(厦门大学 海洋与地球学院,近海海洋环境科学国家重点实验室,福建 厦门 361102)
(State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science,College of Ocean and Earth Sciences,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361102,China)
Scylla paramamosain; population; mitochondrial respiration rate; enzyme activity; latitude difference
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201709015
备注
已有研究显示分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)可能已分化为南、北2个种群.在低温季节从不同纬度的3个海域采集拟穴青蟹的野生个体,比较其南、北种群线粒体呼吸速率和酶活性的差异.结果如下:除了乳酸脱氢酶、丙酮酸激酶以及肝胰腺细胞色素C氧化酶外,无论是北方种群还是南方种群,生活在纬度较高的宁波海域的拟穴青蟹的线粒体呼吸速率和酶活性都显著高于生活在纬度较低的儋州海域的个体; 同一海域的南、北种群间,鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺线粒体呼吸速率和细胞色素C氧化酶活性总体上都是北方种群高于南方种群,纬度越高的海域的南、北种群间差异越显著; 南、北种群肌肉的乳酸脱氢酶、丙酮酸激酶和己糖激酶活性相比,宁波海域北方种群的己糖激酶活性显著高于该海域的南方种群.上述结果表明,分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹的北方种群比南方种群对温度有更有效的代谢补偿能力,且纬度越高,二者的差异越显著,由此可见分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹的北方种群比南方种群更能适应低温环境.
Recent research has identified that the mud crab,Scylla paramamosain,in the southeast coast of China can be sub-divi-ded into northern and southern populations.The present study measured and compared the mitochondrial respiration rates and enzyme activities of northern and southern populations of the mud crab,S. paramamosain,sampled during low temperature seasons and from three locations at different latitudes.It was shown that for both northern and southern populations,with the exception of lactate dehydrogenase,pyruvate kinase and cytochrome C oxidase in hepatopancreas,the mitochondrial respiration rates and enzyme activities of crabs collected from higher latitude Ningbo coastal waters were significantly higher than those from Danzhou coastal waters at lower latitude.As for northern and southern populations collected at the same location,the mitochondrial respiration rates and cytochrome C oxidase activities in the gill,muscle and hepatopancreas of crabs of the northern population were generally higher than those of the southern population from all three locations with the differences increasing with latitude.For lactate dehydrogenase,pyruvate kinase and hexokinase activities in muscle,hexokinase activities of crabs of the northern population were also significantly higher than those of the southern population collected from Ningbo coastal waters.The results of the present study indicated that the northern population of S. paramamosain had strong metabolic compensation capacity than the southern population under cold environments,especially at higher latitude,confirming the hypothesis that the northern population of S. paramamosain adapted better to low temperature than the southern population.
引言
青蟹隶属于甲壳纲(Crustacea)十足目(Decapoda)梭子蟹科(Portunidae)青蟹属(Scylla).一般认为青蟹属有4个种,主要分布于暖温带和热带海域.形态学以及12S rRNA、16S rRNA和CO1基因序列分析结果表明,我国沿海的青蟹优势种为拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain),主要分布于长江口以南的东南沿岸水域,是一种重要的经济蟹类[1-8].我国拟穴青蟹养殖规模较大,相关的研究也较多[9],但其种群生物学的研究较少[10].本课题组曾从形态学、生理学和遗传学等方面对拟穴青蟹种群生物学进行了一些研究,结果表明:分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹可能已分化为南、北2个种群,且南、北种群的个体混杂分布于我国不同海域,随纬度变化,同一海域不同种群所占的比例不同.北方种群的个体主要分布于纬度较高的江浙沿岸海域,纬度越低则个体数量越少; 南方种群的个体主要分布于纬度较低的海南岛和北部湾沿岸海域,纬度越高则个体数量越少.南、北2个种群适应环境温度的能力不同,北方种群比南方种群更能适应低温环境,在高温环境下则是南方种群比北方种群生长得更好[10-12].
最近,本课题组分析了分布在我国不同海域的拟穴青蟹的线粒体呼吸速率和代谢酶活性的季节性变化,发现分布在北方海域的拟穴青蟹的线粒体呼吸速率和细胞色素C氧化酶(CCO)活性明显高于分布在南方海域的个体,说明分布于北方海域的拟穴青蟹比分布于南方海域的个体更能适应低温环境[12],这一结果进一步支持了分布在我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹可能已分化为南、北2个不同种群的观点.前已述及,拟穴青蟹南、北种群的个体是混杂分布于我国不同海域的,随纬度变化,同一海域中不同种群所占的比例不同.为了进一步探究在同一海域中是否北方种群比南方种群更能适应低温环境,本研究在我国东南沿海不同纬度的海域采集低温季节的拟穴青蟹野生样品,比较南、北种群的线粒体呼吸速率以及CCO、乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)、丙酮酸激酶(PK)、己糖激酶(HK)活性的差异,以期了解分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹的种群分化情况、不同种群的分布规律及其生理特征,为我国拟穴青蟹种质资源的开发和保护以及水产养殖的生产和管理提供理论依据.
