(1.水声通信与海洋信息技术教育部重点实验室(厦门大学),福建 厦门 361005; 2.麻省州立大学波士顿分校环境学院,美国 波士顿 02125)
(1.Key Laboratory of Underwater Acoustic Communication and Marine Information Technology,Ministry of Education,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361005,China; 2.School for the Environment,University of Massachusetts Boston,Boston,MA 02125,USA)
DOI: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.201610008
备注
浮游植物的光合作用对海洋吸收太阳辐射的升温过程有一定的调节作用.为了更好地阐释这一调节作用,设定490 nm光照条件,采用3组吸收特征不同的水样,同步进行光照试验.结果显示,浮游植物的光合作用对海水的升温幅度产生17.9%~20.0%的减弱作用,说明次表层(10~50 m)海水因太阳辐射导致的升温幅度很可能与目前通用的海洋环流模式估算结果不一致,而影响程度会因不同海域的叶绿素浓度不同而有所差异.这一结果对于进一步完善海洋环流及气候模式中对各参数的模拟,更好地认识海洋浮游植物在调节气候变化中的作用,有一定的参考意义.
Photosynthesis of phytoplankton has a modulation effect in warming of the upper water column by absorbing solar radiation.To elucidate this modulation effect,in this study,we presents results of an experiment where three kinds of water samples were heated by light at 490 nm.It is found that the heating effect is reduced by 17.9% to 20.0% for phytoplankton dominant waters compared with that of yellow-substance dominant waters,although both have similar absorption properties at 490 nm.The result indicates that the heating effect of the upper water column(10 m to 50 m)due to solar radiation may not be as high as that presently estimated in the oceanic circulation models.It supplies references to improve existing circulation and climate models in order to better represent the modulation effect by phytoplankton.
引言
海洋热量的主要来源是到达地球的太阳辐射,而太阳辐射的能量分布于从紫外到红外的很宽波长范围内(250~3 000 nm),且大部分光都只能穿透很浅的水体.海洋表层能有效地吸收波长大于700 nm的太阳辐射,并将其转化为热量; 而波长处于400~700 nm的可见光则能穿透海洋表层并至一定深度,对较深层的海水进行加热.太阳辐射在可见光区间的能量大约占到达海面的太阳总辐射能量的47%,因此,穿透进入海洋内部的可见光的辐射能量对海洋上层的热平衡、动力学及海洋生态过程都可能产生较大影响[1].
在海洋中,浮游植物利用太阳辐射能进行光合作用,通过调节太阳辐射能在海洋上层的分配比例可以影响海洋的热状况,并通过热动力学过程影响海洋环流和气候.如果海洋上层聚集的浮游植物较多,上层海水被光合作用所利用的太阳辐射能所占比例就会较大,而相应到达海洋深层的太阳辐射能就较少[2],反之亦然.因此,上层海水浮游植物含量的不同会影响海水对穿透性辐射的吸收,影响垂向温度结构,进而通过热动力学过程影响海洋环流与气候.
在过去的几十年里,学者们对于穿透性太阳辐射对深层水体的可能影响开展了大量研究,Platt[3]认为短波辐射对气候模型的影响取决于该海域的生物量,而Lewis等[4]论证了穿透辐射和叶绿素浓度会导致海水垂直混合和海水温度的垂直分布受到影响.然而在大部分海水动力学模型中,为了计算更加方便,仍然采用Jerlov[5]提出的纯水模型,即不考虑除海水外的其他成分,海水内部的温度变化取决于上层海水向下的扩散和对流作用,浮游植物含量对海洋热平衡的影响也被忽视,这将导致对上层海水温度评估的不准确.Nakamoto等[6]比较了上述纯水模型和考虑叶绿素浓度的模型的差异,发现考虑叶绿素浓度的模型得到的海表面温度比不考虑叶绿素影响的情况下低了2 ℃.Murtugudde等[7]的研究也发现,考虑叶绿素浓度会很大程度提升模型模拟结果的精确度.
