(厦门大学附属第一医院心血管内科,福建 厦门 361003)
巨噬细胞; 急性心肌梗死; microRNA-155; 炎症因子; 心室重构
(Department of Cardiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University,Xiamen 361003,China)
macrophage; acute myocardial infarction; microRNA-155; inflammatory factor; ventricular remodelingdoi:10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201803011
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201804028
备注
为探究巨噬细胞中microRNA-155(miR-155)表达水平对急性心肌梗死(AMI)后心室重构的影响及其机制,将miR-155基因过表达(miR-155+/+)和基因敲除(miR-155-/-)小鼠的骨髓细胞分别移植给野生型(WT)小鼠进行血液重建,并建立AMI模型,检测血浆及心肌组织中炎症因子TNF-α和IL-10的表达水平,评价小鼠心脏功能并观察巨噬细胞浸润、心室重构的情况,进而利用病毒包装技术敲降细胞因子信号传导抑制蛋白1(SOCS1)基因后验证其作为miR-155靶基因的影响.结果显示:miR-155+/+组较miR-155-/-组小鼠的心脏收缩功能显著受限(p<0.01); 巨噬细胞中miR-155表达水平显著影响血浆中炎症因子的释放(p<0.01),并促进心室重构的发生(p<0.01); miR-155表达水平与SOCS1的mRNA及蛋白质表达水平呈显著负相关(p<0.01).综上可知,抑制AMI后巨噬细胞中miR-155的表达可以促进靶基因SOCS1的表达,从而减轻AMI后的炎症反应,有利于减轻心室重构.
To investigate the effect of microRNA-155(miR-155)expression in macrophages on ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction(AMI)and its mechanism,miR-155+/+ and miR-155-/- mouse bone marrow cells were transplanted to the wild type mice for blood reconstruction and the AMI model was established.In this study,the levels of inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-10 in plasma were detected,and the cardiac function of mice,macrophage infiltration and ventricular remodeling were observed.In addition,the SOCS1 gene was knocked down with virus packagingtechnology to verify the function of SOCS1 as the target regulatorygene of miR-155.Theresults showed as following:the systolic function of miR-155+/+ group was significantly lower than that of miR-155-/- group(p<0.01).MiR-155 significantly affected the release of inflammatory factors in plasma(p<0.01),and promoted the occurrence of ventricular remodeling(p<0.01).Moreover,the expression level of miR-155 was negatively correlated with SOCS1 mRNA and protein expression(p<0.01).In conclusion,inhibition of the expression of miR-155 in macro-phages after AMI can promote the expression of target gene SOCS1 and reduce the inflammatory reaction after AMI,which will be beneficial to reduce ventricular remodeling.
引言
目前急性心肌梗死(AMI)是世界范围内导致心源性死亡的主要原因[1],而AMI后心室重构是导致心衰的主要致病因素,对AMI后心室重构的预防及治疗是当今心血管病学研究面临的主要挑战[2].神经体液因素一直被认为是AMI后导致心室重构的重要机制,但是临床上即便广泛使用了“金标准”的拮抗神经体液因子的药物,如β受体阻滞剂、血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂/血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂(ACEI/ARB)以及醛固酮受体拮抗剂,心室重构仍然有很高的发生率,并不能完全阻止心室重构的进程[3].也有学者提出炎症因子可能参与了AMI后心室重构的过程,尤其是M1与M2型巨噬细胞之间的平衡影响着心室重构的进程,决定着AMI的预后[4].
最近有研究报道许多miRNAs也参与到AMI后心室重构的这一过程中[5].研究发现,miRNA-155(miR-155)通过靶向调控白介素13受体α1(IL13Rα1),阻滞M1型巨噬细胞向M2型分化,在M1和M2型的平衡维持中发挥着举足轻重的作用,而过表达miR-155基因可以促进M1型巨噬细胞的大量生成,从而极大地加剧炎症反应[6].在这些炎症因子中最具代表性的为促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和抗炎因子IL-10,TNF-α/IL-10比值变化对AMI后心室重构的影响具有重要意义[7],但是两者的表达是否受miR-155调控目前还未见报道.目前关于miR-155的研究主要集中在免疫系统疾病、感染性疾病及肿瘤等方面,越来越多的证据表明miR-155在炎症与自身免疫紊乱、肿瘤等疾病中起着非常重要的桥梁作用[8-9].已有研究证实miR-155可以直接靶向调控细胞因子信号传导抑制蛋白1(suppressor of cytokine signaling 1,SOCS1)、含肌醇磷酸激酶1的原癌基因蛋白-c(Src)同源体2(Src homology 2-containing inositol phosphatase-1,SHIP-1)等的编码基因,并促进炎症因子如IL-1β、干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)等的释放[10].