1 材料与方法
1.1 拟穴青蟹样品采集与处理1.2 线粒体提取及其蛋白质含量测定提取线粒体时,将暂养在实验室的拟穴青蟹经24 h饥饿处理后,剪开其头胸甲取出鳃、肝胰腺和附肢肌肉,其中2只螯足放于-70 ℃超低温冰箱中保存以备酶活分析之用.按照Liu等[12]的方法提取鳃、肝胰腺和肌肉的线粒体.采用BCA(bicinchoninic acid)法[13]测定线粒体制备液的蛋白质含量.在蛋白质含量测定之前,将10 μL的线粒体制备液溶解于1 mL不含牛血清白蛋白(BSA)的提取缓冲液中,在12 000 g、4 ℃条件下离心10 min,沉淀之后再经2次溶解和离心以去除BSA对总蛋白测定的影响[14].
1.3 线粒体呼吸速率测定使用英国Hansatech公司生产的Clark LS2H型氧电极测定线粒体呼吸速率,测定温度为25 ℃,3种组织的测定方法一致,均采用经改良的Hulbert等[15]的方法.首先往反应室中加入1.98 mL 呼吸缓冲液(100 mmol/L KCl、40 mmol/L 蔗糖、5 mmol/L 4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸(HEPES)、10 mmol/L K2HPO4、2 mmol/L MgCl2、1 mmol/L乙二醇二乙醚二胺四乙酸(EGTA)、0.5%(质量分数,下同)BSA,pH=7.2).接着加入50 μL的线粒体制备液,待基线平稳后,线粒体耗氧率接近于零,此时为线粒体的状态1呼吸速率.再加入10 μL 琥珀酸(终浓度为2 mmol/L)或丙酮酸+苹果酸(二者的终浓度均为5 mmol/L),此时测得的耗氧率为线粒体状态2呼吸速率.然后加入10 μL二磷酸腺苷(ADP,终浓度为0.2 mmol/L),此后耗氧率会显著上升,为线粒体状态3呼吸速率,即线粒体最大耗氧率.此状态持续一段时间后,耗氧率随着ADP的消耗而逐渐下降,ADP耗尽后的耗氧率则为线粒体的状态4呼吸速率.线粒体呼吸速率的单位[nmol/(min·mg)]表示为每分钟每毫克线粒体蛋白质消耗的纳摩尔氧.
1.4 线粒体CCO活性分析在CCO活性测定前,将肝胰腺、鳃和肌肉的线粒体制备液稀释于低渗的KCl溶液(10 mmol/L KCl,10 mmol/L Tris,pH=7.6),经冻融破裂线粒体外膜以便能更有效地进行测定[16].CCO活性测定采用美国安捷伦公司生产的Agilent Cary-100型紫外-可见分光光度计在550 nm波长下测定还原态细胞色素C的氧化量,测定温度为25 ℃,反应时间为4 min,反应体系为pH 7.5的100 mmol/L K3PO4 和0.05 mmol/L 的还原态细胞色素C.CCO活性单位(U)表示为每毫克线粒体蛋白1 min内将底物转化为产物的摩尔数.还原态细胞色素C是通过在细胞色素C中加入过量Na2S2O4还原产生的,还原过程通过加入足量的气泡以去除多余的Na2S2O4[17].
1.5 肌肉酶活性分析从每只蟹的螯足中称取0.2 g肌肉,加入2 mL缓冲液(10 mmol/L乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-Na2)、10 mmol/L Tris、0.5% BSA,pH=7.5)进行匀浆.使用Polytron组织匀浆机以20%最大速度匀浆2次,每次45 s,每次间隔1 min.匀浆在4 000 g、4 ℃条件下离心10 min,取上清液用于酶活性测定.酶活性测定的温度为25 ℃.采用修改的Thibault等[17]的方法测定LDH活性,其反应体系为0.1 mol/L K3PO4、0.32 mmol/L烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NADH)、1.6 mmol/L 丙酮酸,pH=7.0.采用修改的Hansen等[18]的方法测定HK和PK活性.HK的反应体系为55 mmol/L Tris、10 mmol/L MgCl2、80 mmol/L葡萄糖、24 mmol/L三磷酸腺苷(ATP)、1.6 mmol/L烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NADP)、14 U 6-磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶,pH=7.4; PK的反应体系为25 mmol/L咪唑、10 mmol/L MgSO4、100 mmol/L KCl、5 mmol/L ADP、2 mmol/L磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸(PEP)、0.3 mmol/L NADH、5.5 U LDH,pH=7.4.上述3种酶活性的测定均使用Agilent Cary-100型紫外-可见分光光度计在340 nm波长下测定NADH或NADP的增减量,活性单位(U)表示为每克组织湿质量1 min内将底物转化为产物的摩尔数.
1.6 数据处理所有数据用平均值±标准差表示.采用SPSS 13.0 统计分析软件,通过t-检验分析同一海域南、北种群的线粒体呼吸速率和酶活性的差异,通过单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和最小显著性差异法(LSD)多重比较分析不同海域南、北种群的线粒体呼吸速率和酶活性的差异.差异显著和极显著水平分别设置为p≤0.05和p≤0.01.
