基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41721005,41720104005,41430967); 国家基金委-山东省联合基金项目(U1606404)
(厦门大学 海洋与地球学院,近海海洋环境科学国家重点实验室,福建 厦门 361102)
(State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science,College of Ocean and Earth Sciences,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361102,China)
ocean acidification; deoxygenation; ocean warming; UV radiation; marine organisms
备注
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41721005,41720104005,41430967); 国家基金委-山东省联合基金项目(U1606404)
海洋以每小时超过100万t的速率,从大气中吸收矿物燃料衍生及人类排放的CO2,引起海水pH下降,导致海洋酸化.与此同时,全球变暖引起海洋升温,使得上部混合层变浅,导致该层内营养盐减少,浮游生物接受可见光和UV的辐射量增加,并且使得O2的溶解度降低,引起低氧化.这些海洋变化问题在全球范围内普遍存在,然而,不同海域的环境响应和生态效应有所不同.主要综述全球海洋酸化问题研究进展,突出升温、UV辐射影响下的酸化效应,进而结合南海相关的研究进展分析未来研究动态.
The oceans are taking up over one million tons of fossil CO2,resulting in increased dissolved CO2 and declining pH,leading to ocean acidification.Meanwhile,global warming due to accumulated CO2 and other greenhouse gases is causing ocean warming,which enhances stratification with thinned upper mixed layers,exposing planktonic cells or individuals within this layer to increasing levels of daytime integrated visible light as well as UV radiation.Ocean warming also reduces dissolved oxygen in seawater,resulting in ocean deoxygenation.All these ocean global changes are supposed to influence marine ecosystems in different regions.However,regional responses and ecological effects are expected to differ based on the documented knowledges.This review overviews the research advances in ocean acidification,highlighting the combined effects of ocean acidification with warming and solar UV radiation,and analyzes future research perspectives and then proposes some scientific hypothesis.
引言
人类活动及矿物燃料的使用导致大气CO2浓度(以CO2分压(pCO2)表示)从工业革命(18世纪60年代)前的28 Pa升高至41 Pa(2016 年11月),增长了约46%,并仍以每年0.5%的速率继续增长[1],从而导致全球变暖,并引起海洋升温.同时,大量CO2溶入海水使pH下降,导致海洋酸化,扰动海水化学环境.另一方面,海洋升温使上部混合层变浅,导致该层内营养盐减少(由下向上的输送量减少),浮游生物接受UV辐射量增加(因为混合路径变短),且海水O2溶解度降低,引起全球海洋低氧化,并使缺氧区不断扩展.
迄今,有关海洋酸化的生物影响与生态效应研究多数基于单个种类、单种条件下的受控实验,而对生物群落和生态系统水平上的响应、多重环境震荡下酸化与升温的生理生态效应等方面研究极少[2].海洋全球变化直接或间接地影响生物代谢、生存及相关生态与生物地球化学过程,在不同海域产生不同的环境效应与生态效应,进而调控碳的汇源过程.因此,认知海洋酸化、升温与低氧化等多重环境影响下的生态系统过程变化并阐明相关机制非常重要,但目前仍存在技术与方法瓶颈[3].本文综述了海洋酸化、升温、UV辐射和低氧化及其叠加对生物的影响.
1 海洋酸化对生物的影响
自工业革命以来,随着大气pCO2的升高,海洋不断吸收人类排放的CO2,其吸收速率(平均)达每小时100万t以上[4],这对缓解全球变暖起着重要的作用,却使海水碱性下降而引起海洋酸化.目前海洋酸化速率是过去3亿年以来最快的[5].有关研究发现,距今2.52亿年前的海洋物种大灭绝与古海洋酸化事件相关[6].在浅海CO2喷口处,随着pH下降,生物量明显减少,生物多样性也降低[7].然而海洋酸化在多重环境压力下对不同物种、不同生态系统或过程的影响尚存在很大的不确定性[2],亟需研究其影响过程与机制以预测其影响趋势.
据预测,至21世纪末,海洋酸化将使上层海水平均pH下降0.4(H+浓度升高150%)[8],近海水域pH下降0.45[9],危及海洋生物及生态系统服务功能[10].已有研究表明,胶州湾表层海水pH[11]和南海表层pCO2[12]存在明显的季节变化,南海近海及珊瑚礁系统的海水pH昼夜变动明显[13-14],渤海夏季低氧区pH与同年6月相比下降0.29(H+浓度增加1倍)[15].在2012年召开的第419次香山会议上,海洋酸化问题得到充分讨论,其对我国海洋生物与水产资源的潜在危害得到广泛关注[16].
1.1 对典型生物过程的影响海洋酸化会减少珊瑚类的钙化及珊瑚礁系统的生物多样性[17],降低珊瑚礁系统的净钙含量[18]; 同时可降低造礁珊瑚藻类的钙化量[19-20]及贝类的钙化量与孵化率[21-22],使得太平洋牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas)的血细胞凋亡和活性氧(ROS)增加,消化腺中的谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平降低[23].此外,海洋酸化可导致虾类触须变短、生长缓慢[24],提高浮游动物的呼吸速率[25],并影响其捕食率与消化功能[26]; 同时会增加有害物种的繁殖[27],恶化病毒对藻类的攻击[28],影响鱼类的嗅觉、听觉与视觉系统[29-32].
1.2 对浮游植物的影响海洋光合生物同化将无机物合成有机物,发挥着重要的碳汇作用.在大洋海域58个站位2 000~4 000 m处的观测结果显示,以硅藻为主的浮游植物从真光层向深海的沉降速率为124~732 m/d[33].在南海不同水域,硅藻丰度决定浮游植物的丰度,是海洋生物碳泵的主要驱动者[34].海洋酸化可能降低硅藻的生物硅含量[35-36],进而影响浮游动物对硅藻的捕食率及粪粒量[37],因此海洋酸化可能通过影响硅藻的硅化作用而间接地影响颗粒有机碳的沉降量.在酸化条件下,南海表层硅藻丰度下降,单位水体或单位叶绿素的固碳量明显下降; 且不同深度的硅藻类因受光量不同对酸化的响应可能不同,在低光下促进生长,而在高光下抑制生长[38].对海链藻属(Thalassiosira)不同种类的研究表明,近海水域的威氏海链藻(T. weissflogii)与分布在大洋的大洋海链藻(T.oceanica)对酸化的响应完全不同:酸化可促进威氏海链藻的呼吸作用进而提高其同化速率,但对其生长没有影响; 而大洋海链藻的生长速率明显受到酸化的抑制[39].酸化还可使苯酚类毒性化合物在浮游植物细胞内和桡足类体内的含量升高,显示出潜在的食物链效应[40].