本研究通过体内实验研究miR-155对AMI时心脏功能及组织形态的影响,进而通过体外实验探讨miR-155的生物学调控机制.
1 材料和方法
2 结果与分析
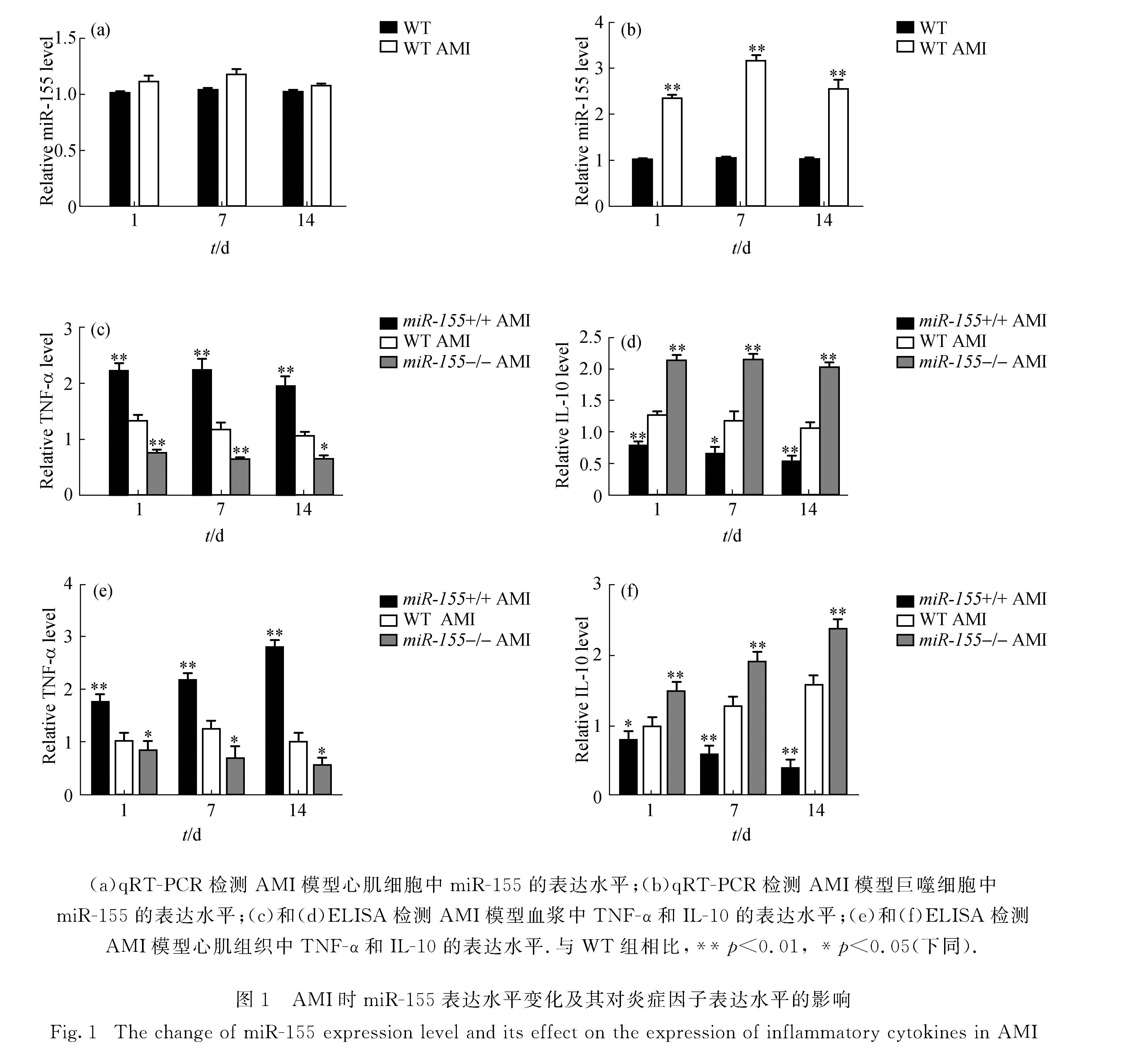
2.1 AMI后miR-155的表达变化及其对炎症因子释放的影响通过qRT-PCR分别检测小鼠AMI后1, 7 和14 d体外分离的心肌细胞和巨噬细胞中miR-155的表达水平变化,结果显示:在心肌细胞中miR-155的表达未见明显变化(图1(a)),而巨噬细胞中miR-155的表达水平却在AMI后1 d内显著升高,之后维持在一定的水平(图1(b)).这说明心肌缺血是诱导巨噬细胞中miR-155表达水平升高的因素之一,这与心肌肥厚重构过程中巨噬细胞的反应相似[14].同时,通过ELISA方法在3个时间节点上分别检测血浆和心肌组织中TNF-α和IL-10的表达水平,结果显示:miR-155+/+组相对于WT组和miR-155-/-组的TNF-α表达水平显著升高,在AMI后1 d达到高峰且维持时间超过7 d,在14 d时略有下降; 而miR-155-/-组的TNF-α始终维持在较低的表达水平,相对于同一时期的WT组均显著下降(图1(c)).IL-10的表达则相反,miR-155+/+组一直维持在较低水平,在不同时期均显著低于WT组; 而在miR-155-/-组中IL-10始终维持在较高表达水平,在不同时期均显著高于WT组(图1(d)).在AMI模型的心肌组织中得到了类似的结果:miR-155+/+组心肌组织中3个时间节点的TNF-α表达水平均较同一时期的WT组显著升高,在1 d时即达到高峰,后维持在较高的水平; miR-155-/-组心肌组织中1 d时TNF-α表达水平均较同一时期的WT组显著降低,之后维持在较低水平,波动不明显(图1(e)).IL-10在心肌组织中的表达水平与在血浆中的相似,miR-155+/+组均显著低于同一时期的WT组,并随时间呈逐渐降低的趋势; miR-155-/-组IL-10表达水平则呈逐渐升高的趋势,均显著高于同一时期的WT组(图1(f)).
图1 AMI时miR-155表达水平变化及其对炎症因子表达水平的影响