2 结果与分析
3 讨 论
拟穴青蟹是生活在热带和亚热带海域的蟹类,在温度较高时进行生长发育和繁殖,低温时摄食和运动量则大为减少[9].拟穴青蟹分布于我国东南沿海海域,位于北部的浙江省宁波海域属亚热带季风气候,四季分明,夏季高温,冬季水温较低,可低至5 ℃以下; 位于南部的海南省儋州海域属热带季风气候,四季不分明,长夏无冬,在最冷的一、二月份水温仍可达到16~21 ℃; 位于上述两海域之间的福建省漳州海域,其气候也介于两者之间[19].由于我国东南沿海不同海域的气候条件相差较大,而且是拟穴青蟹的分布北界,不同地理群体的拟穴青蟹很可能在遗传或表型上出现差异,从而分化为南、北2个种群.倘若分布于我国的拟穴青蟹的确已分化为南、北2个种群,则两者对低温环境的适应能力、温度补偿机制以及生理生化的响应也应有所不同.为此,本研究在上述3个不同纬度的海域采集低温季节的拟穴青蟹野生样品,采样时间为2010年11月、2010年12月和2011年1月,分别为秋末、初冬和中冬,此时这3个海域的水温均是一年中较低的时候.通过分析3个海域不同种群的拟穴青蟹在低温季节的线粒体呼吸速率、CCO活性以及肌肉LDH、PK、HK活性,判断分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹种群分化情况以及不同种群的分布规律.结果表明,上述3个海域不同种群的拟穴青蟹在低温季节的线粒体呼吸速率、CCO活性以及肌肉LDH、PK、HK活性存在显著差异,由此证实了分布于我国的拟穴青蟹已分化为南、北2个种群的推测,且南、北种群的个体混杂分布于我国的不同海域.
3.1 不同种群线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性的差异本研究结果显示,在宁波、漳州和儋州这3个海域的低温季节,拟穴青蟹北方种群的线粒体呼吸速率整体上均高于本海域的南方种群,纬度越高的海域这种差异越明显.在纬度较高的宁波海域,北方种群鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺的线粒体呼吸速率显著高于南方种群,特别是这3种组织的线粒体状态3呼吸速率,北方种群均显著高于南方种群; 在漳州海域,北方种群这3种组织的线粒体呼吸速率也显著高于南方种群,其中在鳃中差异最显著; 在纬度较低的儋州海域,北方种群鳃线粒体呼吸速率显著高于南方种群,而肌肉和肝胰腺组织的线粒体呼吸速率在南、北种群间未呈现显著性差异.由此可见,在低温环境下北方种群的线粒体对温度的补偿比南方种群更为有效,而且纬度越高,南、北种群间的差异越明显.这个结果与本课题组先前测定的拟穴青蟹南、北种群线粒体功能和代谢酶活性的季节变化结果[12]是一致的.
拟穴青蟹鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺线粒体CCO活性与其线粒体呼吸速率的情况相似,在测试的3个不同海域均表现为北方种群整体上高于南方种群,特别是纬度较高的宁波海域,南、北种群间的差异达到显著性水平.此外,拟穴青蟹鳃的线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性在南、北种群间的差异很明显,在测试的3个不同海域均是北方种群显著高于南方种群.这个结果再次表明,在低温环境下北方种群比南方种群有更高的温度补偿效率.拟穴青蟹南、北种群线粒体呼吸速率的差异与其CCO活性的差异相似,这是因为CCO是线粒体呼吸作用中重要的催化酶,二者是相互关联的,所以表现出一致性的规律.在其他动物中,如不同发育阶段的鳉鱼(Austrofundulus limnaeus)的线粒体呼吸速率与CCO活性也有类似的情况[16].
拟穴青蟹鳃线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性的种群间差异明显高于肌肉和肝胰腺组织的种群间差异.在测试的3个海域,拟穴青蟹鳃线粒体的呼吸速率和CCO活性的种群间差异均达到显著性水平; 在漳州和儋州海域,肌肉和肝胰腺的线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性的种群间差异则明显低于鳃的种群间差异.这可能是因为拟穴青蟹鳃在体液渗透压调节中直接与外界环境接触,受外界水温变化影响最大[20-21].由此可见,拟穴青蟹南、北种群的差异不仅表现在细胞水平上,也表现在组织水平上.
3.2 不同种群代谢补偿的差异一般而言,当环境温度降低时,为了弥补低温对新陈代谢的抑制,在低温下依旧保持活力的动物的机体调控系统会通过温度补偿机制来提高代谢速率,从而维持正常的生命活动[22-24].纬度越高的地区气温变化越明显,生活在高纬度地区的动物会比生活在低纬度地区的动物面临更极端的环境温度变化,因此在寒冷季节同一物种的高纬度地理种群的代谢水平会比低纬度的地理种群更具温度补偿效率,从而维持同等的生长繁殖活动[25-27].
本研究的结果显示,不论是拟穴青蟹的南方种群还是北方种群,在纬度较高的宁波海域其线粒体呼吸速率都较高,在纬度较低的儋州海域其线粒体呼吸速率都较低.除了肝胰腺线粒体CCO活性之外,拟穴青蟹南、北种群鳃和肌肉线粒体CCO活性基本也呈现该趋势.虽然拟穴青蟹南、北种群其LDH和PK活性在测试的3个海域未呈现该趋势,但其HK活性也是宁波海域显著高于儋州海域.因此,从整体上来看,无论是南方种群还是北方种群,生活在较高纬度海域的拟穴青蟹个体的线粒体功能和代谢酶活性都明显高于生活在较低纬度海域的个体,即生活在较高纬度海域的拟穴青蟹个体具有更高的代谢补偿效应.