1.3 对异养细菌的影响海洋异养生物,主要是不能进行光合作用与化能合成作用的细菌类,其降解有机物过程中释放的CO2可增强海水酸化[9].有关酸化如何影响细菌异化作用的问题目前尚缺乏科学认识[41].夏威夷ALOHA站的细菌生产力滞后于初级生产力1~2个月,对升温有明显的响应,却不受短期海水酸化的影响[42].然而,另有研究显示海洋酸化可使细菌消耗额外的能量,上调与质子泵相关基因的表达,可能会影响微生物碳泵效率[43].在亚热带沿岸富营养化水域,细菌群落结构则不受酸化的影响[44].尽管如此,pH的变化会影响细菌、藻类等与病毒的关系,从而影响物质生产及其降解过程,相关的生物地球化学过程也会发生变化.
1.4 对病毒的影响早在20世纪30年代,研究者们就开始探讨病毒对pH变化的响应,发现有些病毒即使在pH<3时也不受影响,而另一些病毒在pH<7时则变得不稳定[45-47].关于海洋酸化对病毒直接影响的研究报道不多.在酸化对病毒与宿主相互作用的影响方面,感染聚球藻(Synechococcus)的病毒Cyanophage S-PM2的隐蔽期随着pH的降低而变长,而其潜伏期却正好相反,单位细胞裂解量也随pH的降低而下降[48].在真核藻类与病毒关系方面,当pH从8.1降到7.7时,病毒PgV可引起球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的光合作用下降,呼吸作用升高,单位细胞裂解量下降; 此外,酸化可使赫氏颗石藻(Emiliania huxleyi)受病毒EhV感染后的裂解时间延长[49].
总之,海洋酸化会直接或间接地引起有机物同化和异化过程的变化,影响颗粒有机碳(POC)和溶解有机碳(DOC)的产量,因此,会使得海洋吸收CO2及碳输送量发生变化[50].然而,该假设需要在不同海域放大实验规模进行研究,认识机制并获得较可靠的量化指标进行集成分析后方能验证.目前存在如下几方面的趋势:1)注重多种环境因子影响下的酸化效应; 2)注重海洋酸化的区域性影响; 3)注重不同尺度水平上的对比; 4)注重长期观测及生态系统过程的研究.
2 海洋升温对生物的影响及其与酸化的复合效应
自工业革命以来,大气中CO2的增加与全球平均升温呈线性相关[51].自20世纪70年代以来,海洋吸收了90%以上的地球热增量,导致全球变暖、海洋升温[8].海洋升温已经辐射到1 000 m深度[52].全球海洋表层平均温度在过去的100多年里升高了1 ℃左右[53]; 到21世纪末预计可增加2~4 ℃[8].过去20年间,厄尔尼诺事件发生明显变化,全球变暖1 ℃可导致台风事件增加高达25%[54].我国东海、南海边缘海域在过去50年间,与全球相比升温速度较快[55-56].
2.1 海洋升温对生物的影响温度是影响生物代谢的重要因子.由于各种酶的活性在一定范围内与温度变化密切相关,生物代谢速率通常会随着温度的上升而升高,在达到最高值后又快速下降.海洋生物在不同时空尺度上经受着温度的连续性(昼夜、季节)或突发性变化,涉及到温跃层、潮汐、台风事件,云或太阳辐射的日变动,以及自然气候循环和人类活动影响所导致的长期变化[51].海洋升温影响生物的适温范围[57]及生理行为[58]可引起多种生物生态位的变化、优势浮游生物种群的季节性变迁、浮游生物群落结构的变化以及全球生产力格局的变化[59-60].如潮间带的贝类,夏季在高温时段耐受其他环境胁迫的能力下降,体内能量水平下降,相关调节因子的表达升高,但不足以应对热胁迫,最终大量死亡[61-62].贝类中苹果酸脱氢酶在不同温度下的稳定性和柔性变化,与其适应生境温度变化能力有关,决定了不同种类对升温的生理学响应及其分布[63].
光合生物在不同海域对升温的响应不同,随着海洋的全球性变化,初级与次级生产力正在发生变化[64].尽管升温在实验室或局部水域可促进浮游植物的生长[65],但从全球规模来看,海洋升温会导致初级生产力下降,异养微生物的降解作用加强,海洋碳汇量下降[64].连续50年(1960—2009)的观测发现,大西洋东北部和北海的甲藻丰度因为海洋升温而降低[66].在一个中尺度生态系统实验中,高温和高光强的叠加明显加速了春季藻华的爆发,也导致优势种群的改变[67].然而,这些现象的内因不一定完全与温度变化直接相关,可能是多种因素的复合效应.阳光辐射增强、平流层臭氧浓度降低(UV-B辐射增高)往往与温度升高同时发生,而温度升高会导致上部混合层变浅及该层内营养盐浓度下降,因而导致浮游植物生物量下降,群落结构中优势种向粒径小的方向演化[64].
异养细菌在海洋碳循环中起着重要的作用[43,68].对东海2000—2001年与黄海春、秋季的研究发现,细菌丰度与生产力主要受温度与溶解有机物的调控[69].然而,近期研究发现细菌生产力在南海水域受磷的限制[70],其代谢需要额外能量以应对海洋酸化[43].一方面,海洋升温会与其他环境变化发生复合或叠加作用,影响细菌生产力; 另一方面,细菌的丰度又受病毒的调控.海洋升温会影响海洋病毒蛋白的结构、酶活性、膜酯等生物分子的弹性(如热变形、敏感性等)[71],而不同种类(甚至不同品系)的病毒,其生物分子组成和特性有所差异[72],温度变化对它们的影响程度也各不相同.在水温高于30 ℃时,多数噬菌体的量会下降[72].温度升高能增加环境中胞外酶(如蛋白酶和核酸酶)的活性,从而促进病毒的降解[73].
2.2 海洋酸化与升温对生物的复合效应海洋酸化及全球变暖与人类CO2排放有密切的关联,进而影响生物地球化学过程及生态系统.近海生态系统在人类活动及海洋全球变化影响下也许会发生演变,然而这些可能的宏观变化需要机制性的阐释,以期提升预测的可靠性.为此,需要在研究单因子影响的基础上探讨双因子或多因子的复合效应.多因子的复合效应有时可同时发生,有时是序列性发生,其复合、叠加或促进效应取决于环境胁迫前后或同时发生的时间与持续时间的长短[74].
处于表层或上部混合层内的浮游生物,无论是近海还是大洋海域,均经受着昼夜与季节性的温度变化.海洋升温会影响表层温度的变化幅度,进而引起上部混合层变浅,由下向上的营养盐输送减少等.因此,上层海洋中的生物面临酸化、升温、营养盐减少(临近人类居住地的沿海水域除外)以及暴露UV辐射量增加等多重环境的胁迫.这些环境变化的复合效应是未来海洋环境科学研究的热点之一.
