等[17]也利用类似方法报道了C:Chl-a在东海夏季表层从长江口到黑潮影响区域的变化,发现受营养盐浓度的影响,C:Chl-a 在长江口明显低于黑潮影响区域.由于需要通过显微镜检测鉴定浮游植物种类和计数,此方法主要适用于细胞粒径较大的类群,例如硅藻(diatom)、甲藻(dinoflagellates)等.对于粒径较小的超微型浮游植物,Chen等[15]在南海通过FCM发现聚球藻、原绿球藻和超微型真核藻类在冬季的C:Chl-a显著小于夏季.
目前南海浮游植物全粒级高分辨率的碳生物量时空分布仍不清楚,且在整个群落水平的C:Chl-a尚未见报道.在当前的南海生物地球化学过程研究中,特别是以碳为基础的生态模型(如NPZD模型)研究,仍是使用其他海区(如夏威夷海洋时间序列站和赤道太平洋高营养盐、低叶绿素区域)的参考数据或是利用经验公式计算C:Chl-a[18].因此,不同区域温度、营养盐、光辐照度和生物群落的变化给C:Chl-a计算结果带来的不确定性严重限制了南海相关研究进展.本研究通过HPLC-CHEMTAX获得超微型浮游植物三大类群(原绿球藻、聚球藻和真核藻类)的叶绿素a浓度,使用同纬度海区C:Chl-a[19]转换成碳生物量; 同时,利用相对较准确的基于FCM获得的三大类群的细胞丰度和体积换算成碳生物量.进而将两种方法获得的结果进行同步对比,分析不同类群之间的差异,并最终计算南海SEATS站的总C:Chl-a.通过系统性分析南海SEATS站浮游植物类群的时空分布,针对C:Chl-a这一生物地球化学过程关键参数展开讨论,以期为进一步开展海洋生态系统和生物地球化学整合研究提供数据参考.
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品数据来源及分析方法本研究通过整合近年来发表的相关数据集,对分别使用FCM和HPLC-CHEMTAX报道的同步采样数据进行数据匹配,并从中挑选了2006年11月至2012年8月期间不同时间段在南海SEATS站采集的样品数据[12,15,20](表1).环境参数通过Sea-Bird Electronics公司的SBE25温盐深剖面仪测得,方法详见文献[12].光合色素的含量通过HPLC分析,再使用CHEMTAX v1.95软件进行基于总叶绿素a浓度的各主要类群相对贡献分析,方法详见文献[12,21].FCM样品使用Becton-Dickson公司的FACSCalibur流式细胞仪的高速模式分析,方法详见文献[15].
1.2 碳生物量的计算基于FCM的浮游植物碳生物量通过各主要类群的细胞数乘以其在对应季节(分为冷季和暖季)浮游植物的细胞碳含量得到.根据文献[11]报道的风场特征,将5月至10月定义为暖季(受西南季风影响),而将11月至次年4月定义为冷季(受东北季风影响).表层浮游植物的单细胞碳含量(fg)如下:原绿球藻暖季11.8,冷季23.4; 聚球藻暖季72.4,冷季76.7; 超微型真核藻类暖季979.1,冷季580.7[15].基于HPLC-CHEMTAX计算各主要类群的碳生物量则首先通过13种特征光合色素浓度反演获得叶绿素a浓度[11-13].
表1 南海SEATS站浮游植物数据统计
Tab.1 Summary of phytoplankton samples in the SEATS station of the South China Sea得到叶绿素a浓度后,参照赤道太平洋经典的C:Chl-a数据[19],50 m以上浅水层使用数值80,50 m及以下使用数值50,分水层计算得到各类群的碳生物量.通过HPLC-CHEMTAX计算获得的绿藻(chlorophytes)和青绿藻的数据之和作为超微型真核藻类的碳生物量[22].浮游植物群落的总碳生物量为使用FCM校正后的三大超微型浮游植物类群的碳生物量与通过经验比值计算的其他浮游植物类群的碳生物量之和.通过SPSS v16软件进行数据统计分析,其中差异比较使用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),设置p<0.05为显著性差异水平,相关性分析中R为皮尔森相关系数.使用Ocean Data View软件作图.