总体而言,我国东南沿海拟穴青蟹北方种群对低温的代谢补偿比南方种群更为有效,在纬度较高的海域更是如此.当低温影响到拟穴青蟹的新陈代谢时,南方种群可能会减少活动甚至进入休眠状态,而北方种群则依旧能保持较高的代谢速率,从而维持正常的生命活动.北方种群的这种生理特性使其比南方种群更适合在我国东南沿海纬度较高的海域生活,因此,在我国东南沿海不同纬度的海域,拟穴青蟹北方种群的个体数量随纬度的升高而增加.拟穴青蟹在我国东南沿海的这种分化情况及其分布规律在养殖上应予以重视,对不同的种群在养殖上要区别对待.
3.3 拟穴青蟹线粒体代谢与细胞基质代谢的差异值得进一步讨论的是,与肌肉线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性相比,拟穴青蟹肌肉LDH和PK活性在南、北种群间的差异很小,均未达到显著性水平.LDH和PK是存在于细胞质基质的代谢酶,拟穴青蟹这2种酶活性的种群间差异不及线粒体呼吸速率和CCO活性的种群间差异显著,说明拟穴青蟹南、北种群在线粒体代谢水平上的差异比在细胞质基质上的差异明显.Dhillon等[25]在底鳉(Fundulus heteroclitus)南、北种群的研究中报道了类似的情况,在不同驯化温度下不同种群底鳉的肌肉柠檬酸合成酶(CS)和LDH的活性有明显差异.CS是线粒体呼吸作用中的另一关键酶,在5和15 ℃的低温条件下北方种群CS活性显著高于南方种群,而在任一驯化温度下南、北种群LDH活性均无显著差异,说明底鳉南、北种群也是线粒体代谢水平上的差异比细胞基质上的差异明显.
综上,本研究对我国东南沿海南、北种群的拟穴青蟹的线粒体呼吸速率、CCO活性以及肌肉LDH、PK、HK活性进行了比较分析。结果显示,分布于我国东南沿海的拟穴青蟹北方种群比南方种群对温度有更有效的代谢补偿能力,且纬度越高,二者的差异越显著。此结果为拟穴青蟹的种群分化以及拟穴青蟹养殖模式的建立提供了科学数据,具有理论意义和实际的应用价值。
2.1 线粒体呼吸速率在本研究中,无论是使用琥珀酸还是丙酮酸+苹果酸作为底物,拟穴青蟹鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺线粒体的状态2和状态4呼吸速率的差异均很小,但状态2或状态4与状态3呼吸速率则有很明显的差异,所以本研究选择拟穴青蟹鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺线粒体状态2与状态3呼吸速率的测试结果进行分析比较.
2.1.1 鳃
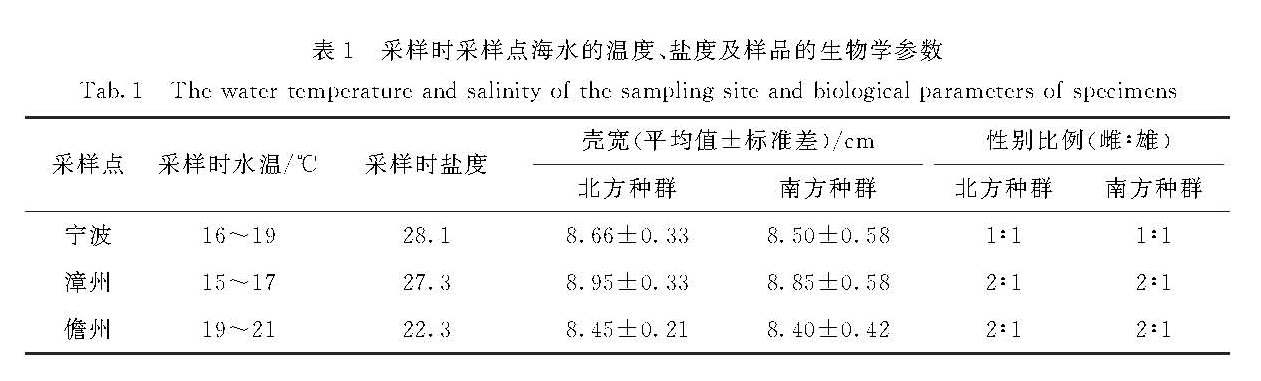
如图1所示:拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群的鳃线粒体呼吸速率在测试的3个海域的变化规律相似,其状态2和状态3呼吸速率均表现为宁波海域最高,儋州海域最低,漳州海域介于两者之间,即北方种群和南方种群的鳃线粒体各状态的呼吸速率均随着纬度的升高而升高.在测试的3个海域,同一海域北方种群鳃线粒体呼吸速率均显著高于同一海域南方种群(p≤0.05).其中宁波海域使用琥珀酸为底物时测得的状态3呼吸速率:北方种群为(70.54±3.35)nmol/(min·mg),南方种群为(50.94±6.05)nmol/(min·mg).漳州海域使用琥珀酸为底物时测得的状态2呼吸速率:北方种群为(11.17±1.93)nmol/(min·mg),南方种群为(7.23±2.05)nmol/(min·mg); 状态3呼吸速率:北方种群为(46.88±12.76)nmol/(min·mg),南方种群为(28.02±6.12)nmol/(min·mg).上述3项在南、北种群间的差异极显著(p≤0.01).