随着研究的不断深入,对太阳辐射穿透性影响的研究开始应用于海气耦合模型中,从不同方面探究了穿透性太阳辐射与叶绿素、透明度等对海水温度及对大气的反馈[8-11]; 但在这些研究中,浮游植物的热容数值多被设定为与黄色物质(CDOM)等其他海水成分一致,而浮游植物的光合作用对辐射的吸收则很少被关注.虽然目前已有一些穿透性太阳辐射以及叶绿素对辐射传输影响的研究[4,6-11],但浮游植物的光合作用这一重要过程对穿透性太阳辐射的影响尚不明确.为解决海洋表层以下的浮游植物的光合作用是否会对海水热收支产生作用,以及将浮游植物的吸收系数等同于CDOM等其他海水成分是否会导致计算结果不准确的问题,首先需要验证浮游植物与CDOM水样在相同吸收系数下,升温幅度是否相同.本研究拟通过试验来探索浮游植物的光合作用在穿透性太阳辐射下对次表层(10~50 m)海水升温的影响.
1 原理和方法
1.1 试验原理太阳辐射能够被海水和海水中具有吸收特性的成分所吸收并转化为能量,从而导致海水温度的上升.海水和海水中各成分的吸收可以用下式表示[12]:
a=aw+ap+ad+ag.(1)
其中:a为总吸收系数; aw、ap、ad和ag分别表示纯水、浮游植物、碎屑颗粒物和CDOM的吸收系数.吸收太阳辐射导致升温的传统计算方式为:根据不同组分的吸收系数确定辐射吸收的权重,再根据不同组分的热容分别计算并累加.可用下式表示[13]:
RHR(z)=(ΔT)/(Δt)=(Q(z))/(ρwCΔZ),(2)
其中,RHR(z)为该层由于吸收辐射升温的热率,Q(z)为该层吸收的能量,ρw为海水密度,C为热容,ΔZ为该层的厚度.浮游植物、CDOM的热容在不考虑光合作用影响的情况下被认为和纯水相同; 但如果考虑光合作用消耗的能量,浮游植物吸收辐射后的升温幅度应该会比CDOM略微偏低,即实际应用中浮游植物的热容应该比CDOM略大.
在真实海水中,一方面海水自身的吸收作用限制了波长较长的黄光和红光的穿透深度z90(辐照度E(λ)衰减为海表下行辐照度的1/e时的深度,e≈2.718); 另一方面溶解有机物和浮游植物的吸收作用又限制了波长较短的紫光和蓝光的穿透深度,因此穿透深度最大的是位于二者之间的波长约490 nm的青光,在较清澈的海水中(如中国南海海域),青光最大穿透深度约为30 m[14].
本研究的主要目的是通过试验来反映浮游植物的存在对海水吸收太阳辐射升温的影响,并探索光合作用对海水温度变化幅度的调节作用.
1.2 试验方法1)试验装置:为避免其他光源对实验的干扰,将试验样品置于密闭空间中,用490 nm单波段LED灯(青光灯)照射试验水样.本试验采用泡沫材料来构建光照密闭空间; 同时,为了进一步保证光源的纯净性,试验过程中关闭室内光源,并将整个试验装置用遮光布盖住.分别设计了用490 nm青光灯顶部照射水样和平行照射水样2种方法,并根据试验结果进行距离调整,具体装置如图1所示.
图1 顶部照射(a)与平行照射(b)试验装置示意图
Fig.1 Sketch of experimental devices for top irradiating(a)and parallel irradiating(b)experiments顶部照射的试验装置如图1(a)所示:用白色泡沫箱作为容器,箱顶开一个洞用来透光,放置490 nm青光灯,泡沫箱中穿插摆放上述3组水样(每组2瓶,共6瓶).
平行照射的试验装置如图1(b)所示:对顶部照射试验装置进行改进,扩大了光源和水样的距离,改为并排5瓶水样,使光源在一定距离外平行照射水样.
2)试验材料:根据试验目的,分别测试自来水、含CDOM的人工海水和含浮游植物的人工海水.为保证结果准确性,每组设置2个重复,采用1 L的锥形瓶存放,每瓶注入500 mL液体.
3)观测方法:每个水样中和箱内空气中各放置一只探针式电子温度计,并将电线通过泡沫箱的小孔引出.每隔0.5 h观察记录水样温度数值,每次试验连续观测时长均大于5 h.
1.3 试验参数试验中样品1为自来水,样品2为含CDOM的人工海水,样品3为含浮游植物的人工海水.试验开始前,调整样品2的CDOM浓度,令其在490 nm波段的吸收系数与样品3相同,即样品2和样品3的区别仅为样品3中存在光合作用.如果在同样光照条件下样品2和样品3升温幅度不同,则证明光合作用会对温度的变化有额外影响.
为保证试验结果的客观性与准确性,分别以不同的光源-水样距离以及水样摆放方式进行了3次试验,具体试验参数见表1.