2 结果与分析
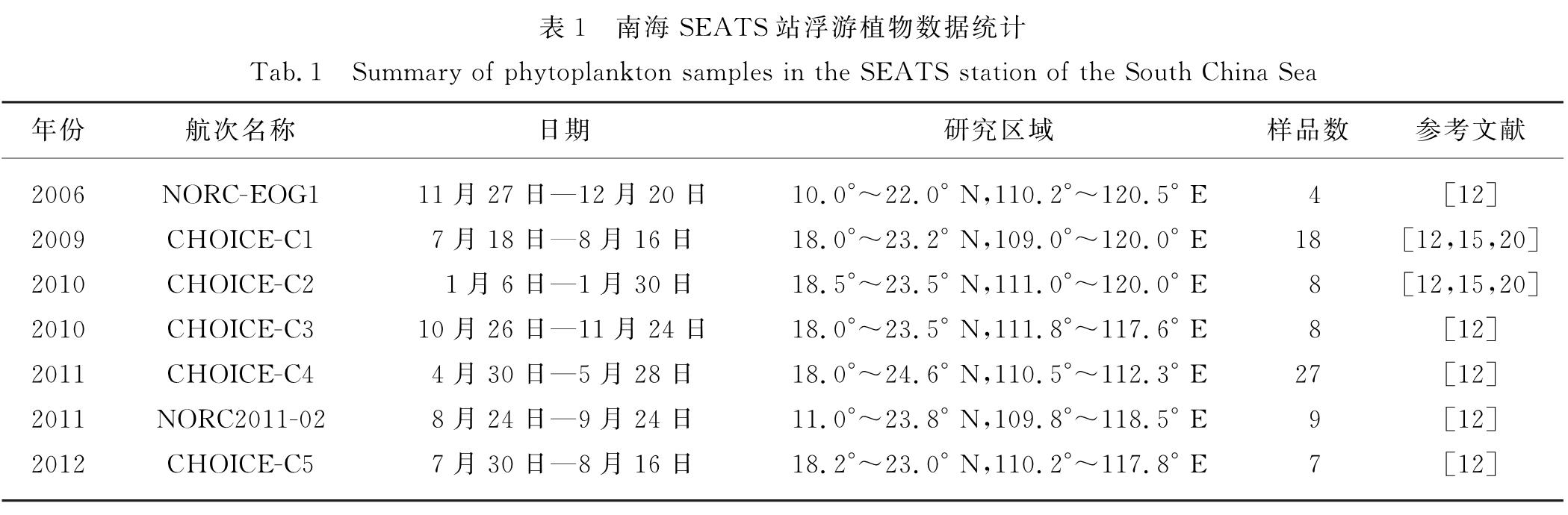
2.1 水文背景如图1(a)所示,暖季水表层水温相对较高(26~30 ℃,中位值为28 ℃),而冷季表层水温则较低(25~26 ℃,中位值为25 ℃),可见当东北季风加强时表层海水温度降低.与温度明显的季节变化相比,盐度的冷暖季差异不明显,暖季表层的盐度相对较低(S<33.5),而季风间期(5月和10月)的盐度相对较高(S>33.5).50 m以上浅水层的温度和盐度均呈现均匀混合(图1(a)和(b)),而总叶绿素a浓度在50 m以上浅水层均表现为冷季高于暖季(图1(c)),且差异显著(p<0.05).由于暖季具有较深的真光层深度和营养盐跃层深度,垂向上出现更明显的DCM层(约在75 m),而在冷季中DCM层变浅或不明显(图1(c)).
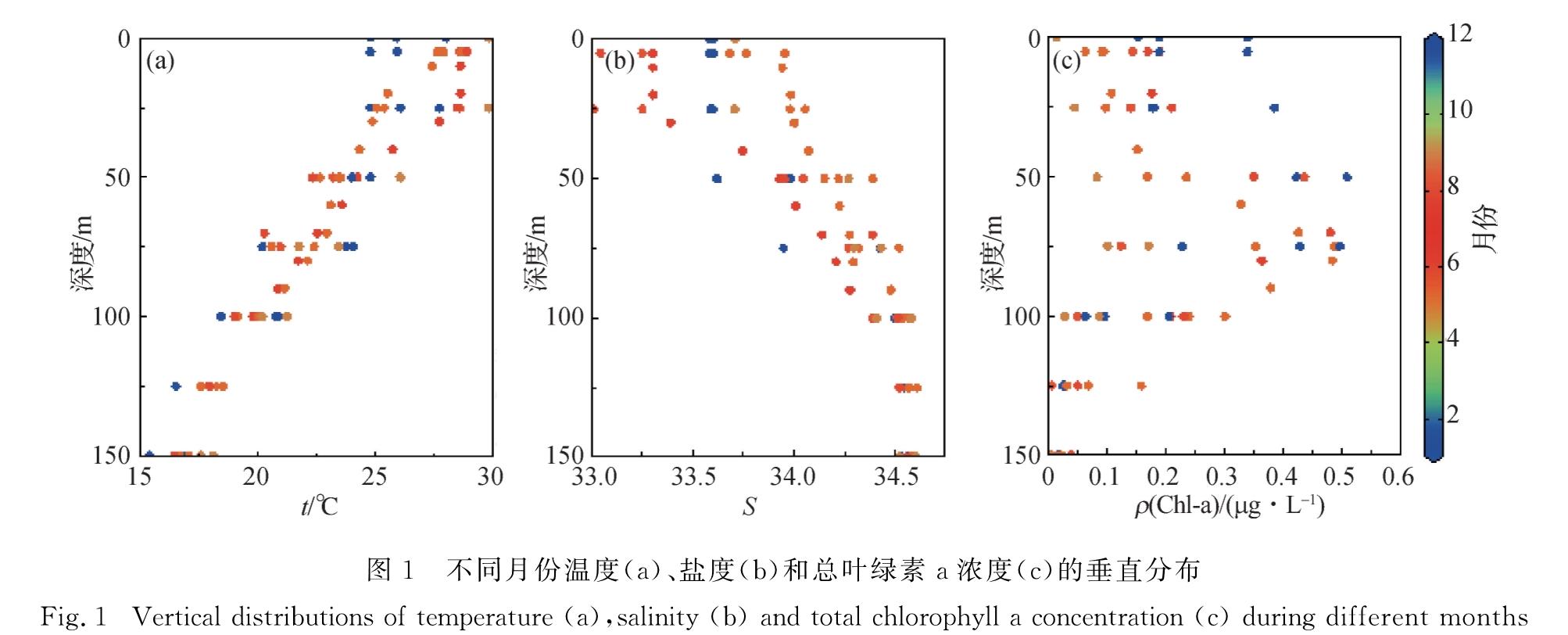
2.2 超微型浮游植物细胞丰度的垂直分布图2显示的是SEATS站超微型浮游植物三大类群细胞丰度的垂直分布及其季节变化.虽然原绿球藻在表层未见显著的季节变化(图2(a)),但是整体上其暖季的细胞丰度显著高于冷季(p<0.05),且最高值比暖季聚球藻和超微型真核藻类的高1~2个数量级; 聚球藻和超微型真核藻类的季节变化更明显,但与原绿球藻相反,暖季50 m以上浅水层两者的细胞丰度均显著低于冷季(p<0.05,图2(b)和(c)).