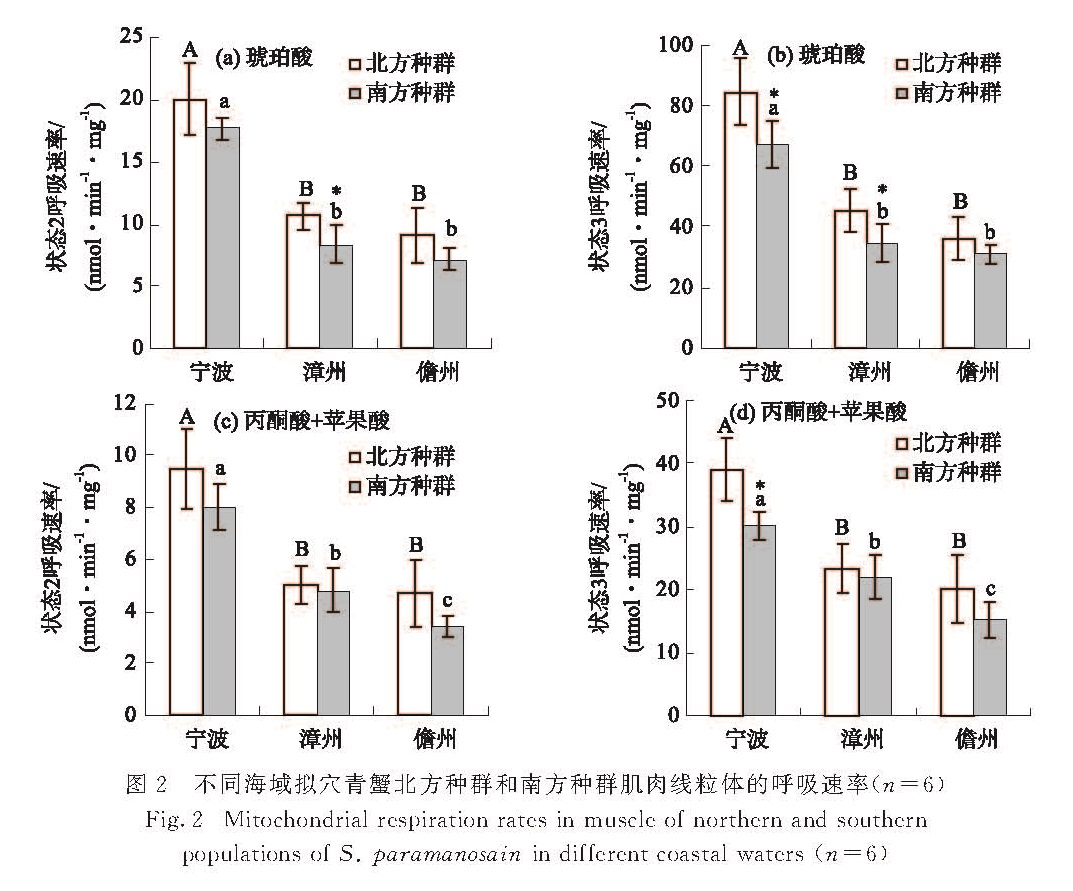
2.1.2 肌 肉如图2所示:宁波海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群的肌肉线粒体各状态的呼吸速率均显著高于漳州海域和儋州海域(p≤0.05).将漳州海域与儋州海域进行比较,肌肉线粒体呼吸速率在北方种群间无显著差异(p>0.05),但在南方种群以丙酮酸+苹果酸为底物时测得的状态2和状态3呼吸速率则表现为漳州海域显著高于儋州海域(p≤0.05).同一海域不同种群间肌肉线粒体呼吸速率的比较结果如下:在宁波海域,北方种群高于南方种群,其中使用琥珀酸和丙酮酸+苹果酸为底物时测得的状态3呼吸速率差异显著(p≤0.05); 在漳州海域,也是北方种群高于南方种群,其中使用琥珀酸为底物时测得的状态2和状态3呼吸速率差异显著(p≤0.05); 而在儋州海域,南、北种群间的差异不显著(p>0.05).
*和**分别表示同一海域的北方种群与南方种群间差异显著(p≤0.05)和极显著(p≤0.01);
不同的大写字母和小写字母分别表示北方种群与南方种群在不同海域间差异显著(p≤0.05)(下同).