2 结果与分析
2.1 顶部照射对水样温度变化的影响顶部照射对水样水温变化的影响试验在2015年1月20日进行(试验1),结果如图2所示.
0为空气,其他为水样,下同.
由图2可以看出:在整个试验过程中,泡沫箱内的空气温度在迅速升高后逐渐趋于稳定,而3种水样则处于持续升温的状态.其中样品2升温最为迅速,并且升温后温度一直高于其他2种水样,在经过4.5 h的光照后,样品2的温度超过了空气温度; 含浮游植物的样品3在试验前期升温速率略大于样品1,但是整个试验过程中温度始终低于空气温度.
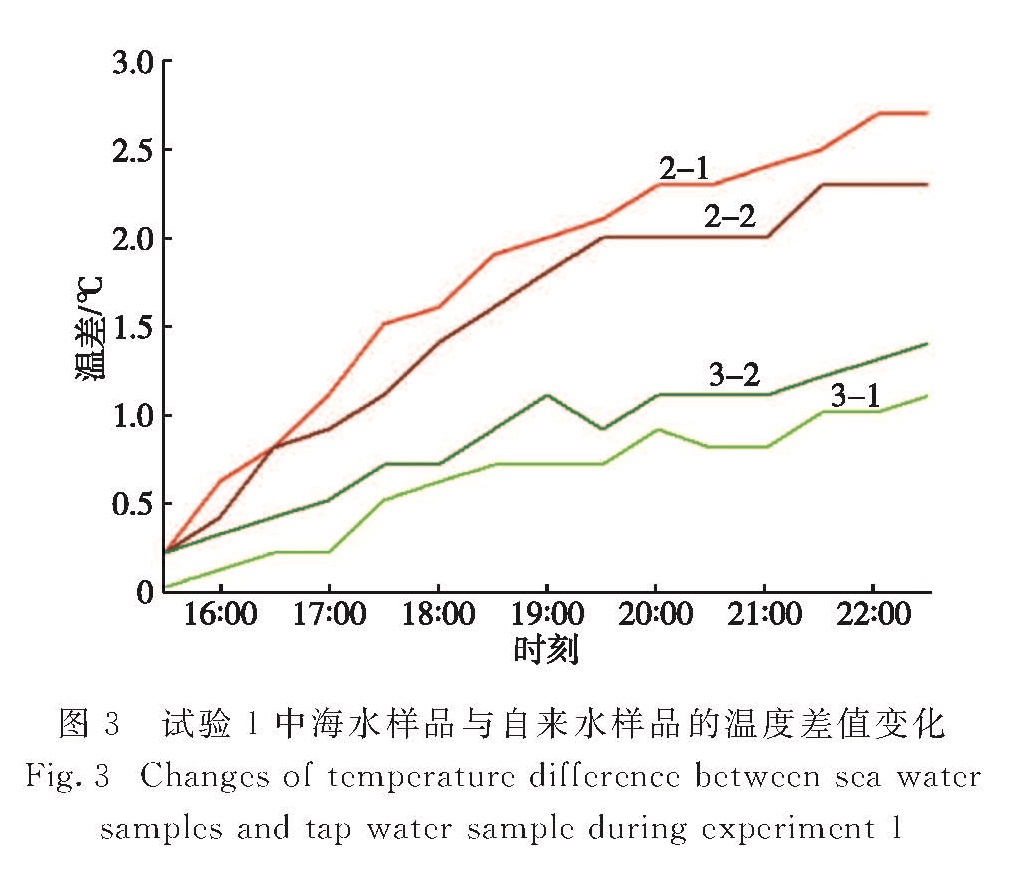
为了更直观地显示试验结果,对试验1中样品2和样品3分别与样品1的温度平均值求差值,绘制温差的变化曲线,结果如图3所示.由图3可以看出:样品2升温更快,最终温差也更大; 试验进行7 h后,样品2平均比样品1高2.5 ℃,样品3平均比样品1高1.2 ℃.
图3 试验1中海水样品与自来水样品的温度差值变化
Fig.3 Changes of temperature difference between sea water samples and tap water sample during experiment 1考虑到试验1所设计的水样与光源之间距离较近,泡沫箱空间狭小,光源发热问题可能影响了箱内空气温度,在前2 h内空气温度升高十分明显,对试验结果也造成了一定影响.针对这一问题,对设计方案改进后再进行试验.