值得注意的是,聚球藻细胞丰度在50~75 m显著下降(图2(b)),而超微型真核藻类在50~75 m观测到细胞丰度的最大值(图2(c)),这与总叶绿素a浓度的垂
图1 不同月份温度(a)、盐度(b)和总叶绿素a浓度(c)的垂直分布
Fig.1 Vertical distributions of temperature(a),salinity(b)and total chlorophyll a concentration(c)during different months图2 不同月份原绿球藻(a)、聚球藻(b)和超微型真核藻类(c)细胞丰度的垂直分布
Fig.2 Vertical distributions of cell abundances of Prochlorococcus(a),Synechococcus(b),pico-eukaryotes(c)during different months直分布特征(图1(c))极为相似.
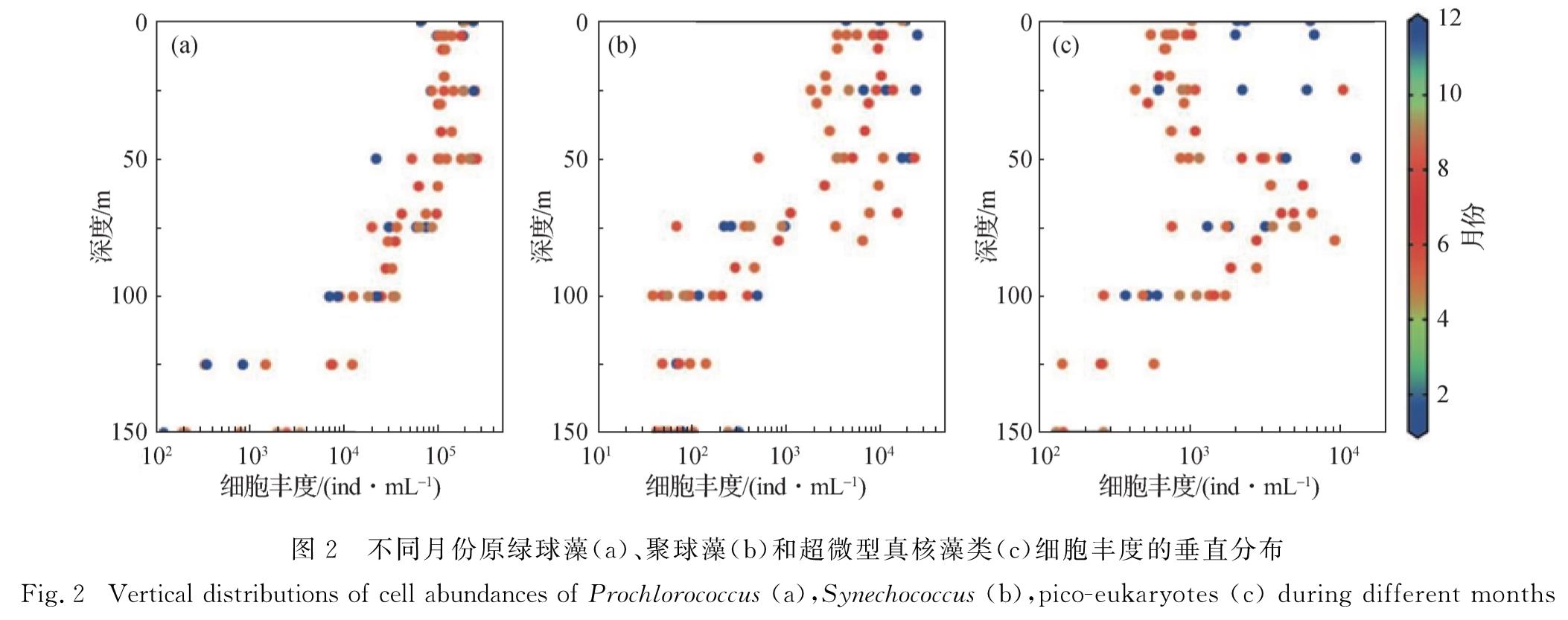
2.3 浮游植物主要类群叶绿素a浓度的垂直分布与FCM分析结果相似,通过HPLC-CHEMTAX得到的超微型浮游植物叶绿素a浓度的垂直分布规律在不同季节呈现显著差异(图3).根据叶绿素a浓度的大小,优势类群依次是原绿球藻、聚球藻和定鞭藻(8型).