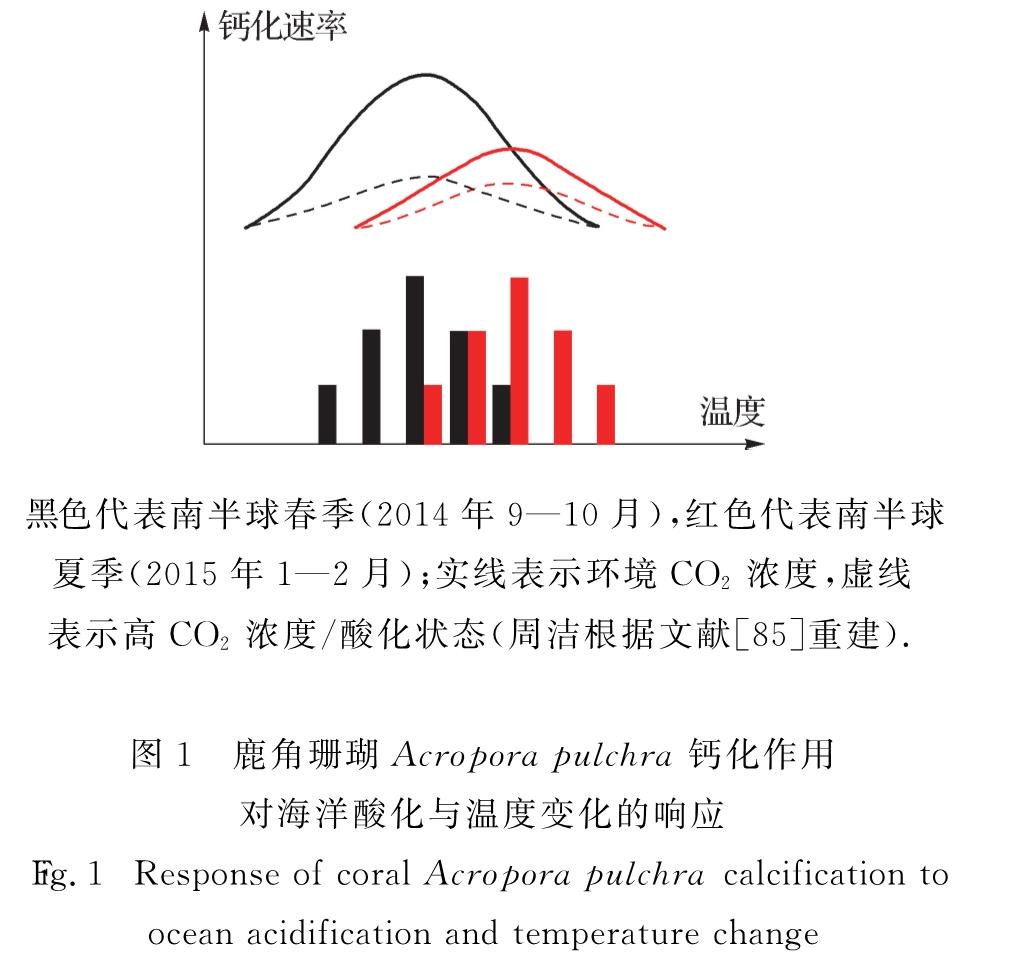
实验室研究显示酸化与升温对不同物种产生的生理生态效应不同.例如:对微微型浮游植物聚球藻和原绿球藻(Prochlorocoecus)的研究表明,升温与酸化协同促进了前者的生长,对后者却没有影响[75]; 酸化和升温4 ℃协同促进了硅藻类骨条藻(Skeletonema)的生长[76],却对海链藻、角毛藻(Chaetoceros)影响不明显[77]; 进行钙化作用的颗石藻类,在酸化与升温条件下生长速率下降[78]; 酸化和升温协同降低了赫氏颗石藻的最适生长温度与最大生长速率[79]; 在2~608 Pa pCO2范围内,升温可使赫氏颗石藻和大洋球石藻(Gephyrocapsa oceanica)颗粒无机碳(PIC)与POC的生产速率增加[80].就大型海藻而言,褐藻羊栖菜(Sargassum fusiforme)的呼吸系数在酸化条件下升高,暗示酸化和升温可协同提高呼吸速率[81].对造礁珊瑚藻类的研究发现,酸化导致其钙化量下降,升温则可进一步降低其钙质量[82].此外,酸化与升温可协同提高固氮蓝藻的固氮作用[83].在德国基尔海湾的研究发现,升温可导致浮游植物群落结构的变化,增加浮游动物的生物量; 而在原位水温条件下,浮游动物受酸化的负面影响,捕食率降低,导致浮游植物的生物量升高[84].总体而言,酸化和升温的复合效应主要体现在酸化会降低生物对温度变化的耐受能力.如鹿角珊瑚Acropora pulchra的钙化速率受到温度与酸化的双重调控[85](图1).木珊瑚科的Balanophyllia europaea 可在pH低至7.3的环境中维持较高的钙化作用,而在温度同时上升的情况下其钙化速率迅速下降[86].Reynaud等[87]在25 ℃考察柱状珊瑚(Stylophora pistillata)对pCO2升高的响应时未发现钙化率有明显下降,而在28 ℃时发现其下降了37%.可见升温与酸化效应可因生物种群、物理化学环境等不同存在区域性的差异,这种现象及其机制需要进一步探讨.
黑色代表南半球春季(2014年9—10月),红色代表南半球
夏季(2015年1—2月); 实线表示环境CO2浓度,虚线
表示高CO2浓度/酸化状态(周洁根据文献[85]重建).
未来海洋对CO2的吸收取决于生物介导的碳汇与碳源过程,即依赖于生物的同化与异化作用.研究推测,海洋升温会影响海洋生物碳泵(MBP)和微型生物碳泵(MCP)及两者的相互作用[88-89].近期研究发现,酸化并没有影响浮游生物生态系统中DOC的组成[90],而是促进了POC的生产[91].有关酸化与升温是否会产生复合效应,进而影响DOC的组成和POC的生产,尚需在不同海域进行研究.海洋中的大部分DOC会通过细菌的裂解在短期内被转换为CO2,然而有部分DOC可抗细菌的裂解而长期(数百至数千年)存在,发挥着较稳定的碳汇作用[92].海洋酸化与升温对MBP和MCP的影响尚存在很大不确定性[8,88].因此,认识海洋生物的碳汇源过程以及同化与异化作用对酸化与升温的响应尤其重要.然而,迄今升温与酸化复合效应的研究结果多数是在单一条件或在实验室受控条件下获得,复合影响及其机制尚不清楚.3 UV辐射对生物的影响及其与酸化的复合效应
阳光UV(280~400 nm)辐射对生物的影响可为正面、负面或正负相抵,表现出中性,这与辐射量、物种及其他环境状况有关.在亚热带地区,到达地面的UV-B(280~315 nm)辐射通常占阳光总能量的1%以下,UV-A(315~400 nm)与可见光(PAR,400~700 nm)分别占其7%~8%和40%~50%,红外辐射能量约占其50%; 中午时段UV-B:UV-A:PAR约为0.5:16:100.UV-B受臭氧浓度变化的影响,而UV-A、PAR不受其影响; UV-B与PAR的比例与天顶角变化有关,早晚低,中午高,而UV-A与PAR的比例不受该影响,一天内持平.大气中的气溶胶及水中的有机物质均可消减这3种波段的阳光辐射.研究表明,平流层臭氧浓度每降低1%,到达地面的UV-B辐射量会提高2%[93].由于《蒙特利尔公约》的履行,臭氧破坏得到了遏制,平流层的臭氧在21世纪中期有望回到1980年以前的水平[94].然而其他因素的作用,如由全球气候变化引起的温度变化、痕量气体的存在与否[95]、大气环流模式的变化,都可能导致低纬地区的UV-B水平提高2%~3%[96].
