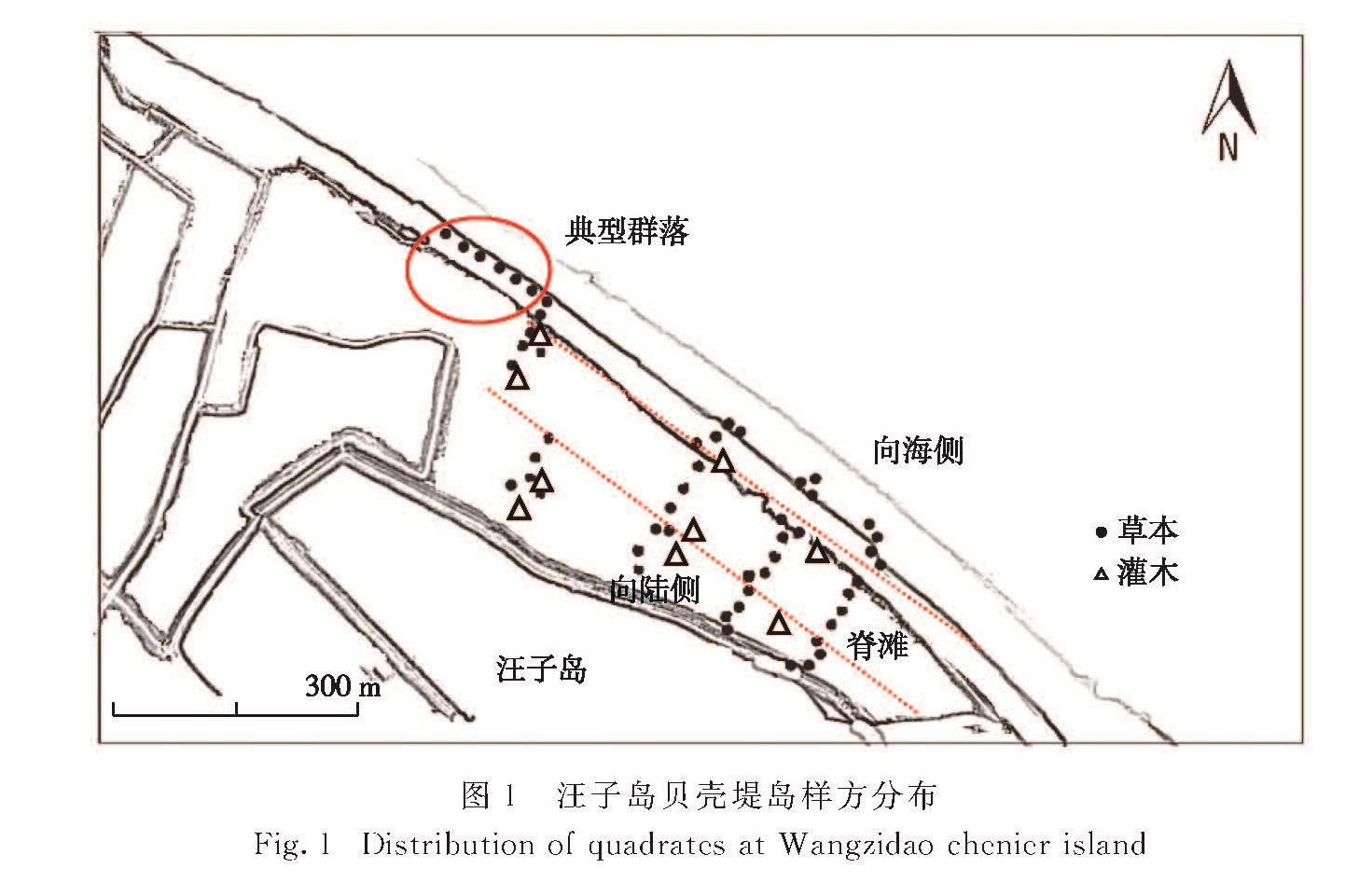
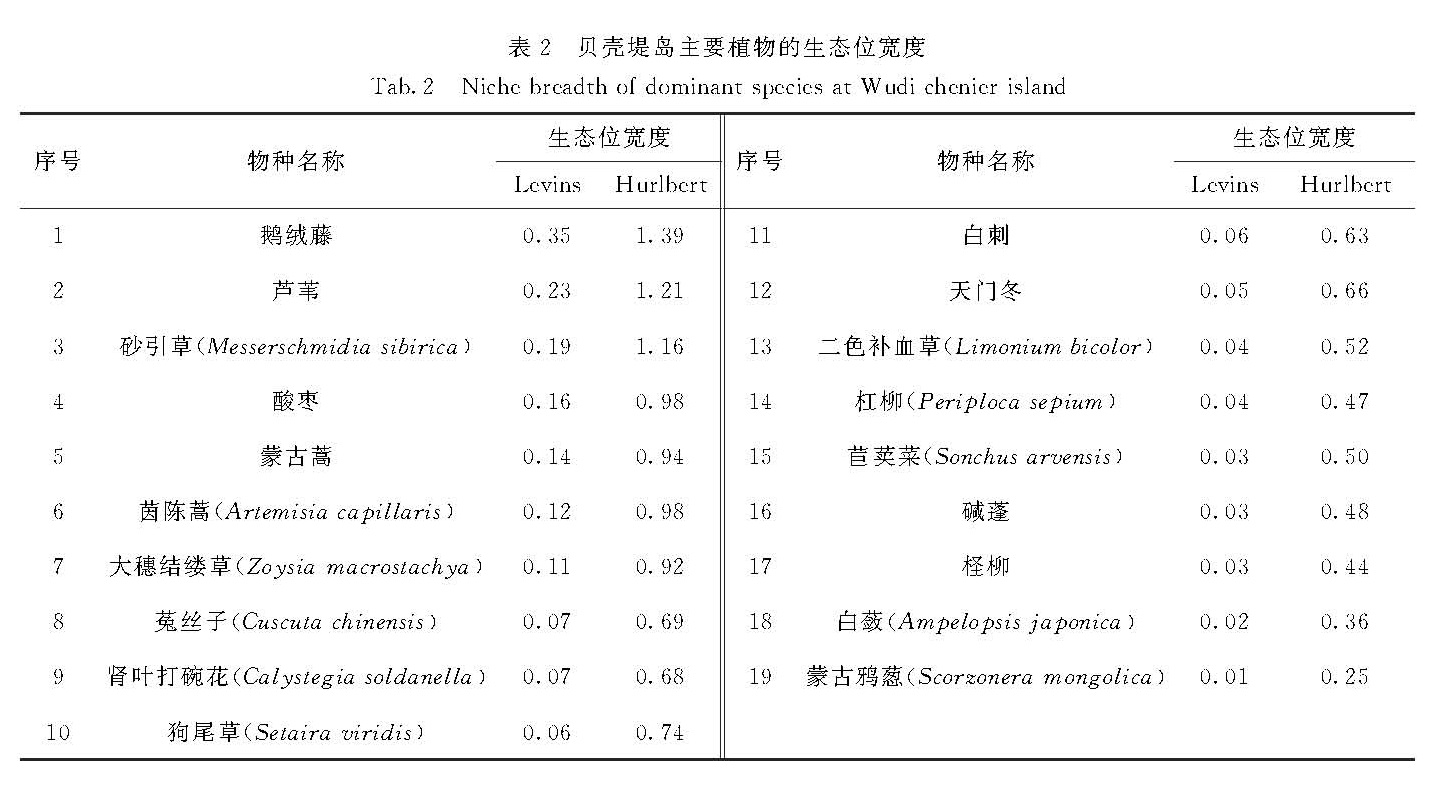
在山东无棣贝壳堤岛保护区的汪子岛设置3个断面,结合踏查和系统抽样的样方调查方法对维管束植物的生态位进行了研究.样方调查共记录到维管束植物30科63属74种,未发现罗布麻(Apocynum venetum)和野大豆(Glycine soja)等原有重要资源植物种类.在植被分类的群系水平上,主要分布有酸枣(Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa)灌丛、柽柳(Tamarix chinensis)灌丛、芦苇(Phragmites australis)草甸、蒙古蒿(Artemisia mongolica)草甸和鹅绒藤(Cynanchum chinense)草甸.维管束植物的生物多样性指数总体水平如下:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数为2.70,Simpson多样性指数为0.91,Margalef多样性指数为3.42,McIntosh's多样性指数为0.49,Berger-Parker均匀度指数和JSW均匀度指数分别为0.15和0.79.在重要值大于1.0的植物种类中,鹅绒藤的生态位宽度最大,其Levins和Hurlbert生态位宽度值分别为0.35和1.39; 其次是芦苇、砂引草(Messerschmidia sibirica)和酸枣等.芦苇和天门冬(Asparagus cochinchinensis)间的生态位重叠值最高,为0.469,其次为菟丝子(Cuscuta chinensis)和肾叶打碗花(Calystegia soldanella).鹅绒藤与大多数物种存在生态位重叠,构成一定的物种间竞争; 多数草本植物间的生态位重叠值小,常以纯群丛方式存在.根据上述结果,在无棣贝壳堤岛保护区,应注重对酸枣和柽柳的保护,同时加强对鹅绒藤和菟丝子的管理.
Three sections of Wangzi Island were set up in the Natural Chenier Island Reserve of Wudi,and the ecological niche of vascular plants was studied using walking investigation and systematic sampling methods.Field surveys showed that there were 74 vascular species,belonging to 63 genera and 30 families in the Natural Chenier Island Reserve of Wudi(Wangzi Island and Dakouhe Island),but native species such as Apocynum venetum and Glycine soja were not found.At the level of vegetation classification,the main plant formations were shrubs of Ziziphus jujube var. spinosa,shrubs of Tamarix chinensis,meadows of Phragmites australis,meadows of Artemisia mongolica and meadows of Cynanchum chinense.The vegetation diversity indexes of Shannon-Wiener,Simpson,Margalef and McIntosh's were 2.70,0.91,3.42 and 0.49,respectively.The Berger-Parker and JSW evenness indexes were 0.15 and 0.79,respectively.Among all plant species with important values greater than 1.0,C. chinense had the biggest niche breath with 0.35 for Levins niche breath and 1.39 for Hurlbert niche breath,showing the strongest adaptation ability to the habitat.The next were P. australis,Messerschmidia sibirica,and Z. jujuba var. spinosa.The highest niche overlapping value was 0.469,occurring between P. australis and Asparagus cochinchinensis.The followed one was that between Cuscuta chinensis and Calystegia soldanella.The niches of C. chinense overlapped with most of other species,leading to significant competitions between them.For most of herbaceous plants,their niche overlap values were small,so they usually existed with pure associations.Accordingly,attentions should be paid on the protection of Z. jujuba var. spinosa and T. chinensis,and on the management of C. chinense and C. chinensis in the Natural Chenier Island Reserve of Wudi.