图1 不同海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群鳃线粒体的呼吸速率(n=6)
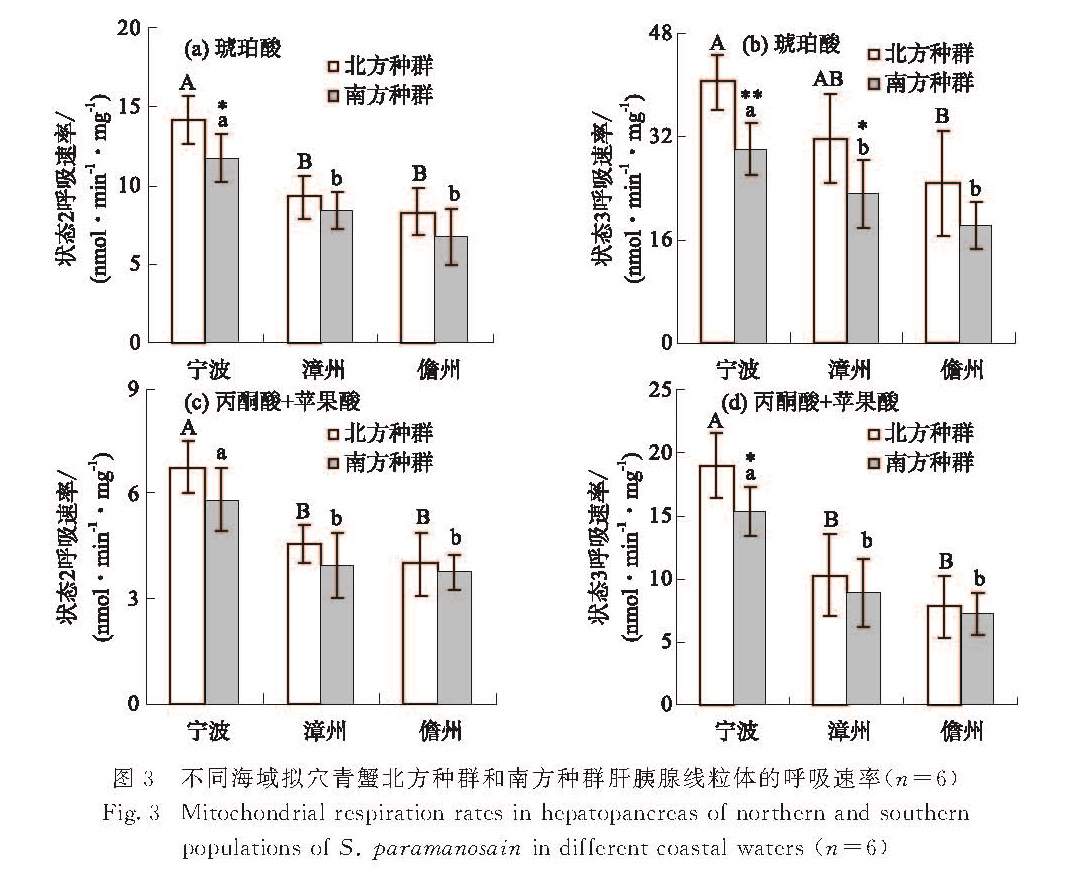
Fig.1 Mitochondrial respiration rates in gill of northern and southern populations of S. paramamosain in different coastal waters(n=6)2.1.3 肝胰腺图3 不同海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群肝胰腺线粒体的呼吸速率(n=6)
Fig.3 Mitochondrial respiration rates in hepatopancreas of northern and southern populations of S. paramanosain in different coastal waters(n=6)如图3所示:在测试的3个海域,宁波海域以琥珀酸为底物时测得的拟穴青蟹北方种群的肝胰腺线粒体状态3呼吸速率与漳州海域北方种群无显著差异(p>0.05),除此之外,宁波海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群肝胰腺线粒体各状态的呼吸速率均显著高于漳州海域和儋州海域(p≤0.05).漳州海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群肝胰腺线粒体各状态的呼吸速率与儋州海域均无显著差异(p>0.05).同一海域不同种群间肝胰腺线粒体呼吸速率的比较结果表明:在宁波海域,除了以丙酮酸+苹果酸为底物测得的状态2呼吸速率外,其他3种状态的呼吸速率均是北方种群显著高于南方种群(p≤0.05); 特别是以琥珀酸为底物测得的线粒体状态3呼吸速率在南、北种群间的差异达到极显著水平(p≤0.01),北方种群为(40.60±4.26)nmol/(min·mg),南方种群为(30.13±3.99)nmol/(min·mg).在漳州海域,北方种群线粒体各状态的呼吸速率也高于南方种群,其中使用琥珀酸为底物测得的状态3呼吸速率差异显著(p≤0.05).在儋州海域,南、北种群线粒体各状态的呼吸速率差异均不显著(p>0.05).
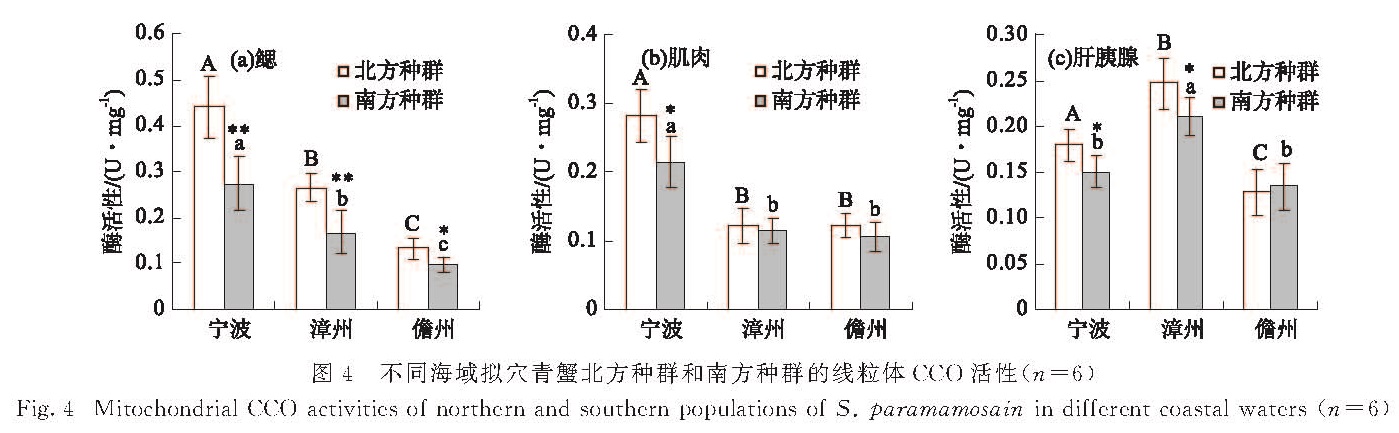
2.2 线粒体CCO活性宁波、漳州和儋州海域拟穴青蟹南、北种群鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺线粒体CCO活性测定结果如图4所示:南、北种群鳃线粒体CCO活性均是在宁波海域最高,漳州次之,儋州最低.南、北种群肌肉线粒体CCO活性也是在宁波海域最高,显著高于漳州和儋州海域(p≤0.05).