Fig.1 The change of miR-155 expression level and its effect on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in AMI这些结果表明,心肌缺血可以诱导巨噬细胞中miR-155 表达水平的升高,并影响血浆中炎症因子TNF-α和IL-10的释放.
2.2 miR-155对AMI后心室重构的影响为了分析miR-155对AMI后心室重构的影响,对心肌梗死周围组织分别进行了HE染色、免疫组织化学染色及Masson染色.在AMI后14 d时,心肌细胞的HE染色结果显示miR-155+/+组心肌细胞最大,WT组居中,miR-155-/-组最小(图2(a)); 用Image J软件对心肌细胞大小进行定量分析,miR-155+/+组心肌细胞较WT组显著增大,miR-155-/-组则较WT组显著减小(图2(d)).应用免疫组织化学方法检测巨噬细胞表面表达的CD68分子,观察各组巨噬细胞浸润情况,结果如图2(b)所示,在AMI后14 d,miR-155 +/+组巨噬细胞浸润的数量显著高于WT组; 集成光学密度(IOD)定量分析也表
明,miR-155+/+组巨噬细胞浸润数量较WT组显著增多,miR-155-/-组则较WT组显著减少(图2(e)).此外,通过Masson染色观察比较心肌纤维化程度,结果显示miR-155+/+组心肌纤维化程度最强,而miR-155-/-组心肌纤维化程度最轻(图2(c)),通过Image J软件定量分析胶原蛋白表达水平,结果也显示miR-155+/+组心肌纤维化程度较WT组显著增强,miR-155-/-组则较WT组显著减弱(图2(f)).这些结果表明miR-155可以诱导巨噬细胞向心肌细胞浸润,增强心肌细胞的纤维化和梗死程度,促进心室负性重构的发生.
2.3 miR-155对心脏功能的影响通过心脏彩超检测miR-155对心脏功能的影响,分别在miR-155+/+组、miR-155-/-组和WT组小鼠AMI后1, 7和14 d观察其心脏功能的改变.结果发现AMI后1 d时,3组小鼠心脏收缩功能未见明显差异,7 d时miR-155+/+组的小鼠心脏收缩功能显著下降,到14 d时更明显(图3).