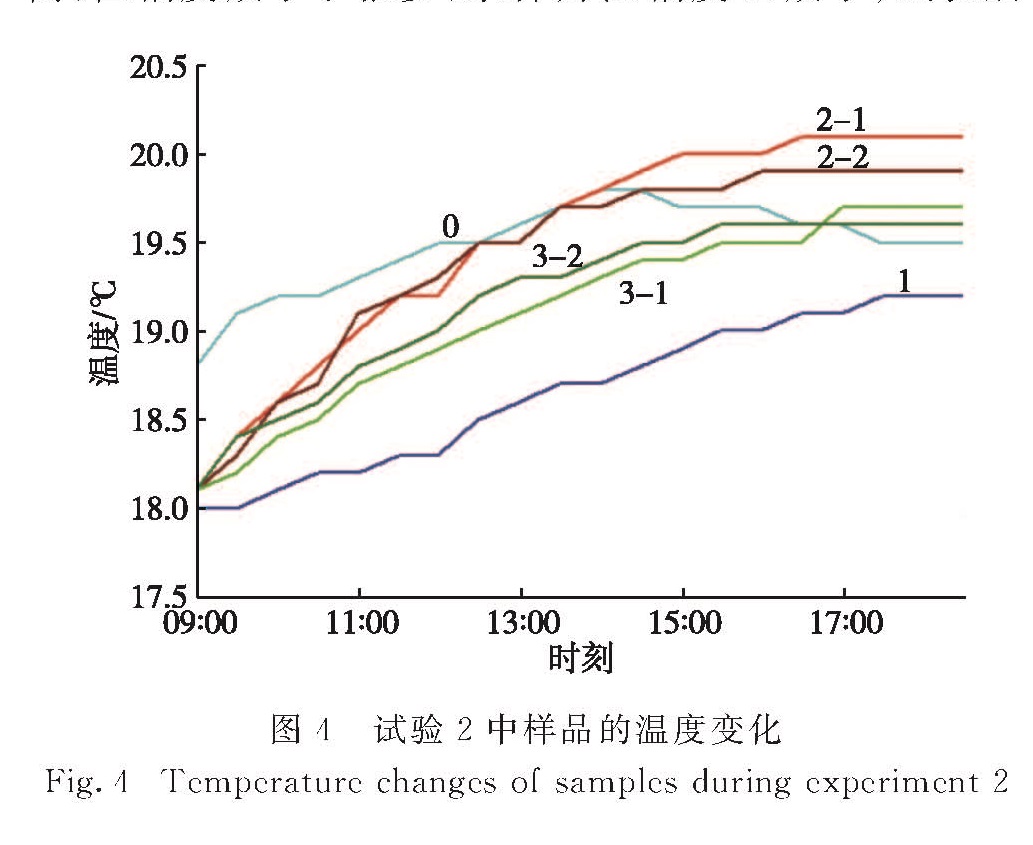
2.2 平行照射对水样温度变化的影响平行照射对水样温度变化的影响试验在2015年1月28日进行(试验2),改进后的试验装置将光源与水样的距离从0.5 m增大为1.0 m,以减少青光灯自身升温导致水样升温的情况.试验结果如图4所示.
由图4可以看出:试验中空气温度仍有略微升高,但幅度减小了很多,水样升温幅度也减小; 试验后期因时间接近傍晚,空气温度略有下降; 与试验1的结果类似,样品2的升温幅度最大,且在光照5 h后其温度超过了空气温度; 样品3的升温幅度次之,但也大于样品1的温度.
海水样品与自来水样品温差变化如图5所示.从图5可以看出:2种海水样品与自来水样品的温差区别明显,样品2的最大温差比样品3高0.4 ℃左右; 试验后期样品2和样品3温度趋于平稳,海水样品和自来水样品的温差减小,这可能是因为室温下降所致.