在中国南海外海海域,PAR透射深度(真光层深度)超过80 m,UV-A和UV-B透射深度分别为50和38 m,可到达真光层深度的62%和47%.在汕头近岸海域,有些地方可见光透射深度仅为6~8 m; UV-A、UV-B透射深度分别为3.0~3.5 m和1.7~2.3 m,占真光层深度的50%和30%[97-98].在大洋海域,UV辐射可到达深度超过80 m[99].分布在上部混合层的浮游生物,通常均会暴露于阳光UV辐射下.然而无论是全球海洋通量联合研究(JGOFS)还是我国海洋调查规范,只要求在测定初级生产力等参数时采用透明容器,而普通玻璃或聚碳酸酯透明材料不透或仅透过少量UV-A辐射,因此迄今的多数调查研究忽略了UV辐射的效应.UV辐射对浮游植物固碳量的影响取决于水深和阳光辐射强度的高低,低或中水平的UV-A辐射可促进藻类固碳[97,100].UV辐射也是调控桡足类垂直分布的主要因子,并影响其水平分布[101].
UV辐射影响水域中的光化学与光生物学过程,其作用不容忽视[102].然而,室内实验或多数甲板培养实验忽视了阳光UV辐射的作用(非石英材质容器无法透过UV-B辐射),海洋酸化生理生态效应能否反映酸化的原位影响还有待于探讨[38].UV-A在低强度(阴天或较深层)时促进浮游植物的光合固碳,在高强度(晴天中午)时抑制其光合作用,而UV-B则始终导致损伤[97]; UV辐射还可改变某些蓝藻的形态[103-104],损伤其DNA[104],并抑制钙化藻类的钙化作用[20,105].酸化与UV辐射叠加,进一步降低了钙化藻类的钙化作用[20,105-106].由于UV的透射深度可达80 m(南海外海水域可达50~60 m),PAR和UV的比例在不同深度明显不同,所以海洋酸化与阳光辐射对初级、次级生产过程的复合效应在不同深度会存在明显差异.
热带水域的浮游动物、亚热带水域的鱼类等均受到UV辐射的伤害,而其受影响程度与其他环境状态有关[102].在近岸海域,端足类通过摄食定生藻类获得UV屏障物质.尽管鱼类等游动性动物可以逃避UV辐射,然而其生殖细胞(卵、精子)及幼体仍受到UV辐射的影响.目前这方面的研究报道很少,有关酸化与UV辐射叠加影响的研究更少.
4 海洋低氧化对生物的影响及其与酸化的复合效应
海洋低氧化是指海水中溶解O2浓度(以O2分压(pO2)表示)下降的现象.该环境问题是由于升温引起的海水O2溶解度降低,上层海洋层化加重导致的表层向深层O2输送量减少,以及富营养化与生物耗氧量的增加等诸多环境变化叠加所致.无论是在大洋海域还是近海水域,pO2在过去50年均明显下降[107].
海洋中O2的消耗主要由呼吸作用与细菌对有机碳的降解所致.MBP将POC向深海输送的过程中消耗了O2,增加了CO2和营养盐.因此,海水pCO2的不断增加(海洋酸化)与微生物耗O2的叠加会在500~700 m深处形成生物死亡区[108](图2).过去50年间,在太平洋海域,缺氧(溶解O2质量浓度小于2 mg/L)深度从400 m减少到300 m,pO2明显下降[109],这与气候变化有密切关系[110].
黑色表示实际观测值,红色表示大气pCO2加倍
情况下的估测值(根据文献[108]重建).
海洋生物与其他生物一样,代谢过程需要O2; 当溶解O2低于一定浓度后,低氧胁迫会导致其死亡.不同生物的半致死溶解O2质量浓度不同,可相差几倍或十几倍,较典型的缺氧区溶解O2质量浓度在2 mg/L以下.通常缺氧现象与温度和pCO2有关(低氧区往往pCO2较高而pH较低),如温跃层下溶氧量少、pH低.近岸海域由于海洋低氧化与富营养化相互作用,缺氧区正以每年约5.5%的速率增加[111]; 且与海洋酸化叠加后导致酸化的速率比大洋海域快[9].另外,低氧化会促进反硝化作用,减少硝酸根离子的量,影响海洋的氮循环、初级生产力及MBP效率.然而海洋低氧化如何影响各种生物(尤其是光合生物)的代谢及关键生态过程,目前科学界认识甚微.图2 海水pCO2(a)与pO2(b)随深度变化的趋势
Fig.2 The relationship of seawater pCO2(a)and pO2(b) with water depths伴随着海洋酸化、升温等,海水pO2和pCO2的比值越来越小,且在深层海水中变化得更快[108]; 其次,物理混合过程引起深层海水向表层输送,也影响了真光层内pO2和pCO2的比值; 再者,上升流区的物理与化学环境受大气pCO2升高及相关气候变化的影响也在不断发生变化,如在加州海岸上升流区,pO2和pCO2的比值不断下降,对当地的贝类养殖造成重大经济损失,浮游动物的现存量也在不断减少[112].显然,这些生态与经济效应,除了与pH变化有关外,还与海水pO2和pCO2的比值变化相关.
海洋低氧化与酸化均会影响POC与PIC的生产量,也会影响浮游动物及底栖生物的生理活性.理论上看,pO2降低或pCO2与pO2比值增大均有利于光合固碳酶的羧化作用,并下调该酶催化的氧化作用,因此,pCO2与pO2比值的变化会影响藻类的光合作用[113].低氧、酸化或pO2与pCO2比值的降低会对光合固碳、呼吸、光呼吸、生长及钙化作用产生复合影响.此外,浮游动物响应酸化胁迫,增加其呼吸作用的同时增加了其摄食率[25].因为海洋低氧化也会影响动物的呼吸作用,所以低氧与酸化必然产生复合效应,影响生物的呼吸作用及其能量供给平衡.
5 展 望
海洋酸化与全球变暖是由人类碳排放引起的,同时也是当今社会面临的两个重大环境问题,威胁海洋生态系统.为此,对其生态学效应的研究已经在全球广泛开展.酸化对POC生产的影响尚有争议,不同区域研究展现的生态效应不同.有报道酸化对异养细菌没有影响,也有报道其影响它们的代谢及基因表达; 关于升温与酸化的复合效应,有报道叠加的,有报道没有复合效应的,也有报道有拮抗作用的.这些争议性较大的研究结果大都基于实验室受控条件下的实验,难以反映自然环境震荡下升温与酸化的影响,不能阐明多重环境变化的复合效应[3].
