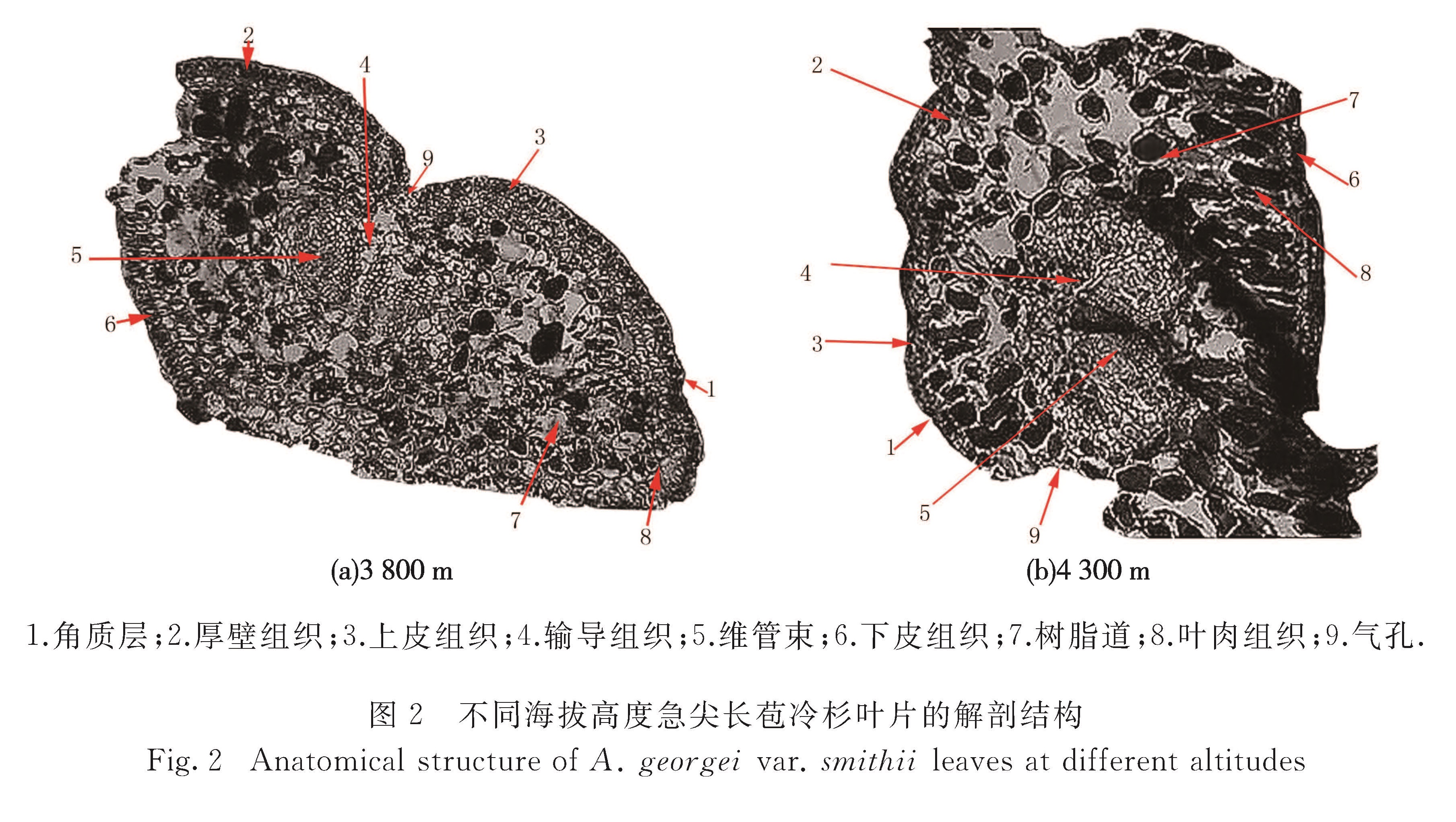
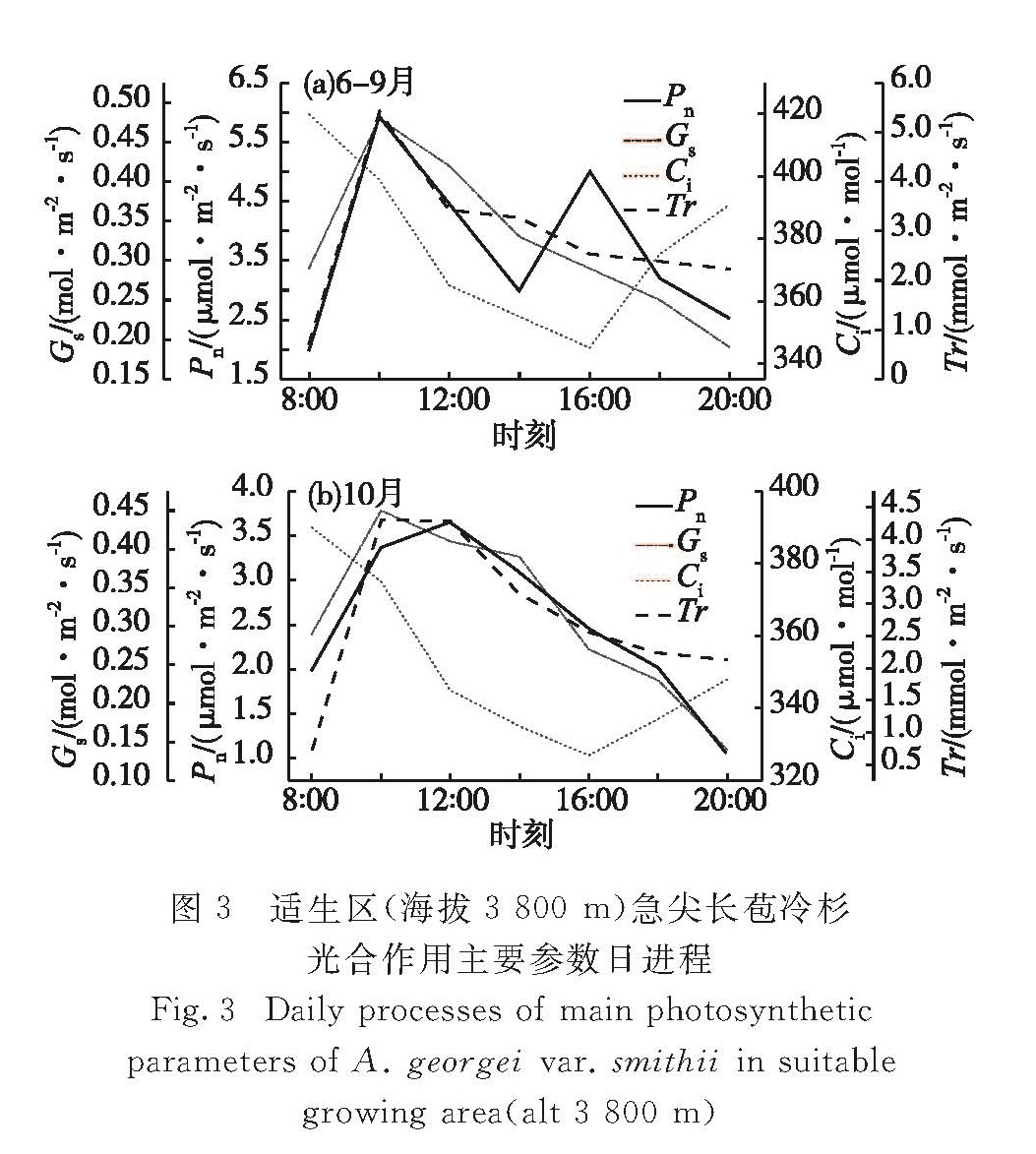
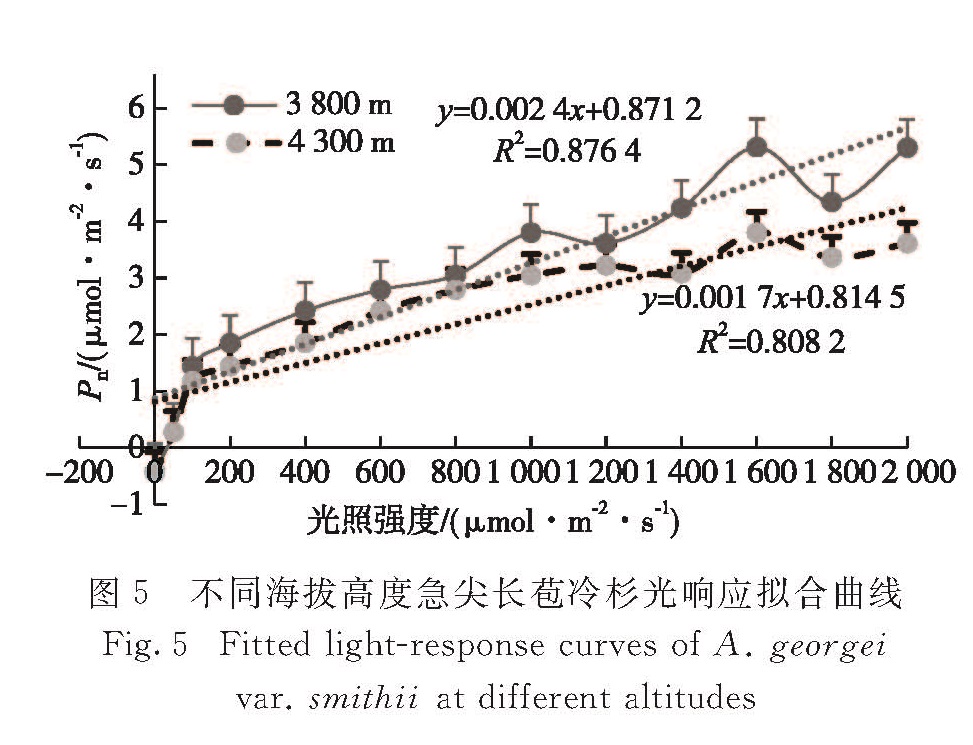
为探究急尖长苞冷杉(Abies georgei var. smithii)对不同海拔高度的响应机制,在急尖长苞冷杉集中分布区,按垂直高度100 m高差梯度进行采样,采用石蜡切片法及Li-6400光合测定系统对急尖长苞冷杉叶片结构与光合特性进行测定分析.结果表明:1)急尖长苞冷杉的叶片组织结构随海拔的变化表现出不同的形态特征,随着海拔的升高叶片扭曲变小,海拔4 100 m是叶片组织结构变化的拐点.2)在海拔3 800 m适生区,急尖长苞冷杉6—9月的光合作用日进程呈双峰曲线,高峰分别出现在10:00与16:00时,14:00时出现“午休”现象,随着气温的降低,10月光合作用日进程呈单峰曲线; 海拔4 300 m林线区6—10月的光合作用日进程均呈单峰曲线,12:00时出现最大值,与适生区10月的曲线表现类似.3)急尖长苞冷杉保持了较高的光能转化效率,净光合速率随着光照强度的增加而增加,这有利于光合作用产物的有效积累,为其在极端环境条件生长创造了有利条件.4)急尖长苞冷杉在林线区具有光饱和点较低、光补偿点较高的特点,表现出其对弱光照和低温环境的较强适应性.
In order to explore the response mechanism of Abies georgei var. smithii at different altitudes with the change of environment,sampling was carried out at a vertical height gradient of 100 m in the concentrated