原绿球藻的叶绿素a浓度在所有类群中贡献最高,在50 m层出现峰值,且在100 m层仍能观测到较高值,最大值出现在暖季(图3(a)); 聚球藻表层的叶绿素a浓度较高,随深度增加逐渐减少,整体上冷季高于暖季(图3(b)); 定鞭藻(8型)的叶绿素a浓度和FCM观测到的超微型藻类细胞丰度的时空变化规律极为相似,且冷季高于暖季.定鞭藻(8型)的叶绿
图3 不同月份原绿球藻(a)、聚球藻(b)、青绿藻(c)、定鞭藻(8和6型,d和e)和甲藻(f)叶绿素a浓度的垂直分布
Fig.3 Vertical distributions of chlorophyll a concentrations in Prochlorococcus(a),Synechococcus(b),prasinophytes(c),haptophytes(type 8 and 6,d and e)and dinoflagellates(f)during different months素a浓度全年都在DCM层出现最大值,且在100 m层仍保持100 ng/L(图3(d)).其他类群如青绿藻、定鞭藻(6型)、甲藻和硅藻的叶绿素a浓度都不高,均与定鞭藻(8型)相似,最大值主要在DCM层(图3(c),(e)和(f)).
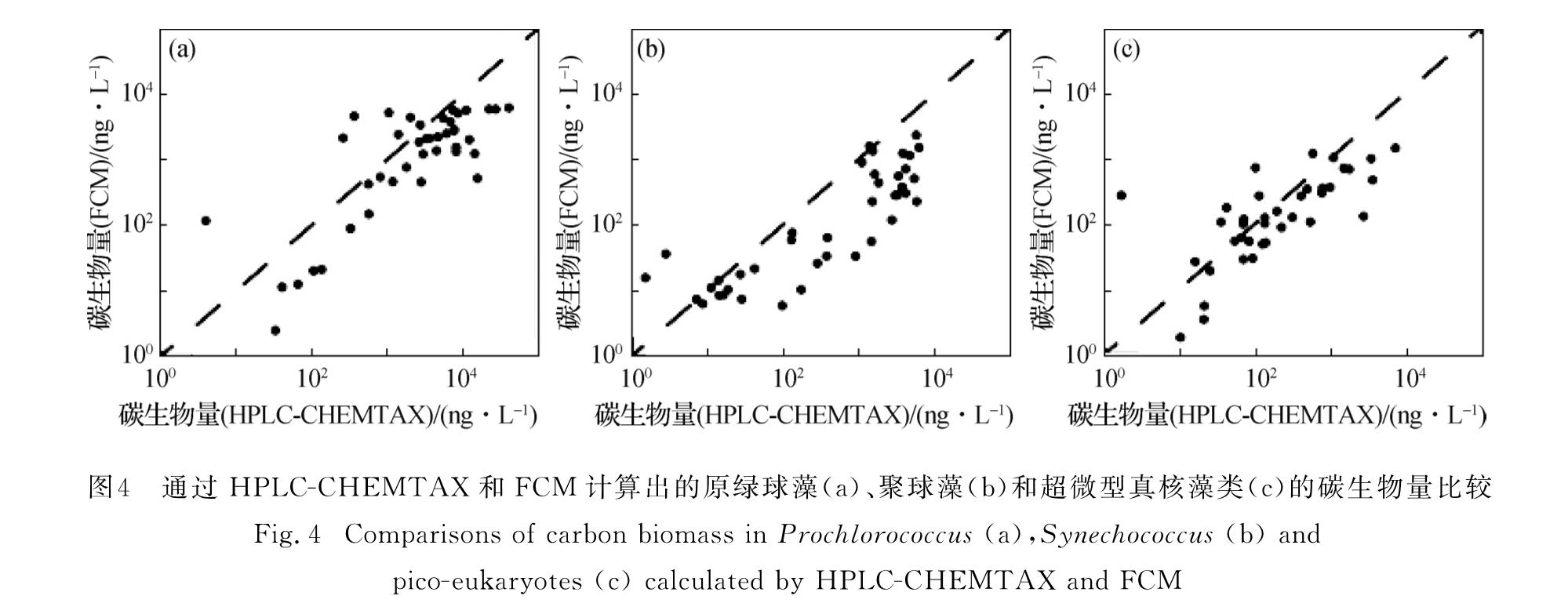