2.4 体外细胞学实验验证分别分离miR-155+/+、miR-155-/-及WT巨噬细胞进行鉴定,采用免疫细胞化学法检测细胞表面CD68分子的表达,结果显示3组分离培养获得的巨噬细胞质量及数量上无明显差异(图4(a)).然后进行培养并给予LPS刺激,利用Western blot方法检测间皮标志物vimentin的表达变化,同时利用免疫组织化学染色方法观察α-SMA的染色情况,再分不同时间节点用ELISA方法检测TNF-α和IL-10的表达水平.结果显示:miR-155+/+组vimentin表达水平较WT组显著升高,miR-155-/-组较WT组显著降低(图4(b)和(d)),α-SMA表现出相同的变化趋势(图4(c)和(e)); 同时,miR-155+/+巨噬细胞中TNF-α表达水平较WT组显著升高,IL-10表达水平较WT组显著降低,miR-155-/-组则刚好相反(图4(f)和(g)).IL-10与TNF-α是作用相互拮抗的一对炎症因子,TNF-α/IL-10的比值代表了机体内的促炎与抗炎因子之间的平衡,可见miR-155在控制AMI后炎症反应程度方面具有重要作用.
3 讨 论
AMI后,心肌组织释放大量的热休克蛋白(heat shock protein,HSP)、高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mo-bility group protein B1,HMGB1)、活性氧等内源性因子,能够趋化、募集、激活单核巨噬细胞.在AMI早期主要以M1型巨噬细胞为主,引起瀑布级联反应,导致早期心肌细胞及间质的损伤[15].在AMI后期主要以M2型巨噬细胞为主,终止炎症反应并修复心肌组织,在晚期心室重构过程中发挥着促进血管新生及纤维增生等作用.M1和M2型巨噬细胞在多种细胞因子的作用下维持着一种微妙的平衡,而IL-13在其中发挥着至关重要的作用[16].miR-155能够靶向调控人类巨噬细胞上的IL13Rα1而阻止M1型巨噬细胞向M2型分化[6].
本研究发现骨髓移植了过表达miR-155基因的单核细胞的小鼠,在发生AMI后1, 7和14 d时各组心肌组织中的巨噬细胞浸润均明显增加,这可能与miR-155调控炎症趋化因子MCP-1的表达有关.然而,miR-155+/+组的炎症因子表达与其他2组存在差别,尤其是TNF-α,在AMI后1 d达到顶峰,且显著高于WT组和miR-155-/-组; 而IL-10在miR-155+/+组中一直维持在较低水平,miR-155-/-组中却维持在较高水平,与TNF-α的变化趋势刚好相反,充分表明miR-155在平衡促炎因子与抗炎因子中具有非常突出的作用.体内实验也证实miR-155+/+组AMI后14 d时心肌梗死组织面积最大,心肌细胞增大最明显,心肌纤维化程度明显加剧,并且心脏收缩功
图4 miR-155对体外巨噬细胞的作用及对炎症因子表达的影响
Fig.4 Effects of miR-155 on macrophages in vitro and the expression of inflammatory cytokines能明显受抑制,LVEF值显著减小.
SOCS又被称为细胞因子信号抑制物[17],能够通过多种负反馈调控机制抑制细胞因子的过度活化,其家族含有8个成员.其中SOCS1在炎症因子的调控中具有重要的作用,尤其能够避免促炎因子的过度活化[18].SOCS1的表达水平决定了炎症反应的程度,其表达水平越低,炎症反应越严重.本研究采用反义寡核苷酸方法特异性阻断miR-155分子,使之在巨噬细
图5 靶基因SOCS1验证及其对炎症因子表达水平的影响
Fig.5 Verification of the target gene SOCS1 and its effect on the expression of inflammatory factors胞中低表达或不表达,在LPS刺激后通过qRT-PCR方法检测SOCS1的mRNA表达水平,并且通过Western blot方法检测SOCS1的蛋白表达水平,均发现miR-155表达水平与SOCS1表达水平呈显著负相关.另外,在WT巨噬细胞中利用病毒包装技术敲降SOCS1基因后,通过ELISA检测发现敲降SOCS1基因后TNF-α的表达水平较对照组显著升高,而IL-10却显著降低.这些结果表明miR-155可能通过作用于SOCS1基因而扮演着“分子开关”的作用,最终影响了促炎因子与抗炎因子之间的平衡,调控AMI后心室重构的进程.