生态系统中生物生产与异化作用,受酸化与升温的复合效应,可能是叠加、增效或拮抗,与自养和异养生物代谢、群落结构及多重环境压力有关.东海航次观测与甲板实验显示,浮游植物释放的二甲基硫量与叶绿素浓度呈现正相关,其降解在UV-B辐射和低pH影响下加快[114].显然,海洋初级、次级生产过程、生物的异化作用及有机物的光降解等受多种环境因子的影响,如何在震荡或接近原位复杂环境条件下开展升温与酸化效应的研究,目前面临技术上的挑战.
海洋酸化中尺度生态系统实验类似于海洋中的围隔实验,可在原位环境震荡或变化条件下研究酸化的生态效应.这类中尺度水平的实验在德国、挪威、比利时、美国(借用德国的设施)、中国(厦门大学等)、秘鲁(借用德国的设施)、韩国、西班牙等国家均有开展.德国、挪威及比利时等国家的科学家使用27 t海水的中尺度实验设施,发现pCO2升高增加了浮游植物的固碳量,使其有机碳氮质量比增加了30%以上,降低了其饵料价值[115]; 另有研究使用50 t海水的中尺度实验设施,发现酸化没有影响浮游生物生态系统中的溶解无机碳组分[90].韩国学者使用2 t海水的中尺度实验设施,发现pCO2升高仅促进了中肋骨条藻(S.costatum)的生长,而对其他浮游植物类群影响不明显[116].我国科学家使用4 t海水的中尺度实验设施,发现pCO2升高可使浮游植物细胞内苯酚类毒性物质含量升高,且使捕食这些浮游植物的桡足类体内苯酚类含量也升高[40]; 此外,初级生产力与细菌生长效率也明显升高[117].然而,升温效应的中尺度实验因水量大、温控难度高,基本没有开展(有用电热棒加热的,但加热棒局部温度很高,不理想).总之,中尺度生态系统实验由于用水量大,升温与酸化控制技术难度大,运行成本高,至今在全球开展的次数有限,有待于在不同地区进一步开展.
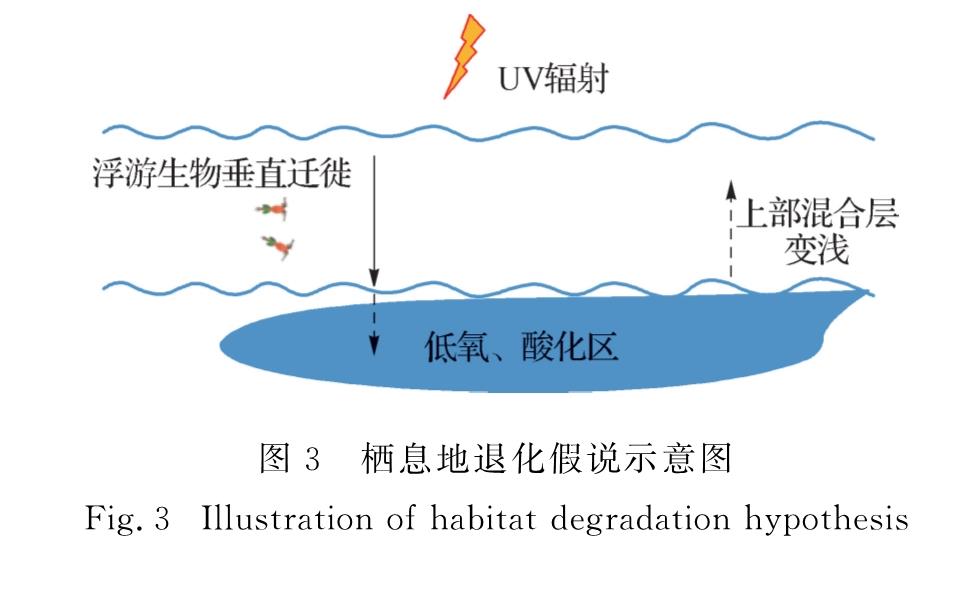
在海洋酸化、升温、低氧化及UV辐射等多重环境胁迫下,生物的栖息地或水域正在退化或缩小.根据已有的科学认知可以建立如下科学假设,即栖息地或可栖息水域退化假说(图3):可垂直游动的生物为躲避较高水温或UV辐射向下移动,然而温跃层以下低氧和酸化的海水又会对其增添新的环境胁迫,其结果导致这类生物可栖息的水域缩小或栖息地退化.这可能是导致近年来典型渔场捕鱼量下降的主要原因.这一假说还需要在开展受控实验的同时结合原位调查数据进行验证.
- [1] NOAA.Global warming update 2016[EB/OL].[2018-07-07].https:∥www.co2.earth/.
- [2] RIEBESELL U,GATTUSO J P.Lessons learned from ocean acidification research[J].Nature Climate Change,2015,5(1):12-14.
- [3] BOYD P W,COLLINS S,DUPONT S,et al.Experimental strategies to assess the biological ramifications of multiple drivers of global ocean change:a review[J].Global Change Biology,2018,24(6):2239-2261.
- [4] SABINE C L,FEELY R A,GRUBER N,et al.The oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2[J].Science,2004,305(5682):367-371.
- [5] HÖNISCH B,RIDGWELL A,SCHMIDT D N,et al.The geological record of ocean acidification[J].Science,2012,335(6072):1058-1063.
- [6] GARBELLI C,ANGIOLINI L,SHEN S Z.Biomineralization and global change:a new perspective for understanding the end-Permian extinction[J].Geology,2017,45(1):19-22.
- [7] FABRICIUS K E,LANGDON C,UTHICKE S,et al.Losers and winners in coral reefs acclimatized to elevated carbon dioxide concentrations[J].Nature Climate Change,2011,1(3):165.
- [8] GATTUSO J P,MAGNAN A,BILL R,et al.Contrasting futures for ocean and society from different anthropogenic CO2 emissions scenarios[J].Science,2015,349(6243):aac4722.
- [9] CAI W J,HU X,HUANG W J,et al.Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication[J].Nature Geoscience,2011,4(11):766-770.
- [10] IGBP IOC SCOR.Ocean acidification summary for policymakers:third symposium on the ocean in a high-CO2 world [C/OL].[2018-07-07].Stockholm:IGBP,2013.http:∥www.igbp.net/publications/summariesfo-rpolicymakers/summariesforpolicymakers/oceanacidifica-tionsummaryforpolicymakers2013.5.30566fc6142425d6c
- [11] 邓雪,胡玉斌,刘春颖,等.胶州湾表层海水碳酸盐体系的季节变化[J].海洋与湖沼,2016,47(1):234-244.
- [12] CHAI F,LIU G,XUE H,et al.Seasonal and interannual variability of carbon cycle in South China Sea:a three-dimensional physical-biogeochemical modeling study[J].Journal of Oceanography,2009,65(5):703-720.
- [13] DAI M,LU Z,ZHAI W,et al.Diurnal variations of surface seawater pCO2 in contrasting coastal environments[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2009,54(3):735-745.
- [14] WANG G,JING W,WANG S,et al.Coastal acidification induced by tidal-driven submarine groundwater discharge in a coastal coral reef system[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(22):13069-13075.