2.4 浮游植物C:Chl-a的垂直分布以FCM和HPLC-CHEMTAX计算碳生物量,结果显示在3个超微型浮游植物类群中都存在极显著的正相关关系(图4,n=41,p<0.01).原绿球藻的结果在高值区比较离散(R=0.57),聚球藻的结果则大部分位于1:1参考线下方(R=0.65),指示基于HPLC-CHEMTAX计算会对碳生物量产生系统性高估; 而超微型真核藻类的相关性最好,数值基本分布在1:1参考线两侧(R=0.70),暗示2种方法所得结果之间有很好的一致性.
为了获得全粒径浮游植物群落的总C:Chl-a比
图4 通过HPLC-CHEMTAX和FCM计算出的原绿球藻(a)、聚球藻(b)和超微型真核藻类(c)的碳生物量比较
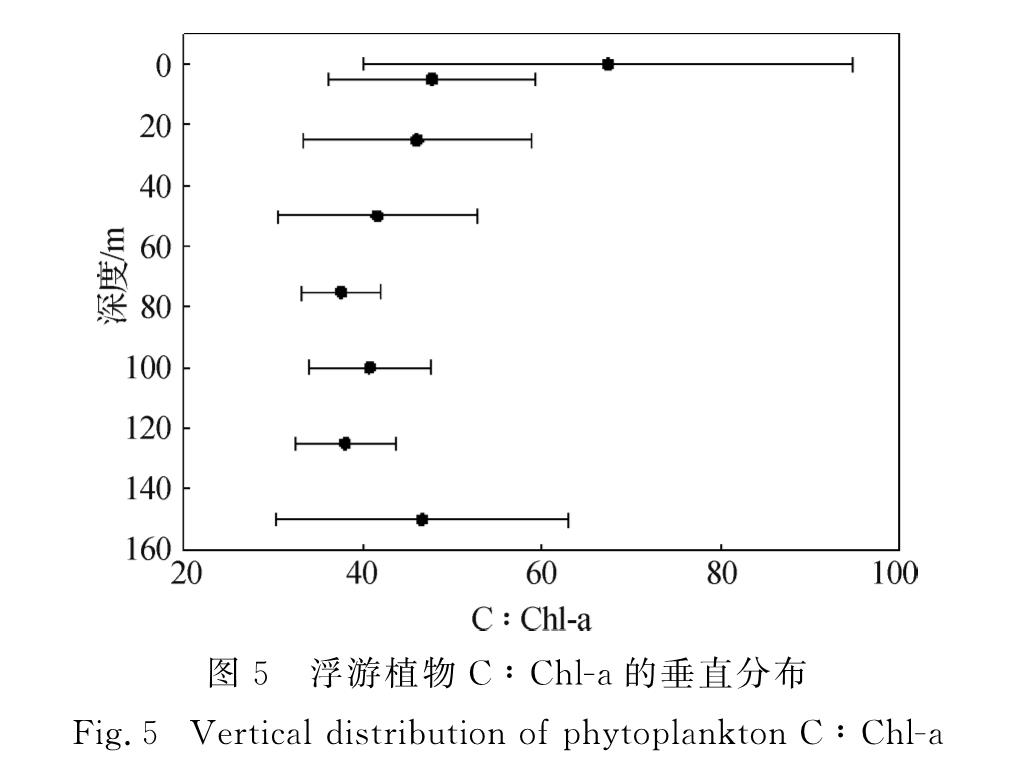
Fig.4 Comparisons of carbon biomass in Prochlorococcus (a),Synechococcus (b)and pico-eukaryotes(c)calculated by HPLC-CHEMTAX and FCM值,将通过FCM获得的三大超微型浮游植物类群与通过HPLC-CHTMAX估算的其他类群碳生物量相加,并除以总叶绿素a浓度,得到C:Chl-a的垂直分布(图5).总体上南海海盆SEATS浮游植物总C:Chl-a随水深呈递减趋势,从表层的67±27到75 m层的38±4,再到150 m层的47±16.