综上,本研究证明了巨噬细胞中的miR-155通过作用于靶基因SOCS1促进TNF-α表达而抑制IL-10 表达,在调控TNF-α/IL-10的比值方面具有重要意义.miR-155促进心室不良重构主要是通过介导促炎与抗炎介质的不平衡而引起的,而抑制巨噬细胞中miR-155的表达上调能够改善心室重构,提高心脏功能,为干预AMI后心室重构提供了有效的靶点.因此,通过干预AMI后炎症细胞尤其是巨噬细胞中miR-155的表达水平使炎症反应维持在适当程度,将有望成为一种全新的治疗心室重构的手段.
- [1] MOZAFFARIAN D,BENJAMIN E J,GO A S,et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics 2015 update:a report from the American Heart Association[J].Circulation,2015,131(4):e29-322.
- [2] WHITE H D,NORRIS R M,BROWN M A,et al.Left ventricular end-systolic volume as the major determinant of survival after recovery from myocardial infarction[J].Circulation,1987,76(1):44-51.
- [3] ZDROJEWSKI T,GAUDRON P,WHITTAKER P,et al.Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction and effects of ACE inhibition on hemodynamics and scar formation in SHR[J].Cardiovasc Pathol,2002,11(2):88-93.
- [4] LIU W,ZHANG X,ZHAO M,et al.Activation in M1 but not M2 macrophages contributes to cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats:a critical role of the cal-cium sensing receptor/NRLP3 inflammasome[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2015,35(6):2483-2500.
- [5] SMALL E M,FROST R J,OLSON E N,et al.Micro-RNAs add a new dimension to cardiovascular disease[J].Circulation,2010,121(8):1022-1032.
- [6] MARTINEZ-NUNEZ R T,LOUAFI F,SANCHEZ-ELSNER T.The interleukin 13(IL-13)pathway in human macrophages is modulated by microRNA-155 via direct targeting of interleukin 13 receptor α1(IL13Rα1)[J].J Biol Chem,2011,286(3):1786-1794.
- [7] FRANGOGIANNIS N G.The mechanistic basis of infarct healing[J].Antioxid Redox Sign,2006,8(11/12):1907-1939.
- [8] LENG R X,PAN H F,QIN W Z,et al.Role of micro-RNA-155 in autoimmunity[J].Cytokine Growth Factor Rev,2011,22(3):141-147.
- [9] CHEN Z,MA T,HUANG C,et al.The pivotal role of microRNA-155 in the control of cancer[J].J Cell Physiol, 2014,229(5):545-550.
- [10] TAN Y,YANG J,XIANG K,et al.Suppression of micro-RNA-155 attenuates neuropathic pain by regulating SOCS1 signalling pathway[J].Neurochem Res,2015,40(3):550-560.
- [11] Committee for the Biological Characterization of Experimental Animals.Guidelines for data on experimental animals and their care based on results of animal experiments[J].Zeitschrift Für Versuchstierkunde,1985,27(1):49-52.
- [12] GAO E,LEI Y H,SHANG X,et al.A novel and efficient model of coronary artery ligation and myocardial infarction in the mouse[J].Circ Res,2010,107(12):1445-1453.
- [13] SATO S,HUGHES R C.Regulation of secretion and surface expression of Mac-2,a galactoside-binding protein of macrophages[J].J Biol Chem,1994,269(6):4424-4430.
- [14] XU X,HUA Y,SREEJAYAN N,et al.Cardiac macro-phage migration inhibitory factor activates mitophagy to prevent the exacerbation of pressure overload-induced hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mice[J].Circulation,2012,126(21):A13344.
- [15] VAN DEN AKKER F,DEDDENS J C,DOEVENDANS P A,et al.Cardiac stem cell therapy to modulate inflammation upon myocardial infarction[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1830(2):2449-2458.
- [16] TENG Y,ZHANG R,LIU C,et al.MiR-143 inhibits interleukin-13-induced inflammatory cytokine and mucus production in nasal epithelial cells from allergic rhinitis patients by targeting IL13Rα1[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2015,457(1):58-64.
- [17] WILSON H M.SOCS proteins in macrophage polarization and function[J].Front Immunol,2014,28(5):357.
- [18] TAKAHASHI R,NAKATSUKASA H,SHIOZAWA S,et al.SOCS1 is a key molecule that prevents regulatory T cell plasticity under inflammatory conditions[J].J Immunol,2017,199(1):149-158.