图5 试验2中海水样品与自来水样品的温度差值变化
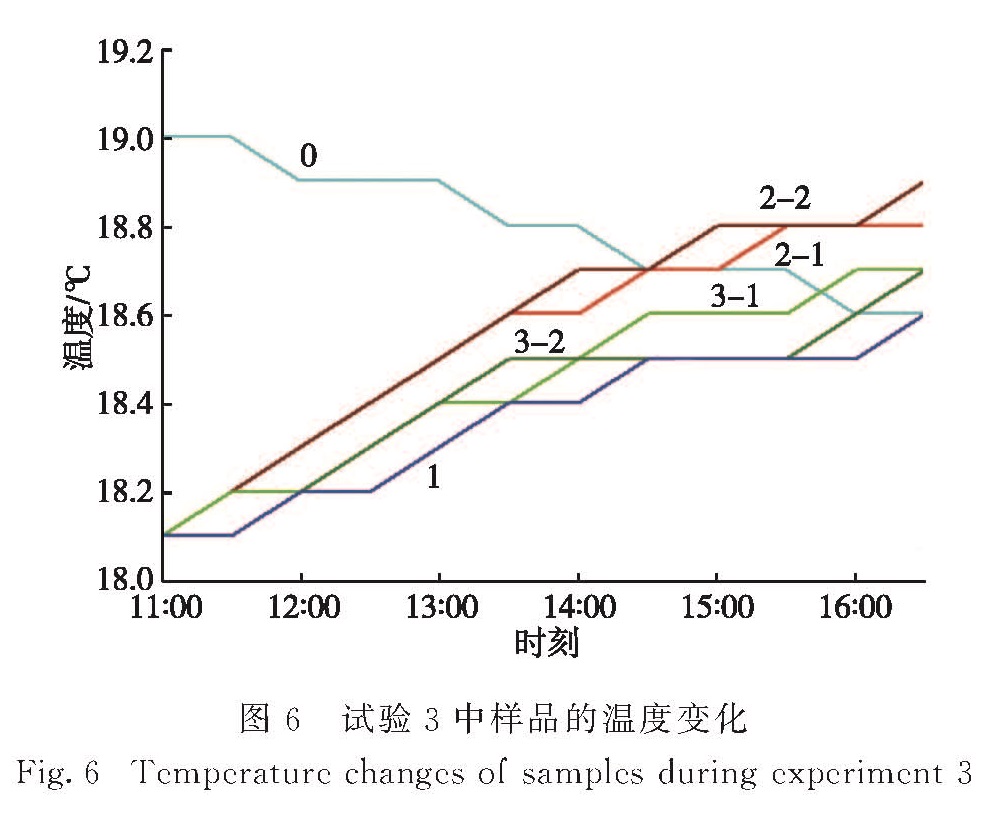
Fig.5 Changes of temperature difference between sea water samples and tap water during experiment 2试验2中的空气升温问题虽然得到了改善,但是仍然不能完全避免青光灯自身升温的影响.因此,将水样和光源的距离拉长为3.0 m后,在2015年1月30日再次进行了试验(试验3),结果如图6所示.
由图6可以看出:光源与样品间的距离增加后,样品接收到的光照能量减弱,升温变得十分缓慢,但样品2的平均升温幅度比样品3仍然高0.15 ℃.
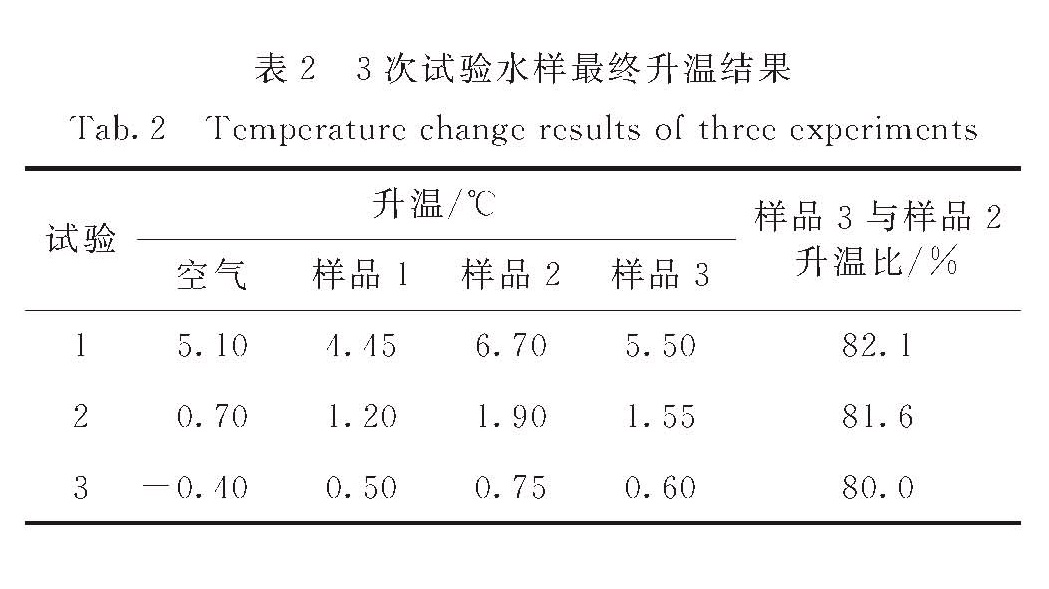
2.3 3次试验的升温结果比较将3次试验数据进行整理后,结果如表2所示:在吸收系数相同、光照相同的条件下,含浮游植物的样品3升温幅度显著低于不含浮游植物的样品2,3次试验中样品3升温幅度分别比样品2低17.9%,18.4%,20.0%.