3 讨 论
3.1 浮游生物群落的时空变化由于SEATS站所处的南海属于低纬度海区,本研究观测到的海水表层水温均高于23 ℃(图1),这与此前Chao等[23]报道在南海中部表层水温不会低于22 ℃的结果相吻合.暖季强的层化现象使得上层海水处于营养盐耗尽的状态,真光层内浮游生物的生物量和初级生产水平都非常低[23]; 而且由于真光层和营养盐跃层深度增加,出现DCM层下移的现象(图1(c)).Du等[24]基于夏季在南海SEATS站对湍流微结构与营养盐的高分辨率观测,同时定量分析了硝酸盐等生源要素跨密度面的扩散通量与平流通量,从营养盐通量垂向结构的角度揭示了SEATS站真光层的双层结构.该研究结果显示在营养盐跃层上部存在营养盐耗尽层(nutrient-depleted layer,NDL),溶解无机氮的有效通量极低; 从NDL以下到真光层底部称为富营养盐层(nutrient-replete layer,NRL),该层内溶解无机氮浓度及其有效通量快速增加,其底部通量比NDL大3个数量级,支持DCM层的生物生产[24].本研究发现,在冷季较强的东北季风减弱了海水层化的结构,混合层深度增加,可以达到50~75 m(图1).根据已有报道,SEATS站的营养盐状况因此呈现明显的季节变化[25].在冷季强盛的东北季风和表层降温的双重影响下,富含营养盐的海水从营养盐跃层上部进入到混合层,真光层内的营养盐浓度显著提升.这可能是SEATS站冷季的总叶绿素a浓度(本研究)和初级生产力[11,23]高于暖季的原因.
从浮游植物群落的角度来看,原绿球藻、聚球藻等超微型浮游植物在高温和低营养盐环境下具有竞争优势,使它们和其他浮游植物的时空分布呈现明显区别[14],本研究结果显示原绿球藻的这种特征表现尤为明显(图2(a)); 而就总叶绿素a浓度而言,聚球藻和超微型真核藻类的生物量都在冷季相对较高(图1(a),2(b)和2(c)).此外,超微型真核藻类的细胞丰度与总叶绿素a浓度的垂直分布特征相似,对总叶绿素a浓度的贡献也非常高(图1~3).SEATS站的这种分布模式和已报道南海北部海盆其他区域的浮游植物群落基本一致,而与北部陆架及近岸区域差异显著[12,15,26-27].同时,本研究发现季节内的各类群生物量也存在较显著的变化.一方面,近年来南海北部海盆中尺度涡和内波非常活跃[28-29],给浮游植物群落的时空分布带来的影响非常明显,且不同类群对这类物理过程的响应机制也不同[30-31]; 另一方面,浮游动物摄食压力的变化也会影响浮游植物生物量、初级生产力和群落特征[32-33].
3.2 C:Chl-a的变化规律浮游植物的碳生物量、初级生产力及叶绿素a浓度通常具有相关关系.然而,浮游植物的叶绿素a浓度和碳生物量之间因为存在细胞大小和细胞碳含量的种间差异而使得两者之间未呈现清晰的线性关系[34]; 同时,光照的限制以及营养盐的可利用性对两者都存在显著影响[6,35].这些研究结果显示,浮游植物趋向于在高光和寡营养盐环境下降低单细胞叶绿素a浓度,而在低光和富营养盐环境下则相反.
本研究中3个超微型浮游植物类群的碳生物量在基于FCM和HPLC-CHEMTAX的计算结果之间呈现显著的正相关关系.考虑2种方法的原理,通过FCM获得细胞丰度与体积计算的结果应更为准确; 而利用HPLC-CHEMTAX计算叶绿素a浓度后,使用同一C:Chl-a数据计算不同类群的碳生物量会引入误差.Chen等[15]的研究表明,在超微型浮游植物的三大类群之间以及同一类群在不同季节之间,C:Chl-a均呈现显著差异.通过比较FCM计算的结果,本研究发现HPLC-CHEMTAX计算的聚球藻碳生物量存在系统性高估,而超微型真核藻类则较为准确.这可能是因为聚球藻主要分布在表层,因为光照强度的变化,在不同季节之间它们会通过调整细胞体内的光合色素组成进行光适应,这将显著改变特征色素与叶绿素a浓度之间的比值,造成叶绿素a浓度的计算误差; 而且本研究中并未使用不同季节的C:Chl-a经验值进行计算,进而影响最终的碳生物量结果.与之相反,超微型真核藻类则主要分布在DCM层,在不同季节它们所在的深度会根据光照和营养盐状态调整,比如暖季表层光照强度较强、营养盐浓度较低时,DCM层深度较深,而冷季则相反,这样的变化可能使得它们的C:Chl-a相对稳定.