肝胰腺线粒体CCO活性有所不同,北方种群在漳州海域最高,宁波海域次之,儋州海域最低; 而南方种群在漳州海域最高,显著高于宁波和儋州海域(p≤0.05).同一海域不同种群间线粒体CCO活性的情况如下:在宁波海域,北方种群鳃、肌肉和肝胰腺的线粒体CCO活性都显著高于南方种群(p≤0.05),特别是鳃的线粒体CCO活性,在南、北种群间的差异达到极显著水平(p≤0.01),北方种群鳃线粒体CCO活性为(0.441±0.067)U/mg,南方种群为(0.274±0.058)U/mg; 在漳州海域,北方种群鳃和肝胰腺的线粒体CCO活性也显著高于南方种群(p≤0.05),北方种群分别为(0.266±0.030)U/mg和(0.246±0.027)U/mg,南方种群分别为(0.168±0.048)U/mg和(0.210±0.020)U/mg; 在儋州海域,肌肉和肝胰腺的线粒体CCO活性在南、北种群间的差异不显著(p>0.05),鳃的线粒体CCO活性在南、北种群间则有显著性差异(p≤0.05),北方种群为(0.132±0.023)U/mg,南方种群为(0.097±0.017)U/mg.
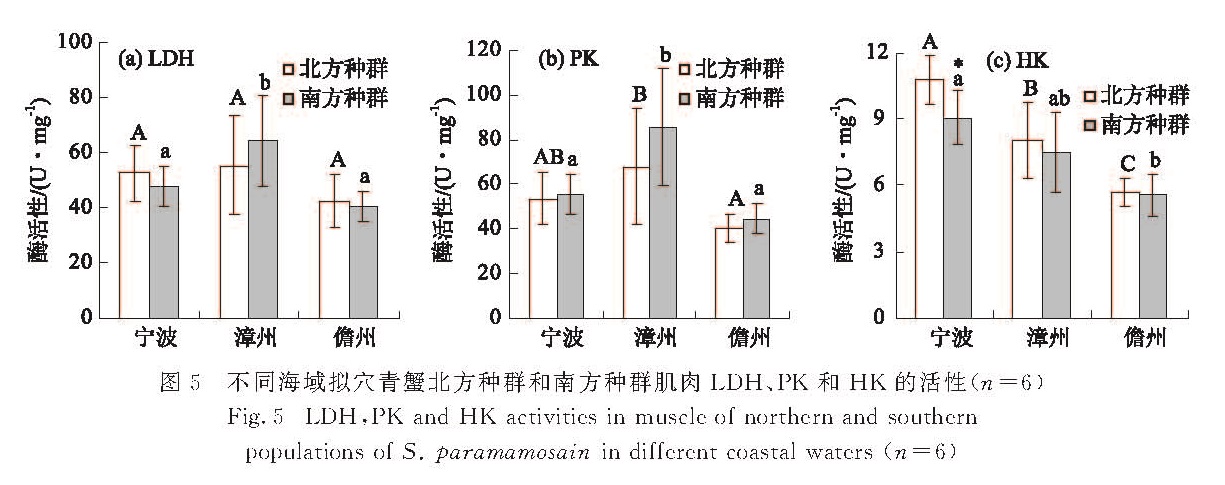
2.3 肌肉中相关酶的活性图4 不同海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群的线粒体CCO活性(n=6)
Fig.4 Mitochondrial CCO activities of northern and southern populations of S. paramamosain in different coastal waters(n=6)图5 不同海域拟穴青蟹北方种群和南方种群肌肉LDH、PK和HK的活性(n=6)
Fig.5 LDH,PK and HK activities in muscle of northern and southern populations of S. paramamosain in different coastal waters(n=6)拟穴青蟹南、北种群肌肉LDH、PK和HK活性在不同海域的情况比较复杂,如图5所示:漳州海域的南方种群肌肉LDH活性显著高于宁波和儋州海域的南方种群(p≤0.05),而北方种群肌肉LDH活性在测试的3个海域间无显著差异(p>0.05).漳州海域的南方种群肌肉PK活性也显著高于宁波和儋州海域的南方种群(p≤0.05),而北方种群肌肉PK活性仅显著高于儋州海域的北方种群(p≤0.05).宁波海域的南方种群肌肉HK活性仅显著高于儋州海域的南方种群(p≤0.05); 而北方种群肌肉HK活性在测试的3个海域间差异显著(p≤0.05),宁波海域最高,漳州海域次之,儋州海域最低.同一海域的南、北种群间肌肉LDH、PK和HK活性的比较结果显示:宁波海域拟穴青蟹北方种群HK活性显著高于该海域的南方种群(p≤0.05),北方种群HK活性为(10.79±1.13)U/mg,南方种群HK活性为(9.02±1.20)U/mg,除此之外,其余均无显著性差异(p>0.05).