3 结论与讨论
针对浮游植物光合作用是否会影响次表层海水温度的问题,本研究设计并开展了光源持续照射不同水样的温度观测试验.从3次试验结果看,虽然试验中光源方向、光源-水样距离都有所调整,水样升温幅度不同,但含浮游植物的水样与含CDOM的水样的升温幅度比值均在80%以上.从试验结果可知:在490 nm波长(很多大洋水体穿透性最深的波长)光源的照射条件下,吸收系数高的水体升温更快; 浮游植物的光合作用会对海水升温造成负反馈,即在同等照射条件下含浮游植物水样的升温幅度明显低于含CDOM的水样.本研究中,含浮游植物水样的升温幅度比含CDOM的水样低17.9%~20.0%,即影响约1/5的升温幅度,说明浮游植物的光合作用会减弱穿透性短波辐射对次表层海水升温过程的影响.
在通常的海洋环流模型中,目前并未考虑浮游植物对其中热量计算分项的影响.根据本研究的结果,这一忽略有可能导致整个海洋热量平衡的计算出现一定程度的失真,进而通过海气相互作用和海气耦合对气候变化预测的精确计算产生一定影响.因此,本研究对分析海水温度与穿透性太阳辐射的关系具有一定的参考意义.
致谢:感谢厦门大学近海海洋环境国家重点实验室林森杰课题组在海藻培养方面的支持与帮助.
- [1] ZANEVELD J R V,KITCHEN J C,PAK H.The influence of optical water type on the heating rate of a constant depth mixed layer[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,1981,86(C7):6426-6428.
- [2] 梁曦.副热带海区浮游植物对海洋环流与气候的影响[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2014.
- [3] PLATT T.The concept of energy efficiency in primary production[J].Limnology & Oceanography,1969,14(5):653-659.
- [4] LEWIS M R,CARR M E,FELDMAN G C,et al.Influence of penetrating solar radiation on the heat budget of the equatorial Pacific Ocean[J].Nature,1990,347(6293):543-545.
- [5] JERLOV N G.Marine optics[M].Amsterdam:Elesvier,1976:229.
- [6] NAKAMOTO S,KUMAR S P,OBERHUBER J M,et al.Response of the equatorial Pacific to chlorophyll pigment in a mixed layer isopycnal ocean general circulation model[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2001,28(10):2021-2024.
- [7] MURTUGUDDE R,BEAUCHAMP J,MCCLAIN C R,et al.Effects of penetrative radiation on the upper tropical ocean circulation[J].Journal of Climate,2002,15(5):470-486.
- [8] SHELL K M,FROUIN R,NAKAMOTO S,et al.Atmospheric response to solar radiation absorbed by phytoplankton[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2003,108(D15):10--1029.
- [9] ANDERSON W G,GNANADESIKAN A,HALLBERG R,et al.Impact of ocean color on the maintenance of the Pacific Cold Tongue[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(11):224-238.
- [10] LENGAIGNE M,MENKES C,AUMONT O,et al.Influence of the oceanic biology on the tropical Pacific climate in a coupled general circulation model[J].Climate Dynamics,2007,28(5):503-516.
- [11] GNANADESIKAN A,ANDERSON W G.Ocean water clarity and the ocean general circulation in a coupled climate model[J].Journal of Physical Oceanography,2009,39(2):314.
- [12] MOREL A.Optical properties of pure water and pure seawater[M]∥JERLOV N G,NIELSEN E S.Optical aspects of oceanography.London,New York:Academic Press,1974:1-24.
- [13] OHLMANN J C D,SIEGEL D A.Ocean radiant heating.Part Ⅱ:parameterizing solar radiation transmission through the upper ocean[J].Journal of Physical Oceanography,2000,30(8):1849-1865.
- [14] 刘玉光.卫星海洋学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2009:119.