从群落水平上来看,本研究中获得的C:Chl-a从海水表层到深层存在明显梯度(图5),这与赤道太平洋等海区的观测结果[8,17]一致.垂向上递减的趋势则主要是由于表层光照强度强、营养盐浓度低,小粒径浮游植物具有优势,所以趋向具有较高的C:Chl-a; 而在DCM层,营养盐条件得到改善且光照强度减弱,浮游植物可能出现潜在的光限制而大量产生叶绿素a以捕获光能,也因此表现为较低的C:Chl-a.本研究的结果总体上偏小,如果忽略HPLC-CHEMTX分析的误差,可能的解释是该结果为全年平均值.冬季真光层内营养盐浓度的升高和光照强度的减弱使浮游植物群落趋向低的C:Chl-a[15].此外,本研究结果显示在150 m水层C:Chl-a有再度上升的趋势,这一现象可能是由于光限制了浮游植物的生长,浮游植物细胞死亡后叶绿素a浓度快速下降导致的.
4 结 论
本研究通过整合近年来发表的相关数据,分析了南海SEATS站不同类群叶绿素a和细胞丰度垂直分布的季节变化差异,并利用基于FCM所得的细胞丰度和体积换算结果,评估了超微型浮游植物三大类群通过HPLC-CHEMTAX获得叶绿素a浓度后使用文献中的C:Chl-a转换的碳生物量,进一步计算了南海SEATS站的总C:Chl-a.结果表明3个超微型浮游植物类群利用FCM和HPLC-CHEMTAX计算的碳生物量都呈现极显著正相关.聚球藻基于HPLC-CHEMTAX计算的碳生物量存在一定的高估; 而超微型真核浮游植物的相关性最好.南海SEATS站表层浮游植物总C:Chl-a为67±27,且随水深递减.本研究结果显示,尽管使用文献中的C:Chl-a计算碳生物量存在较大的不确定性,但是通过分析叶绿素a浓度与碳生物量之间的定量转换关系可为深入阐明浮游植物群落在生物地球化学过程中的作用奠定数据基础.
- [1] 黄邦钦,柳欣.边缘海浮游生态系统对生物泵的调控作用[J].地球科学进展,2015,30(3):385-395.
- [2] CLOERN J E,GRENZ C,VIDERGARLUCAS L.An empirical model of the phytoplankton chlorophyll:carbon ratio:the conversion factor between productivity and growth rate[J].Limnology and Oceanography,1995,40(7):1313-1321.
- [3] SATHYENDRANATH S,STUART V,NAIR A,et al.Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio and growth rate of phyto-plankton in the sea[J].Marine Ecology Progress Series,2009,383:73-84.
- [4] BEHRENFELD M J,O'MALLEY R T,BOSS E S,et al.Revaluating ocean warming impacts on global phyto-plankton[J].Nature Climate Change,2015,6(3):323-330.
- [5] STRICKLAND J D H.Measuring the production of marine phytoplankton[M].Ottawa:Fisheries Research Board of Canada,1960:172.
- [6] GEIDER R J,MACINTYRE H L,KANA T M.A dynamic model of photoadaptation in phytoplankton[J].Limnology and Oceanography,1996,41(1):1-15.
- [7] GEIDER R J,MACINTYRE H L,KANA T M.A dynamic regulatory model of phytoplanktonic acclimation to light,nutrients,and temperature[J].Limnology and Oceano-graphy,1998,43(4):679-694.
- [8] LI Q P,FRANKS P J S,LANDRY M R,et al.Modeling phytoplankton growth rates and chlorophyll to carbon ratios in California coastal and pelagic ecosystems[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2010,115:G04003.
- [9] JAKOBSEN H H,MARKAGER S.Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio for phytoplankton in temperate coastal waters:Seasonal patterns and relationship to nutrients[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2016,61(5):1853-1868.
- [10] HARRISON P J,ZINGONE A,MICKELSON M J,et al.Cell volumes of marine phytoplankton from globally distributed coastal data sets[J].Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2015,162:130-142.
- [11] WONG G,KU T,MULHOLLAND M,et al.The South East Asian Time-series Study(SEATS)and the biogeo-chemistry of the South China Sea:an overview[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2007,54(14/15):1434-1447.
- [12] XIAO W,WANG L,LAWS E,et al.Realized niches explain spatial gradients in seasonal abundance of phyto-plankton groups in the South China Sea[J].Progress in Oceanography,2018,162:223-229.