- [1] KEENAN C P,DAVIE P J F,MANN D L.A revision of the genus Scylla de Hann,1833(Crustacea:Decapoda:Brachyura:Portunidae)[J].Raffles Bulletin of Zoology,1998,46:217-245.
- [2] 黎中宝,李少菁,王桂忠.中国东南沿海锯缘青蟹群体的形态判别分析[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2004,43(1):101-106.
- [3] 黎中宝,李少菁,王桂忠,等.锯缘青蟹等位酶的生化遗传分析[J].中国生态农业学报,2004,12(2):61-64.
- [4] LI Z B,LI S J,WANG G Z.Genetic diversity and differentiation of mud crab Scylla serrate[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2004,23(2):309-316.
- [5] 马凌波,张凤英,乔振国,等.中国东南沿海青蟹线粒体CO1基因部分序列分析[J].水产学报,2006,30(4):463-468.
- [6] 高天翔,王玉江,刘进贤,等.基于线粒体12S rRNA序列探讨4种青蟹系统发育关系及中国沿海青蟹的分类地位[J].中国海洋大学学报,2007,37(1):57-60.
- [7] 林琪,李少菁,黎中宝,等.中国东南沿海青蟹属(Scylla)的种类组成[J].水产学报,2007,31(2):211-219.
- [8] 林琪,李少菁,黎中宝,等.中国东南沿海青蟹属不同种类的mtDNA CO1基因序列分析及其系统发育[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2008,47(2):268-273.
- [9] 李少菁,王桂忠.锯缘青蟹生物学及人工育苗和养成技术[M].厦门:厦门大学出版社,2007:806.
- [10] 王桂忠,李少菁,陈志刚.青蟹(Scylla spp.)养殖现状及拟穴青蟹(S. paramamosain)种群生物学研究[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2016,55(5):617-623.
- [11] 许晓军.拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)微卫星标记的开发和应用[D].厦门:厦门大学,2009:118.
- [12] LIU Z M,WANG G Z,WU L S,et al.Seasonal change in mitochondrial function and metabolic enzyme activity of different populations of the mud crab,Scylla paramamosain,from China[J].Aquaculture,2012,376/377/378/379:68-75.
- [13] SMITH P K,KROHN R I,HERMANSON G T,et al.Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid[J].A-nalytical Biochemistry,1985,150(1):176-185.
- [14] KRAFFE E,MARTY Y,GUDERLEY H.Changes in mitochondrial oxidative capacities during thermal acclimation of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss:roles of membrane proteins,phospholipids and their fatty acid compositions[J].The Journal of Experimental Biology,2006,210:149-165.
- [15] HULBERT A J,TURNER N,HINDE J,et al.How might you compare mitochondria from different tissues and different species?[J].Journal of Comparative Phy-siology B,2006,176:93-105.
- [16] DUERR J M,PODRABSKY J E.Mitochondrial physio-logy of diapausing and developing embryos of the annual killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus:implications for extreme anoxia tolerance[J].Journal of Comparative Phy-siology B,2010,180(7):991-1003.
- [17] THIBAULT M,BLIER P U,GUDERLEY H.Seasonal variation of muscle metabolic organization in rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J].Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,1997,16(2):139-155.
- [18] HANSEN J I,MUSTAFA T,DEPLEDGE M.Mechanisms of copper toxicity in the shore crab,Carcinus maenas. Ⅱ.Effects on key metabolic enzymes,metabolites and energy charge potential[J].Marine Bio-logy,1992,114(2):259-264.
- [19] 李孝聪.中国区域历史地理[M].北京:北京大学出版社,2004:258-302.
- [20] WANG G Z,KONG X H,WANG K J,et al.Variation of specific proteins,mitochondria and fatty acid composition in gill of Scylla serrata(Crustacea,Decapoda)under low temperature adaptation[J].Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology,2007,352(1):129-138.
- [21] KONG X H,WANG G Z,LI S J.Seasonal variations of ATPase activity and antioxidant defenses in gills of the mud crab Scylla serrata(Crustacea,Decapoda)[J].Marine Biology,2008,154(2):269-276.
- [22] LESSER M P,KRUSE V A.Seasonal temperature compensation in the horse mussel,Modiolus modiolus:me-tabolic enzymes,oxidative stress and heat shock proteins[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A,2004,137(3):495-504.
- [23] BERNER N J,BESSAY E P.Correlation of seasonal acclimatization in metabolic enzyme activity with preferred body temperature in the Eastern red spotted newt(Notophthalmus viridescens viridescens)[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A,2006,144(4):429-436.
- [24] YAN Y L,XIE X J.Liver mitochondrial and whole-animal level metabolic compensation in a catfish during seasonal acclimatization[J].Current Zoology,2011,57(1):109-115.
- [25] DHILLON R S,SCHULTE P M.Intraspecific variation in the thermal plasticity of mitochondria in killifish[J].The Journal of Experimental Biology,2011,214(21):3639-3648.
- [26] LUCASSEN M,KOSCHNICK N,ECKERLE L G,et al.Mitochondrial mechanisms of cold adaptation in cod(Gadus morhua L.)populations from different climatic zones[J].The Journal of Experimental Biology,2006,209(13):2462-2471.
- [27] FANGUE,N A,RICHARDS J G,SCHULTE P M.Do mitochondrial properties explain intraspecific variation in thermal tolerance?[J].The Journal of Experimental Bio-logy,2009,212(4):514-522.