- [15] ZHAI W D,ZHAO H,ZHENG N,et al.Coastal acidification in summer bottom oxygen-depleted waters in northwestern-northern Bohai Sea from June to August in 2011[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2012,57(9):1062-1068.
- [16] 唐启升,陈镇东,余克服,等.海洋酸化及其与海洋生物及生态系统的关系[J].科学通报,2013,58(14):1307-1314.
- [17] SUNDAY J M,FABRICIUS K E,KROEKER K J,et al.Ocean acidification can mediate biodiversity shifts by changing biogenic habitat[J].Nature Climate Change,2017,7(1):81.
- [18] ALBRIGHT R,TAKESHITA Y,KOWEEK D A,et al.Carbon dioxide addition to coral reef waters suppresses net community calcification[J].Nature,2018,555(7697):516-519.
- [19] GAO K,ARUGA Y,ASADA K,et al.Calcification in the articulated coralline alga Corallina pilulifera,with special reference to the effect of elevated CO2 concentration[J].Marine Biology,1993,117(1):129-132.
- [20] GAO K,ZHENG Y.Combined effects of ocean acidification and solar UV radiation on photosynthesis,growth,pigmentation and calcification of the coralline alga Corallina sessilis(Rhodophyta)[J].Global Change Biology,2009,16(8):2388-2398.
- [21] 张明亮,邹健,方建光,等.海洋酸化对栉孔扇贝钙化,呼吸以及能量代谢的影响[J].渔业科学进展,2011,32(4):48-54.
- [22] GAZEAU F,PARKER L M,COMEAU S,et al.Impacts of ocean acidification on marine shelled molluscs[J].Marine Biology,2013,160(8):2207-2245.
- [23] WANG Q,CAO R,NING X,et al.Effects of ocean acidification on immune responses of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2016,49:24-33.
- [24] KURIHARA H,MATSUI M,FURUKAWA H,et al.Long-term effects of predicted future seawater CO2 conditions on the survival and growth of the marine shrimp Palaemon pacificus[J].Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology,2008,367(1):41-46.
- [25] LI W,GAO K.A marine secondary producer respires and feeds more in a high CO2 ocean[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2012,64(4):699-703.
- [26] STUMPP M,HU M,CASTIES I,et al.Digestion in sea urchin larvae impaired under ocean acidification[J].Nature Climate Change,2013,3(12):1044-1049.
- [27] HALL-SPENCER J M,ALLEN R.The impact of CO2 emissions on "nuisance" marine species[J].Research and Reports in Biodiversity Studies,2015,4:33-46.
- [28] CHEN S,GAO K,BEARDALL J.Viral attack exacerbates the susceptibility of a bloom-forming alga to ocean acidification[J].Global Change Biology,2015,21(2):629-636.
- [29] MUNDAY P L,DIXSON D L,DONELSON J M,et al.Ocean acidification impairs olfactory discrimination and homing ability of a marine fish[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2009,106(6):1848-1852.
- [30] NILSSON G E,DIXSON D L,DOMENICI P,et al.Near-future carbon dioxide levels alter fish behaviour by interfering with neurotransmitter function[J].Nature Climate Change,2012,2(3):201-204.
- [31] DIXSON D L,JENNINGS A R,ATEMA J,et al.Odor tracking in sharks is reduced under future ocean acidification conditions[J].Global Change Biology,2015,21(4):1454-1462.
- [32] 王晓杰,宋佳坤,范纯新,等.海洋酸化对鱼类感觉和行为影响的研究进展[J].生态毒理学报,2015,10(6):13-20.
- [33] AGUSTI S,GONZLEZ-GORDILLO J I,VAQU D,et al.Ubiquitous healthy diatoms in the deep sea confirm deep carbon injection by the biological pump[J].Nature Communications,2015,6:7608.
- [34] 薛冰,孙军,李婷婷.2014 年夏季南海北部浮游植物群落结构[J].海洋学报,2016,38(4):54-65.
- [35] MILLIGAN A J,VARELA D E,BRZEZINSKI M A,et al.Dynamics of silicon metabolism and silicon isotopic discrimination in a marine diatomas a function of pCO2[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2004,49(2):322-329.
- [36] XU K,FU F X,HUTCHINS D A.Comparative responses of two dominant Antarctic phytoplankton taxa to interactions between ocean acidification,warming,irradiance,and iron availability[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2014,59(6):1919-1931.
- [37] LIU H,CHEN M,ZHU F,et al.Effect of diatom silica content on copepod grazing,growth and reproduction[J].Frontiers in Marine Science,2016,3:89.
- [38] GAO K,XU J,GAO G,et al.Rising CO2 and increased light exposure synergistically reduce marine primary productivity[J].Nature Climate Change,2012,2(7):519-523.
- [39] LI F,WU Y,HUTCHINS D A,et al.Physiological responses of coastal and oceanic diatoms to diurnal fluctuations in seawater carbonate chemistry under two CO2 concentrations[J].Biogeosciences,2016,13(22):6247.
- [40] JIN P,WANG T,LIU N,et al.Ocean acidification increases the accumulation of toxic phenolic compounds across trophic levels[J].Nature Communications,2015,6:8714.
- [41] WANG Y,ZHANG R,ZHENG Q,et al.Bacterioplankton community resilience to ocean acidification:evidence from microbial network analysis[J].ICES Journal of Marine Science,2015,73(3):865-875.
- [42] VIVIANI D A.Variability and controls of production,partitioning,and utilization of organic matter in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre [D].Manoa:University of Hawaii,2016.
- [43] BUNSE C,LUNDIN D,KARLSSON C M,et al.Response of marine bacterioplankton pH homeostasis gene expression to elevated CO2[J].Nature Climate Change,2016,6(5):483-487.
- [44] LIN X,HUANG R,LI Y,et al.Interactive network configuration maintains bacterioplankton community structure under elevated CO2 in a eutrophic coastal mesocosm experiment[J].Biogeosciences,2018,15(2):551-565.
- [45] KRUEGER A P,FONG J.The relationship between bacterial growth and phage production[J].The Journal of General Physiology,1937,21(2):137-150.
- [46] WEIL M,BEARD D,BEARD J.pH stability,response to antibiotics and factors influencing egg-culture of mumps virus[J].Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine,1948,68(2):308-309.
- [47] JIN S,ZHANG B,WEISZ O A,et al.Receptor-mediated entry by equine infectious anemia virus utilizes a pH-dependent endocytic pathway[J].Journal of Virology,2005,79(23):14489-14497.
- [48] TRAVING S J,CLOKIE M R,MIDDELBOE M.Increased acidification has a profound effect on the interactions between the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp.WH7803 and its viruses[J].FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2014,87(1):133-141.
- [49] CARREIRA C,HELDAL M,BRATBAK G.Effect of increased pCO2 on phytoplankton-virus interactions[J].Biogeochemistry,2013,114(1/2/3):391-397.