- [13] HO T Y,PAN X,YANG H H,et al.Controls on temporal and spatial variations of phytoplankton pigment distribution in the northern South China Sea[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2015,117:65-85.
- [14] LIU H,CHANG J,TSENG C,et al.Seasonal variability of picoplankton in the northern South China Sea at the SEATS station[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2007,54(14/15):1602-1616.
- [15] CHEN B Z,WANG L,SONG S Q,et al.Comparisons of picophytoplankton abundance,size,and fluorescence between summer and winter in northern South China Sea[J].Continental Shelf Research,2011,31(14):1527-1540.
- [16] SUN J,LIU D Y.Geometric models for calculating cell biovolume and surface area for phytoplankton[J].Journal of Plankton Research,2003,25(11):1331-1346.
- [17] CHANG J,SHIAH F,GONG G,et al.Cross-shelf variation in carbon-to-chlorophyll a ratios in the East China Sea,summer 1998[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(6/7):1237-1247.
- [18] LI Q P,WANG Y,DONG Y,et al.Modeling long-term change of planktonic ecosystems in the northern South China Sea and the upstream Kuroshio Current[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2015,120(6):3913-3936.
- [19] LANDRY M R,SELPH K E,TAYLOR A G,et al.Phytoplankton growth,grazing and production balances in the HNLC equatorial Pacific[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2011,58(3/4):524-535.
- [20] CHEN B,ZHENG L,HUANG B,et al.Seasonal and spatial comparisons of phytoplankton growth and mortality rates due to microzooplankton grazing in the northern South China Sea[J].Biogeosciences,2013,10(4):2775-2785.
- [21] HUANG B Q,HU J,XU H Z,et al.Phytoplankton community at warm eddies in the northern South China Sea in winter 2003/2004[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2010,57(19/20):1792-1798.
- [22] UITZ J,CLAUSTRE H,GENTILI B,et al.Phyto-plankton class-specific primary production in the world's oceans:seasonal and interannual variability from satellite observations[J].Global Biogeochemical Cycles,2010,24:GB3016.
- [23] CHAO S Y,SHAW P T,WU S Y.El Niño modulation of the South China Sea circulation[J].Progress in Oceanography,1996,38(1):51-93.
- [24] DU C,LIU Z,KAO S J,et al.Diapycnal fluxes of nutrients in an oligotrophic oceanic regime:the South China Sea[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2017,44(22):11510-11518.
- [25] CHEN Y L.Spatial and seasonal variations of nitrate-based new production and primary production in the South China Sea[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ:Oceano-graphic Research Papers,2005,52(2):319-340.
- [26] WONG G,TSENG C,WEN L,et al.Nutrient dynamics and N-anomaly at the SEATS station[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2007,54(14/15):1528-1545.
- [27] WU W,HUANG B,ZHONG C.Photosynthetic pico-eukaryote assemblages in the South China Sea from the Pearl River estuary to the SEATS station[J].Aquatic Microbial Ecology,2014,71(3):271-284.
- [28] WU W X,WANG L,LIAO Y,et al.Spatial and seasonal distributions of photosynthetic picoeukaryotes along an estuary to basin transect in the northern South China Sea[J].Journal of Plankton Research,2017,39(3):423-425.
- [29] XIU P,CHAI F,SHI L,et al.A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993—2007[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2010,115:C03012.
- [30] LEE I H,WANG Y H,YANG Y,et al.Temporal variability of internal tides in the northeast South China Sea[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2012,117:C02013.
- [31] WANG L,HUANG B,CHIANG K P,et al.Physical-biological coupling in the western South China Sea:the response of phytoplankton community to a mesoscale cyclonic eddy[J].PLoS One,2016,11(4):e0153735.
- [32] WU W,WANG L,LIAO Y,et al.Microbial eukaryotic diversity and distribution in a river plume and cyclonic eddy-influenced ecosystem in the South China Sea[J].Microbiologyopen,2015,4(5):826-840.
- [33] CHEN B Z,LIU H B,LANDRY M R,et al.Close coupling between phytoplankton growth and microzooplankton grazing in the western South China Sea[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2009,54(4):1084-1097.
- [34] GEIDER R J.Light and temperature-dependence of the carbon to chlorophyll-a ratio in microalgae and cyano-bacteria:implications for physiology and growth of phytoplankton[J].New Phytologist,1987,106(1):1-34.
- [35] GEIDER R J,MACINTYRE H L,KANA T M.Dynamic model of phytoplankton growth and acclimation:responses of the balanced growth rate and the chlorophyll a:carbon ratio to light,nutrient-limitation and temperature[J].Marine Ecology Progress Series,1997,148(1/2/3):187-200.