distribution area of A. georgei var. smithii,and the differences in leaf structure and photosynthetic characteristics at different altitudes were studied using paraffin method and Li-6400 photosynthesis system.Results showed as following:1)The leaf anatomical structure of A. georgei var. smithii changed and the twist of leaf became smaller with altitude increasing,and the elevation of 4 100 m was the inflection point of leaf anatomical structure. 2)The photosynthetic daily process in suitable growing area(an altitude of 3 800 m)showed a bimodal curve from June to September,with the peaks appearing at 10:00 and 16:00,and a midday depression at 14:00.As the temperature decreases,a single peak curve was shown in October.The photosynthetic daily process in timberline area(an altitude of 4 300 m)was a single peak curve from June to October with the maximum at 12:00,consistent with the curve for the suitable growing area in October. 3)The rapid growth of A. georgei var. smithii was maintained by a higher photoenergy conversion efficiency.The net photosynthetic rate increased with the increase of light intensity,which is beneficial to the effective accumulation of photosynthate and to create favorable conditions for its growth in extreme environmental conditions. 4)In timberline area the A. georgei var. smithii was characterized by a relatively low light saturation point and a relatively high light compensation point,indicating that it had strong adaptation to weak light and low temperature.
![表1 色季拉山不同海拔的气候条件及林分特征[15]<br/>Tab.1 Climatic and forest characteristics at different altitudes on Sejila mountain[15]](2018年04期/pic54.jpg)