1.1 动物实验1.1.1 小鼠来源及骨髓移植所有的小鼠实验均遵守相关的操作指南[11].从武汉大学模式动物中心购买8~10周龄,体质量20~22 g,雄性,miR-155基因过表达(miR-155+/+)、miR-155基因敲除(miR-155-/-)及野生型(WT)C57BL/6小鼠.小鼠骨髓移植:每天给予6 J/kg吸收剂量的射线连续2 d照射WT小鼠,然后从WT、miR-155+/+、miR-155-/-的小鼠股骨和胫骨中分别获得约2×107个髓细胞,经静脉注入射线照射后的WT小鼠重建造血系统,继续饲养8周后分组建模.
1.1.2 分组及AMI模型建立共分为6组,分别为WT组、miR-155+/+组、miR-155-/-组、WT AMI组、miR-155+/+ AMI组和miR-155-/- AMI组,每组各8只.经腹腔注射60 μg/g戊巴比妥钠麻醉后,将小鼠仰卧固定于手术台上,进行气管插管,并给予小动物呼吸机支持,结扎冠状动脉左前降支后关胸,假手术组(WT组、miR-155+/+组和miR-155-/-组)仅开胸挂线不结扎[12].于1,7 和14 d后分别进行心脏彩超检查,抽血进行相关指标检查后予以安乐死,迅速开胸取出心脏,锌-甲醛溶液固定,石蜡包埋后进行组织学检查,或者迅速冰冻后储藏在-80 ℃液氮中用于RNA抽提.
1.1.3 组织学分析及免疫组化检查小鼠心脏用锌-甲醛溶液固定后进行石蜡包埋,并将其横切成3 μm厚度,分别用抗α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)抗体、大鼠抗小鼠巨噬细胞表面标记CD68抗体进行免疫组织化学染色、苏木精伊红(HE)染色及Masson染色检查[13].
1.1.4 心脏彩超检测心功能在实验前及AMI后1,7和14 d分别进行心脏彩超检查.采用8 MHz探头,短轴M型超声检查心室收缩及舒张功能,分别检测左室舒张末期容积、左室收缩末期容积.射血分数(LVEF)=(左室舒张末期容积-左室收缩末期容积)/左室舒张末期容积×100%.
1.1.5 炎症因子检测TNF-α和IL-10在血清及心肌组织中的表达采用酶联免疫吸附实验(ELSIA)检测.在不同时间节点采血后取血清样品进行检测; 取各组-80 ℃冻存心肌梗死周围组织,每份约100 mg,剪碎,加入2 mL生理盐水于玻璃匀浆器制备组织匀浆,加0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH=7.4)至5 mL,高速低温(12 000 r/min,3 ℃)离心10 min后取上清液检测.具体实验步骤参照R&D Systems试剂盒说明书操作.
1.2 体外实验1.2.1 分离培养巨噬细胞分别从WT、miR-155+/+、miR-155-/-小鼠股骨及胫骨分离骨髓细胞.用含10%(体积分数),热灭活胎牛血清、青霉素(100 U/mL)、链霉素(100 μg/mL)及L-谷氨酰胺(2 mmol/L)的RPMI-1640培养液进行细胞培养,并补充15%(质量分数)L929处理介质(LCM)培养8~9 d以产生骨髓来源的巨噬细胞.WT巨噬细胞、miR-155+/+巨噬细胞和miR-155-/-巨噬细胞分别给予1 μg/mL脂多糖(LPS)刺激6, 12, 24 h.
1.2.2 炎症因子及蛋白质检测通过ELISA检测各组巨噬细胞分泌的TNF-α和IL-10水平; 采用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和蛋白质免疫印迹(Western blot)法分别检测SOCS1的mRNA及蛋白水平.
1.2.3 靶基因验证按1.2.1小节方法将分离培养的巨噬细胞分为WT巨噬细胞和miR-155-/-巨噬细胞两组,然后每组分别用腺病毒包装si-SOCS1转染以沉默SOCS1基因,采用空病毒组作为组内对照.给予1 μg/mL LPS刺激6, 12, 24 h,分别用1.2.2方法检测TNF-α和IL-10表达水平及SOCS1的mRNA和蛋白质水平.
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS 22软件行统计学分析.数据采用平均值±标准差表示,组间比较采用t-检验,p<0.05表示有显著性差异.