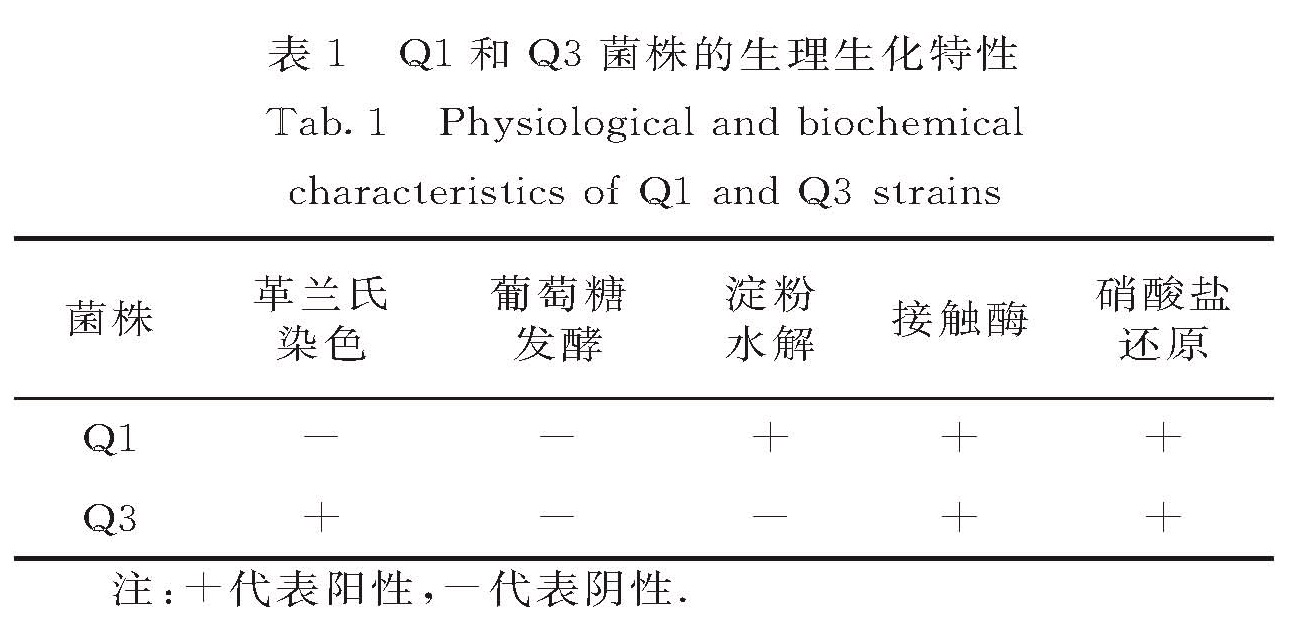
从湖北省武汉市黄家湖底泥中分离出2株能耐受20 mmol/L Al3+的细菌菌株Q1和Q3,研究其在不同Al3+浓度下对氨氮和硝氮的去除性能.通过生理生化鉴定、扫描电镜(SEM)形态观察和16S rRNA基因序列分析,确定Q1为鞘氨醇杆菌(Sphingobacterium sp.),Q3为蜡状芽孢杆菌(Bacillus cereus).在Al3+浓度为15 mmol/L时,Q1可以去除83.54%的氨氮,Q3可以去除93.03%的硝氮.当Al3+浓度从0升高到15 mmol/L时,Q1对硝氮的去除率下降91.10个百分点,对氨氮的去除率上升30.26个百分点; 而Q3对硝氮的去除率不受影响,对氨氮的去除率下降18.25个百分点; 2株菌株对总氮的去除率均下降.X射线衍射(XRD)分析结果表明Q1中Al元素存在的主要形态为CaAl2Si2O8·4H2O和(Mg,Fe,Al)3-x(AlSiO5)(OH)4-2x,Q3中Al元素存在的主要形态为Al4(SO4)(OH)10·36H2O和Al0.47Si0.15P0.38O2,说明Al元素可以取代细菌所需的微量元素从而降低酶活性.研究结果可以为细菌耐铝机制的研究和铝盐应用于化学协同脱氮除磷提供理论依据.
In order to study the nitrogen removal performance of bacteria under different concentrations of aluminum,two strains(Q1 and Q3)of bacteria,which could withstand 20 mmol/L Al3+,were isolated from the sediment of the Huangjia Lake in Wuhan,Hubei province of China.Q1 was most similar to Sphingobacterium sp. and Q3 was identified as Bacillus cereus based on the results of physiological and biochemical properties,scanning electron microscopy(SEM)and phylogenic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences.When the concentration of Al3+ was 15 mmol/L,Q1 could achieve 83.54% NH4+-N removal while Q3 could achieve 93.03% NO3--N removal.When the concentrations of Al3+ rose from 0 to 15 mmol/L,the NO3--N removal rate of Q1 decreased by 91.10 percentage points and NH4+-N removal rate increased by 30.26 percentage points.The NO3--N removal rate of Q3 was not affected by the increase of Al3+ concentration from 0 to 15 mmol/L,while the NH4+-N removal rate decreased by 18.25 percentage points.The total nitrogen removal rate of the two strains decreased in general.Moreover,X ray diffraction(XRD)results showed that the main forms of the existence of Al element in Q1 were CaAl2Si2O8·4H2O and(Mg,Fe,Al)3-x(AlSiO5)(OH)4-2x,and the main forms of the existence of Al element in Q3 were Al4(SO4)(OH)10·36H2O and Al0.47Si0.15P0.38O2.Al was closely bound up with the intracellular elements of bacteria,indicating that Al could replace the essential trace elements of bacteria,thus reducing the enzyme activity.The results could provide a theoretical basis for the study of mechanisms of aluminum-tolerant bacteria as well as the application of aluminum salt aided chemical nitrogen and phosphorus removal.