- [50] FLYNN K J,CLARK D R,MITRA A,et al.Ocean acidification with(de)eutrophication will alter future phytoplankton growth and succession[J].Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B:Biological Sciences,2015,282(1804):20142604.
- [51] IPCC.Climate change 2013:the physical science basis[M].Cambridge and New York:Cambridge University Press,2013:6-10.
- [52] LEVITUS S,ANTONOV J I,BOYER T P,et al.Warming of the world ocean[J].Science,2000,287(5461):2225-2229.
- [53] FISCHETTI M.Deep heat threatens marine life[J].Scientific American,2013,308(4):92.
- [54] BIGG G,HANNA E.Impacts and effects of ocean warming on the weather [C]∥Explaining Ocean Warming:Causes,Scale,Effects and Consequences.Gland:IUCN,2016:359-372.
- [55] BAO B,REN G.Climatological characteristics and long-term change of SST over the marginal seas of China[J].Continental Shelf Research,2014,77:96-106.
- [56] WILLIAMS G A,HELMUTH B,RUSSELL B D,et al.Meeting the climate change challenge:pressing issues in southern China and SE Asian coastal ecosystems[J].Regional Studies in Marine Science,2016,8:373-381.
- [57] PÖRTNER H O.Ecosystem effects of ocean acidification in times of ocean warming:a physiologist's view[J].Marine Ecology Progress Series,2008,373:203-218.
- [58] SINCLAIR B J,MARSHALL K E,SEWELL M A,et al.Can we predict ectotherm responses to climate change using thermal performance curves and body temperatures?[J].Ecology Letters,2016,19(11):1372-1385.
- [59] NIXON S W,FULWEILER R W,BUCKLEY B A,et al.The impact of changing climate on phenology,productivity,and benthic-pelagic coupling in Narragansett Bay[J].Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2009,82(1):1-18.
- [60] EDWARDS K F,THOMAS M K,KLAUSMEIER C A,et al.Phytoplankton growth and the interaction of light and temperature:a synthesis at the species and community level[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2016,61(4):1232-1244.
- [61] HAN G D,ZHANG S,MARSHALL D J,et al.Metabolic energy sensors(AMPK and SIRT1),protein carbonylation and cardiac failure as biomarkers of thermal stress in an intertidal limpet:linking energetic allocation with environmental temperature during aerial emersion[J].Journal of Experimental Biology,2013,216(17):3273-3282.
- [62] DONG Y W,ZHANG S.Ecological relevance of energy metabolism:transcriptional responses in energy sensing and expenditure to thermal and osmotic stresses in an intertidal limpet[J].Functional Ecology,2016,30(9):1539-1548.
- [63] DONG Y W,LIAO M L,MENG X L,et al.Structural flexibility and protein adaptation to temperature:molecular dynamics analysis of malate dehydrogenases of marine molluscs[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2018:201718910.
- [64] DANOVARO R,CORINALDESI C,RASTELLI E,et al.Impacts and effects of ocean warming on microorganisms[C]∥Explaining Ocean Warming:Causes,Scale,Effects and Consequences.Gland:IUCN,2016:57-74.
- [65] SUMMERS J C,KUREK J,KIRK J L,et al.Recent warming,rather than industrial emissions of bioavailable nutrients,is the dominant driver of lake primary production shifts across the Athabasca oil sands region[J].PLoS One,2016,11(5):e0153987.
- [66] HINDER S L,HAYS G C,EDWARDS M,et al.Changes in marine dinoflagellate and diatom abundance under climate change[J].Nature Climate Change,2012,2(4):271-275.
- [67] LEWANDOWSKA A,SOMMER U.Climate change and the spring bloom:a mesocosm study on the influence of light and temperature on phytoplankton and mesozooplankton[J].Marine Ecology Progress Series,2010,405:101-111.
- [68] 张武昌,赵丽,陈雪,等.海洋浮游细菌生长率和被摄食的研究综述[J].海洋科学,2016,40(5):151.
- [69] ZHAO S,XIAO T,LU R,et al.Spatial variability in biomass and production of heterotrophic bacteria in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2010,57(11/12):1071-1078.
- [70] YUAN X,ZHOU W,HUANG H,et al.Bacterial influence on chromophoric dissolved organic matter in coastal waters of the northern South China Sea[J].Aquatic Microbial Ecology,2016,76(3):207-217.
- [71] BRUM J R,HURWITZ B L,SCHOFIELD O,et al.Seasonal time bombs:dominant temperate viruses affect Southern Ocean microbial dynamics[J].The ISME Journal,2016,10(2):437-449.
- [72] MOJICA K D,BRUSSAARD C P.Factors affecting virus dynamics and microbial host-virus interactions in marine environments[J].FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2014,89(3):495-515.
- [73] DELL'ANNO A,CORINALDESI C,DANOVARO R.Virus decomposition provides an important contribution to benthic deep-sea ecosystem functioning[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2015,112(16):E2014-E2019.
- [74] GUNDERSON A R,ARMSTRONG E J,STILLMAN J H.Multiple stressors in a changing world:the need for an improved perspective on physiological responses to the dynamic marine environment[J].Annual Review of Marine Science,2016,8(1):357-378.
- [75] FU F X,WARNER M E,ZHANG Y,et al.Effects of Increased temperature and CO2 on photosynthesis,growth,and elemental ratios in marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus(Cyanobacteria)1[J].Journal of Phycology,2007,43(3):485-496.
- [76] KREMP A,GODHE A,EGARDT J,et al.Intraspecific variability in the response of bloom-forming marine microalgae to changed climate conditions[J].Ecology and Evolution,2012,2(6):1195-1207.
- [77] HYUN B,CHOI K H,JANG P G,et al.Effects of increased CO2 and temperature on the growth of four diatom species(Chaetoceros debilis,Chaetoceros didymus,Skeletonema costatum and Thalassiosira nordenskioeldii)in laboratory experiments[J].J Environ Sci Int,2014,23(6):1003-1012.
- [78] SCHLÜTER L,LOHBECK K T,GUTOWSKA M A,et al.Adaptation of a globally important coccolithophore to ocean warming and acidification[J].Nature Climate Change,2014,4(11):1024-1030.
- [79] LISTMANN L,LEROCH M,SCHLÜTER L,et al.Swift thermal reaction norm evolution in a key marine phytoplankton species[J].Evolutionary Applications,2016,9(9):1156-1164.
- [80] SETT S,BACH L T,SCHULZ K G,et al.Temperature modulates coccolithophorid sensitivity of growth,photosynthesis and calcification to increasing seawater pCO2[J].PLoS One,2014,9(2):e88308.
- [81] ZOU D,GAO K,LUO H.Short- and long-term effects of elevated CO2 on photosynthesis and respiration in the marine macroalga Hizikia fusiformis(Sargassaceae,Phaeophyta)grown at low and high N supplies[J].Journal of Phycology,2011,47(1):87-97.
- [82] MARTIN S,HALL-SPENCER J M.Effects of ocean war-ming and acidification on Rhodolith/Maërl beds[M]∥RIOSMENA-RODRÍGUEZ R,NELSON W,AGUIRRE J.Rhodolith/Maërl beds:a global perspective.Berlin:Springer,2017:55-85.
- [83] HUTCHINS D,FU F X,ZHANG Y,et al.CO2 control of Trichodesmium N2 fixation,photosynthesis,growth rates,and elemental ratios:implications for past,present,and future ocean biogeochemistry[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2007,52(4):1293-1304.
- [84] PAUL C,SOMMER U,GARZKE J,et al.Effects of increased CO2 concentration on nutrient limited coastal summer plankton depend on temperature[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2016,61(3):853-868.
- [85] COMEAU S,CARPENTER R,LANTZ C,et al.Para-meterization of the response of calcification to temperature and pCO2 in the coral Acropora pulchra and the alga Lithophyllum kotschyanum[J].Coral Reefs,2016,35(3):929-939.
- [86] RODOLFO-METALPA R,HOULBRÈQUE F,TAMBU-TTÉ É,et al.Coral and mollusc resistance to ocean acidification adversely affected by warming[J].Nature Climate Change,2011,1(6):308-312.
- [87] REYNAUD S,LECLERCQ N,ROMAINE-LIOUD S,et al.Interacting effects of CO2 partial pressure and temperature on photosynthesis and calcification in a scleractinian coral[J].Global Change Biology,2003,9(11):1660-1668.
- [88] JIAO N,ZHENG Q.The microbial carbon pump:from genes to ecosystems[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2011,77(21):7439-7444.
- [89] 孙军,李晓倩,陈建芳,等.海洋生物泵研究进展[J].海洋学报,2016,38(4):1-21.
- [90] ZARK M,RIEBESELL U,DITTMAR T.Effects of ocean acidification on marine dissolved organic matter are not detectable over the succession of phytoplankton blooms[J].Science Advances,2015,1(9):e1500531.
- [91] CZERNY J,SCHULZ K G,BOXHAMMER T,et al.Implications of elevated CO2 on pelagic carbon fluxes in an Arctic mesocosm study:an elemental mass balance approach[J].Biogeosciences,2013,10(5):3109-3125.
- [92] JIAO N,HERNDL G J,HANSELL D A,et al.Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter:long-term carbon storage in the global ocean[J].Nature Reviews Microbiology,2010,8(8):593-599.
- [93] KERR J,MCELROY C.Evidence for large upward trends of ultraviolet-B radiation linked to ozone depletion[J].Science,1993,262(5136):1032-1034.
- [94] PLUMMER D,SCINOCCA J,SHEPHERD T,et al.Quantifying the contributions to stratospheric ozone changes from ozone depleting substances and greenhouse gases[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2010,10(18):8803-8820.
- [95] OSS A,SOLA Y,BECH J,et al.Evidence for the influence of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the total ozone column at northern low latitudes and midlatitudes during winter and summer seasons[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2011,116(D24):D24122.
- [96] WILLIAMSON C E,ZEPP R G,LUCAS R M,et al.Solar ultraviolet radiation in a changing climate[J].Nature Climate Change,2014,4(6):434-441.
- [97] GAO K,WU Y,LI G,et al.Solar UV radiation drives CO2 fixation in marine phytoplankton:a double-edged sword[J].Plant Physiology,2007,144(1):54-59.
- [98] LI G,GAO K.Variation in UV irradiance related to stratospheric ozone levels affects photosynthetic carbon fixation of winter phytoplankton assemblages from surface coastal water of the South China Sea[J].Marine Biology Research,2012,8(7):670-676.
- [99] TEDETTI M,SEMPR R,VASILKOV A,et al.High penetration of ultraviolet radiation in the south east Pacific waters[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(12):L12610.
- [100] XU J,GAO K.Use of UV-A energy for photosynthesis in the red macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis[J].Photochemistry and Photobiology,2010,86(3):580-585.
- [101] MA Z,LI W,SHEN A,et al.Behavioral responses of zooplankton to solar radiation changes:in situ evidence[J].Hydrobiologia,2013,711(1):155-163.
- [102] BAIS A F,LUCAS R M,BORNMAN J F,et al.Environmental effects of ozone depletion,UV radiation and interactions with climate change:UNEP environ-mental effects assessment panel,update 2017[J].Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences,2018,17(2):127-179.
- [103] WU H,GAO K,VILLAFAÑE V E,et al.Effects of solar UV radiation on morphology and photosynthesis of filamentous cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(9):5004-5013.
- [104] GAO K,LI P,WATANABE T,et al.Combined effects of ultraviolet radiation and temperature on morphology,photosynthesis,and DNA of Arthrospira(Spirulina)platensis(Cyanophyta)[J].Journal of Phycology,2008,44(3):777-786.
- [105] GAO K,RUAN Z,VILLAFANE V E,et al.Ocean acidification exacerbates the effect of UV radiation on the calcifying phytoplankter Emiliania huxleyi[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2009,54(6):1855-1862.
- [106] XU K,GAO K.Solar UV irradiances modulate effects of ocean acidification on the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi[J].Photochemistry and Photobiology,2015,91(1):92-101.
- [107] BREITBURG D,LEVIN L A,OSCHLIES A,et al.Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters[J].Science,2018,359(6371):eaam7240.
- [108] BREWER P G,PELTZER E T.Limits to marine life[J].Science,2009,324(5925):347-348.
- [109] WHITNEY F A,FREELAND H J,ROBERT M.Persistently declining oxygen levels in the interior waters of the eastern subarctic Pacific[J].Progress in Oceanography,2007,75(2):179-199.
- [110] KEELING R F,KÖRTZINGER A,GRUBER N.Ocean deoxygenation in a warming world[J].Annual Review of Marine Science,2010,2(1):199-229.
- [111] VAQUER-SUNYER R,DUARTE C M.Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2008,105(40):15452-15457.
- [112] DONEY S C,RUCKELSHAUS M,DUFFY J E,et al.Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems[J].Annual Review of Marine Science,2012,4(1):11-37.
- [113] GAO K,CAMPBELL D A.Photophysiological responses of marine diatoms to elevated CO2 and decreased pH:a review[J].Functional Plant Biology,2014,41(5):449-459.
- [114] JIAN S,ZHANG H H,ZHANG J,et al.Spatiotem-poral distribution characteristics and environmental control factors of biogenic dimethylated sulfur compounds in the East China Sea during spring and autumn[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2017,63(S1):S280-S298.
- [115] RIEBESELL U,SCHULZ K G,BELLERBY R,et al.Enhanced biological carbon consumption in a high CO2 ocean[J].Nature,2007,450(7169):545-548.
- [116] KIM J M,LEE K,SHIN K,et al.The effect of seawater CO2 concentration on growth of a natural phytoplankton assemblage in a controlled mesocosm experiment[J].Limnology and Oceanography,2006,51(4):1629-1636.
- [117] HUANG Y,LIU X,LAWS E A,et al.Effects of increa-sing atmospheric CO2 on the marine phytoplankton and bacterial metabolism during a bloom:a coastal mesocosm study[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,633:618-629.